For example, a piece of plain text (a password, for example) can be turned into a hashed value, making it very hard to decipher. Hashing is a one-way process that can't be directly reversed (as opposed to encryption, which can be decrypted if you have the appropriate decryption key).To fit the keys to the encryption key length. Most passwords are going to be either longer or shorter than the key space of the encryption function. By hashing your password, the exact key length will be exactly the size of the input key of your encryption function.Why is hashing important Hashing is important because it offers a method for retrieving data that's secure and efficient. It's also quicker than most traditional sorting algorithms, which makes it more efficient for retrieving data.
Why use hash function in cryptography : Hash functions are a way to ensure data integrity in public key cryptography. What I mean by that is that hash functions serve as a check-sum, or a way for someone to identify whether data has been tampered with after it's been signed. It also serves as a means of identity verification.
Why is hashing irreversible
Hashing is generally a one-way function, which means that it is easy to convert a message into a hash but very difficult to “reverse hash” a hash value back to its original message as it requires a massive amount of computing power.
Why can’t hashing be reversed : How does hashing work in crypto When used in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, the end result is typically a 64-digit long string of numbers and letters. Because the conversion is done by a cryptographic algorithm (the “hash function”), the jumbling formula is unknown so the 64-digit string can't be reversed.
No, hashed data cannot be decrypted. Hashing is a one-way process, which means that the original data cannot be obtained from the hash value. It is designed to be irreversible, making it suitable for storing passwords and verifying data integrity. Hashing and encryption can keep sensitive data safe, but in almost all circumstances, passwords should be hashed, NOT encrypted. Because hashing is a one-way function (i.e., it is impossible to "decrypt" a hash and obtain the original plaintext value), it is the most appropriate approach for password validation.
What are the benefits of hashing data
Hashing verifies the file's integrity once it is transferred from one place to another in a file backup program. Users can compare the hash value of both files to ensure that transferred files are not corrupted.Since encryption is two-way, the data can be decrypted so it is readable again. Hashing, on the other hand, is one-way, meaning the plaintext is scrambled into a unique digest, through the use of a salt, that cannot be decrypted.If they successfully crack a hashed password, they may gain unauthorized access to user accounts and steal sensitive information. They may also use the stolen information for ransomware attacks, where the organization has to pay large sums of money to regain the sensitive data hackers have stolen and encrypted. Irreversible: By design, all hash functions such as the SHA 256 are irreversible. You should neither get a plaintext when you have the digest beforehand nor should the digest provide its original value when you pass it through the hash function again.
Why is SHA-256 unbreakable : Because SHA-256 is a one-way cryptographic algorithm, it's impossible to reverse-engineer the input from the output hash. This means that miners can't cheat the system by submitting a fake solution since other nodes on the network can easily verify the answer by checking the hash.
What is the weakness of hashing : Hash tables are widely used data structures that offer efficient data retrieval and storage, but they also have some disadvantages: Collisions: One of the primary disadvantages of hash tables is the potential for collisions. Collisions occur when two different keys hash to the same index in the table.
Why is SHA 256 not reversible
SHA-256 refers to the bit size of the hash output. In other words, the resulting hash value from SHA-256 is 256 bits long, which provides a significantly larger search space compared to its predecessor, making it computationally infeasible to reverse engineer the original input from the hash value. As hashing is extremely infeasible to reverse, hashing algorithms are used on passwords. This makes the password shorter and undiscoverable by attackers. Encryption, on the other hand, tends to be used for encrypting data that is in transit.Overall, the main reason why it is difficult or impossible to recover the original value from a given hash value is that the hash function is designed to be a one-way function, meaning that it is irreversible and computationally infeasible to reverse-engineer the original input data from the hash value.
What are the disadvantages of hashing passwords : Limitations of Password Hashing
Hackers can try a brute-force attack by running random passwords through the hash function until they finally find a match. This is rather inefficient since the hash algorithms designed for securely storing passwords are designed to be slow, making the entire process tedious and long.
Antwort Why use hashing over encryption? Weitere Antworten – Why is hashing better than encryption
For example, a piece of plain text (a password, for example) can be turned into a hashed value, making it very hard to decipher. Hashing is a one-way process that can't be directly reversed (as opposed to encryption, which can be decrypted if you have the appropriate decryption key).To fit the keys to the encryption key length. Most passwords are going to be either longer or shorter than the key space of the encryption function. By hashing your password, the exact key length will be exactly the size of the input key of your encryption function.Why is hashing important Hashing is important because it offers a method for retrieving data that's secure and efficient. It's also quicker than most traditional sorting algorithms, which makes it more efficient for retrieving data.
Why use hash function in cryptography : Hash functions are a way to ensure data integrity in public key cryptography. What I mean by that is that hash functions serve as a check-sum, or a way for someone to identify whether data has been tampered with after it's been signed. It also serves as a means of identity verification.
Why is hashing irreversible
Hashing is generally a one-way function, which means that it is easy to convert a message into a hash but very difficult to “reverse hash” a hash value back to its original message as it requires a massive amount of computing power.
