RAID 1 is a simple mirror configuration where two (or more) physical disks store the same data, thereby providing redundancy and fault tolerance. RAID 5 also offers fault tolerance but distributes data by striping it across multiple disks.RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple drives to be combined into a single storage space. There are different types of RAID, each providing different levels of performance, storage capacity, and reliability.RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.
How does RAID 5 work : RAID 5 is a redundant array of independent disks configuration that uses disk striping with parity. Data and parity are striped evenly across all of the disks, so no single disk is a bottleneck. Striping also enables users to reconstruct data in case of a disk failure.
Is RAID good for NAS
RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
Should I use RAID 1 or RAID 0 NAS : RAID 0 is more cost-effective in terms of raw storage space since all the space on the drives is usable. For instance, if you use two 1TB drives in RAID 0, you'll have 2TB of usable space. In contrast, RAID 1 mirrors data, so with two 1TB drives, you'd only have 1TB of usable space due to redundancy.
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
A RAID controller is a device used to manage hard disk drives in a storage array. It can be used as a level of abstraction between the OS and the physical disks, presenting groups of disks as logical units. Using a RAID controller can improve performance and help protect data in case of a crash.
Is RAID 6 slower than RAID 5
RAID 6 arrays are even slower because they store a greater volume of parity data than RAID 5 arrays do. Organizations must consider how they will implement the RAID 5 or RAID 6 array.This way, even if there is a disk failure, the data can be reconstructed using error correction. RAID 5 also has a fault tolerance of one drive. On the plus side, you get data redundancy and improved performance. It's a cost-effective solution for those who need redundancy and performance.RAID 5 is deprecated and not recommended for new arrays due to its vulnerability during rebuilds with large-capacity drives.
RAID 6 has better fault tolerance than RAID 5 because RAID 6 can survive the simultaneous failure of 2 of its disks. This comes at the cost of higher redundancy.
Do I really need RAID : When should I use RAID You should use a RAID array when you need to guarantee uptime. Also, most RAID arrays can keep you safe in case of hardware failure of an HDD or SSD, since there are data copies between the drives. In many cases, the change of a faulty drive can be performed by hot-swapping the problem.
Why is ZFS better than RAID : So ZFS comes with some other features that traditional RAID doesn't have, which is the L2 Ark and the ZIL, or the ZFS intent log, and what this does is it allows RAM and SSDs to work as a cache for high speed.
Is RAID necessary for NAS
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
From a network perspective, RAID is usually internal to a computer or a server, while NAS is external and accessible by multiple clients. From a user perspective, RAID is more complex and technical to set up and manage, while NAS is more user-friendly and convenient to use.Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.
What is the point of RAID : RAID (redundant array of independent disks) is a way of storing the same data in different places on multiple hard disks or solid-state drives (SSDs) to protect data in the case of a drive failure. There are different RAID levels, however, and not all have the goal of providing redundancy.
Antwort Why use RAID in NAS? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between RAID 1 and RAID 5 NAS
RAID 1 is a simple mirror configuration where two (or more) physical disks store the same data, thereby providing redundancy and fault tolerance. RAID 5 also offers fault tolerance but distributes data by striping it across multiple disks.RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple drives to be combined into a single storage space. There are different types of RAID, each providing different levels of performance, storage capacity, and reliability.RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.
How does RAID 5 work : RAID 5 is a redundant array of independent disks configuration that uses disk striping with parity. Data and parity are striped evenly across all of the disks, so no single disk is a bottleneck. Striping also enables users to reconstruct data in case of a disk failure.
Is RAID good for NAS
RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
Should I use RAID 1 or RAID 0 NAS : RAID 0 is more cost-effective in terms of raw storage space since all the space on the drives is usable. For instance, if you use two 1TB drives in RAID 0, you'll have 2TB of usable space. In contrast, RAID 1 mirrors data, so with two 1TB drives, you'd only have 1TB of usable space due to redundancy.
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
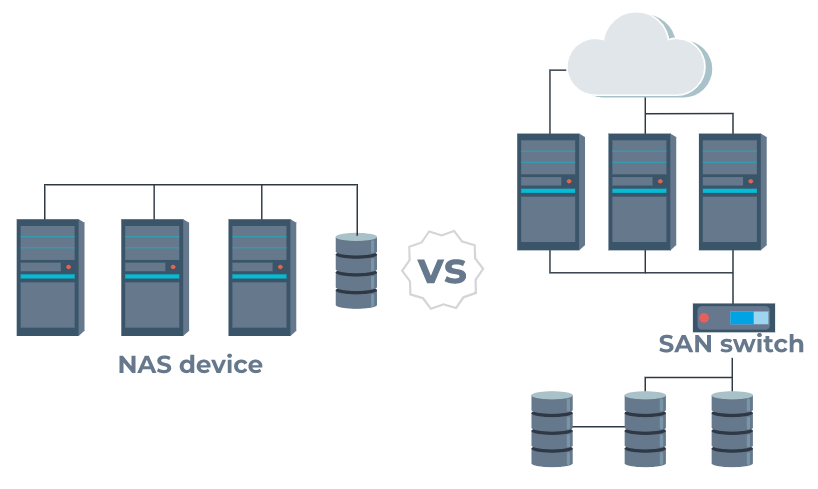
A RAID controller is a device used to manage hard disk drives in a storage array. It can be used as a level of abstraction between the OS and the physical disks, presenting groups of disks as logical units. Using a RAID controller can improve performance and help protect data in case of a crash.
Is RAID 6 slower than RAID 5
RAID 6 arrays are even slower because they store a greater volume of parity data than RAID 5 arrays do. Organizations must consider how they will implement the RAID 5 or RAID 6 array.This way, even if there is a disk failure, the data can be reconstructed using error correction. RAID 5 also has a fault tolerance of one drive. On the plus side, you get data redundancy and improved performance. It's a cost-effective solution for those who need redundancy and performance.RAID 5 is deprecated and not recommended for new arrays due to its vulnerability during rebuilds with large-capacity drives.

RAID 6 has better fault tolerance than RAID 5 because RAID 6 can survive the simultaneous failure of 2 of its disks. This comes at the cost of higher redundancy.
Do I really need RAID : When should I use RAID You should use a RAID array when you need to guarantee uptime. Also, most RAID arrays can keep you safe in case of hardware failure of an HDD or SSD, since there are data copies between the drives. In many cases, the change of a faulty drive can be performed by hot-swapping the problem.
Why is ZFS better than RAID : So ZFS comes with some other features that traditional RAID doesn't have, which is the L2 Ark and the ZIL, or the ZFS intent log, and what this does is it allows RAM and SSDs to work as a cache for high speed.
Is RAID necessary for NAS
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.

From a network perspective, RAID is usually internal to a computer or a server, while NAS is external and accessible by multiple clients. From a user perspective, RAID is more complex and technical to set up and manage, while NAS is more user-friendly and convenient to use.Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.
What is the point of RAID : RAID (redundant array of independent disks) is a way of storing the same data in different places on multiple hard disks or solid-state drives (SSDs) to protect data in the case of a drive failure. There are different RAID levels, however, and not all have the goal of providing redundancy.