Why can’t hashing be reversed : How does hashing work in crypto When used in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, the end result is typically a 64-digit long string of numbers and letters. Because the conversion is done by a cryptographic algorithm (the “hash function”), the jumbling formula is unknown so the 64-digit string can't be reversed.
No, hashed data cannot be decrypted. Hashing is a one-way process, which means that the original data cannot be obtained from the hash value. It is designed to be irreversible, making it suitable for storing passwords and verifying data integrity.
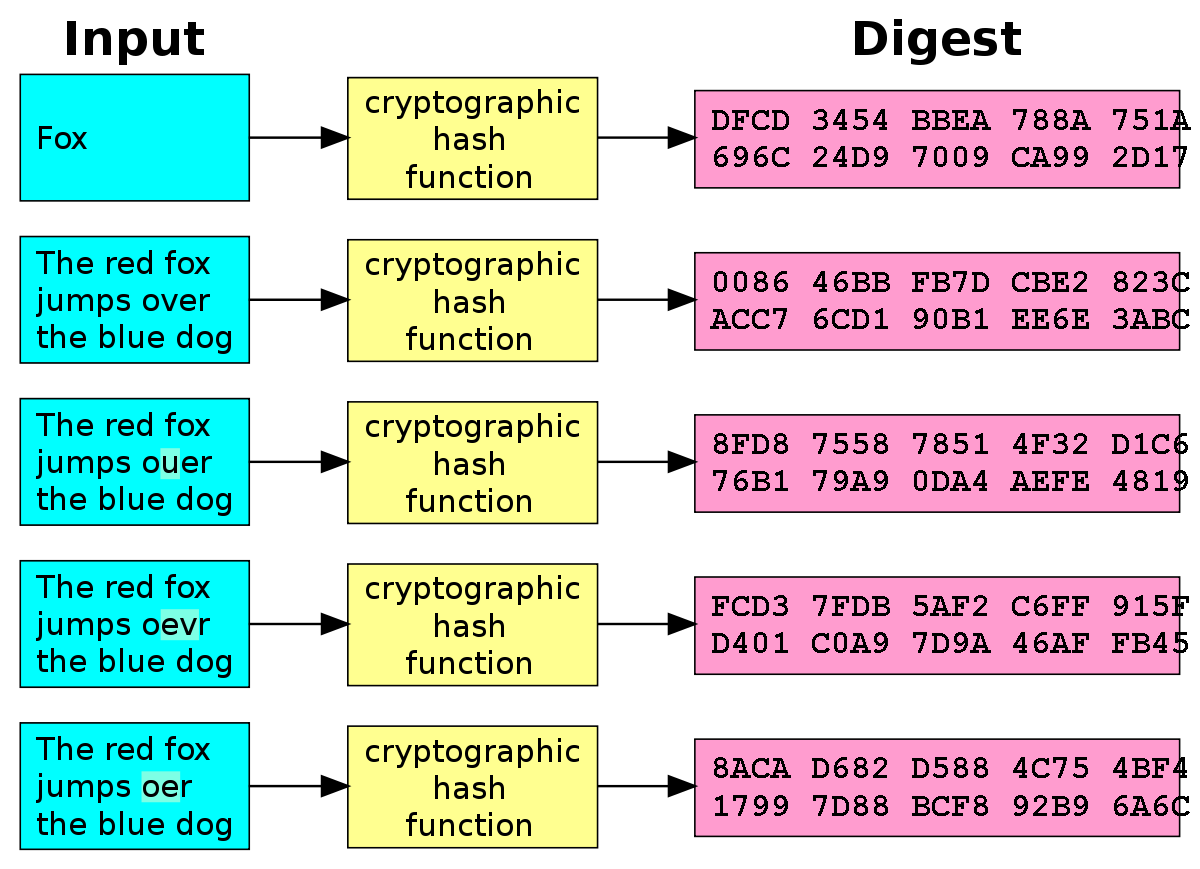
Hashing and encryption can keep sensitive data safe, but in almost all circumstances, passwords should be hashed, NOT encrypted. Because hashing is a one-way function (i.e., it is impossible to "decrypt" a hash and obtain the original plaintext value), it is the most appropriate approach for password validation.
What are the benefits of hashing data
Hashing verifies the file's integrity once it is transferred from one place to another in a file backup program. Users can compare the hash value of both files to ensure that transferred files are not corrupted.Since encryption is two-way, the data can be decrypted so it is readable again. Hashing, on the other hand, is one-way, meaning the plaintext is scrambled into a unique digest, through the use of a salt, that cannot be decrypted.If they successfully crack a hashed password, they may gain unauthorized access to user accounts and steal sensitive information. They may also use the stolen information for ransomware attacks, where the organization has to pay large sums of money to regain the sensitive data hackers have stolen and encrypted.

Irreversible: By design, all hash functions such as the SHA 256 are irreversible. You should neither get a plaintext when you have the digest beforehand nor should the digest provide its original value when you pass it through the hash function again.
Why is SHA-256 unbreakable : Because SHA-256 is a one-way cryptographic algorithm, it's impossible to reverse-engineer the input from the output hash. This means that miners can't cheat the system by submitting a fake solution since other nodes on the network can easily verify the answer by checking the hash.
What is the weakness of hashing : Hash tables are widely used data structures that offer efficient data retrieval and storage, but they also have some disadvantages: Collisions: One of the primary disadvantages of hash tables is the potential for collisions. Collisions occur when two different keys hash to the same index in the table.
Why is SHA 256 not reversible
SHA-256 refers to the bit size of the hash output. In other words, the resulting hash value from SHA-256 is 256 bits long, which provides a significantly larger search space compared to its predecessor, making it computationally infeasible to reverse engineer the original input from the hash value.
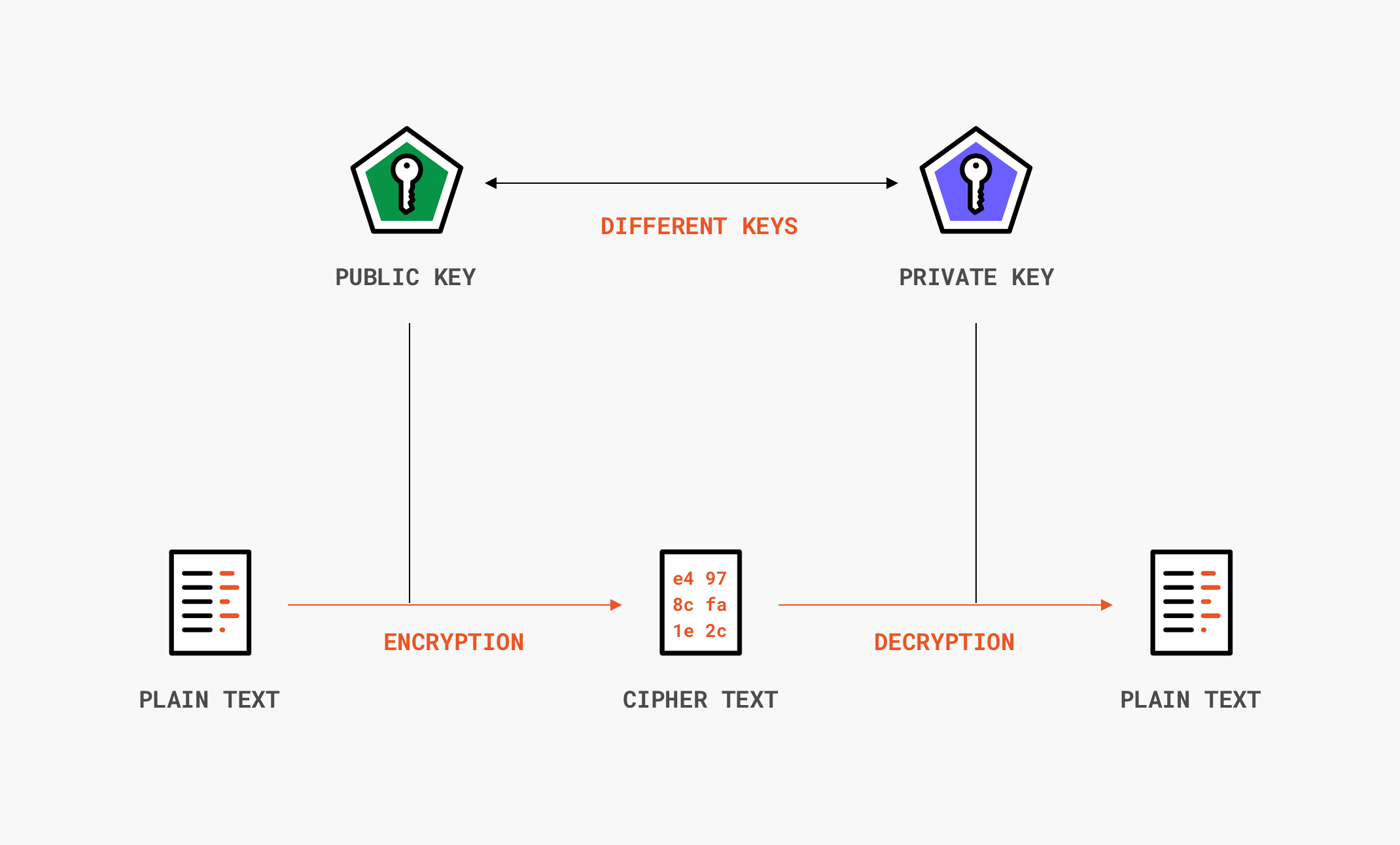
As hashing is extremely infeasible to reverse, hashing algorithms are used on passwords. This makes the password shorter and undiscoverable by attackers. Encryption, on the other hand, tends to be used for encrypting data that is in transit.Overall, the main reason why it is difficult or impossible to recover the original value from a given hash value is that the hash function is designed to be a one-way function, meaning that it is irreversible and computationally infeasible to reverse-engineer the original input data from the hash value.
What are the disadvantages of hashing passwords : Limitations of Password Hashing
Hackers can try a brute-force attack by running random passwords through the hash function until they finally find a match. This is rather inefficient since the hash algorithms designed for securely storing passwords are designed to be slow, making the entire process tedious and long.