The Dow tracks 30 large U.S. companies but has limited representation. The Nasdaq indexes, associated with the Nasdaq exchange, focus more heavily on tech and other stocks. The S&P 500, with 500 large U.S. companies, offers a more comprehensive market view, weighted by market capitalization.The S&P500 is considered less volatile than the DJIA.Answer & Explanation
The S&P 500 covers a broader spectrum of industries, offering better diversification compared to the DJIA, which is more concentrated in industrial companies.
What are the key differences between the S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average Chegg : The S&P 500 represents a much fewer number of companies and is weighted based on company stock prices, while the DJIA represents a much larger number of companies and its index is market cap weighted.
Why is S&P 500 so successful
The S&P is a float-weighted index, meaning the market capitalizations of the companies in the index are adjusted by the number of shares available for public trading. Because of its depth and diversity, the S&P 500 is widely considered one of the best gauges of large U.S. stocks, and even the entire equities market.
Is the S&P 500 the best index : Bottom line. S&P 500 index funds are some of the best investments for investors of all skill levels, but they can be especially beneficial for newer investors, who can enjoy solid returns without needing extensive expertise. Investors have a variety of cheap options to attain those tasty returns.
The key advantage of using the S&P 500 as a benchmark is the wide market breadth of the large-cap companies included in the index. The index can provide a broad view of the economic health of the U.S. because it covers so many companies in so many different sectors. In the Nasdaq vs Dow Jones consideration, investors weigh the Nasdaq's growth potential against the Dow's stability. The S&P 500: This index tracks 500 large US companies listed on stock exchanges. It offers a wider view of the stock market's performance than the Dow.
Why is the S&P 500 so successful
The S&P is a float-weighted index, meaning the market capitalizations of the companies in the index are adjusted by the number of shares available for public trading. Because of its depth and diversity, the S&P 500 is widely considered one of the best gauges of large U.S. stocks, and even the entire equities market.Because the S&P 5 0 0 has a greater number of companies and covers a wider range of industries, providing a more diverse and representative sample of the market.Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general. Several factors influence the index's value besides a company's share price. Instead of adding the constituents' stock prices, the S&P 500 adds the companies' float-adjusted market capitalization. Also, the index does not include gains from cash dividends paid by the companies that comprise the index.
Is S and P 500 overvalued : The S&P 500 is now 20% overvalued based on calculations comparing the stock market with the bond market, says Jack Ablin, chief investment officer at Cresset Capital Management. That's a scary pronouncement as it means a 20% crash is needed just to make the S&P 500 fairly priced.
What is the 20 year return of the S&P 500 : Stock Market Average Yearly Return for the Last 20 Years
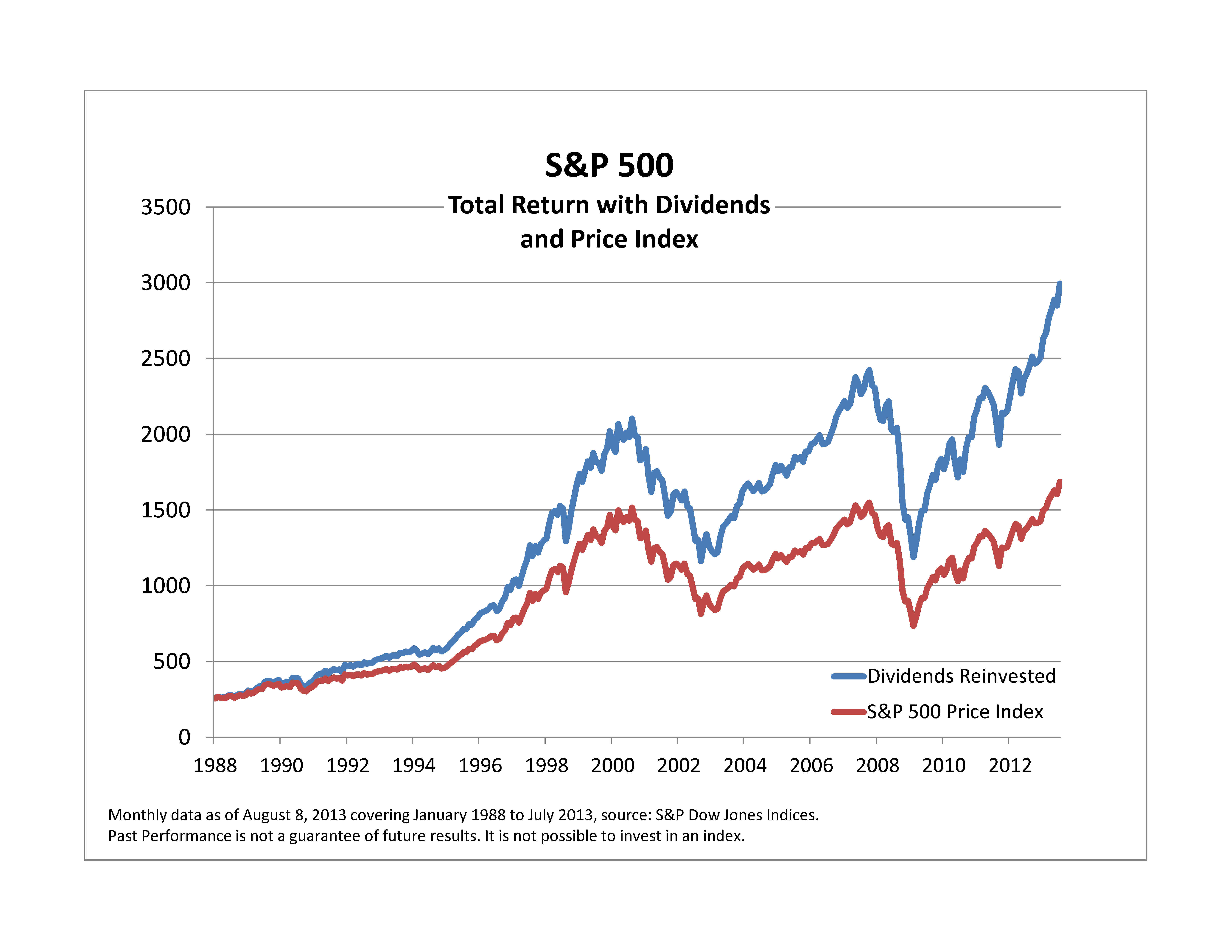
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 9.88% over the last 20 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 20-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 7.13%.
Why is the S&P 500 a leading indicator
The variable that is used to measure movements in stock prices is the quarterly percent change in the Standard and Poor's Composite Index of 500 stocks (SP500). The reason for choosing the S&P500 rather than other stock indexes is because it is a fairly representative measure of the stock market. Nasdaq 100 has outperformed S&P by a wide margin. The average 10-year return of Nasdaq 100 over these 15 years was around 9%, while that of S&P 500 was about 5%.The DJIA is based on the price of stocks for 30 large companies; the S&P 500 is based on the price of stocks for 500 companies.
What is the downside of S&P : The main drawback to the S&P 500 is that the index gives higher weights to companies with more market capitalization. The stock prices for Apple and Microsoft have a much greater influence on the index than a company with a lower market cap.
Antwort Why is S&P 500 better than Dow? Weitere Antworten – Why is the S&P 500 better than the Dow Jones
The Dow tracks 30 large U.S. companies but has limited representation. The Nasdaq indexes, associated with the Nasdaq exchange, focus more heavily on tech and other stocks. The S&P 500, with 500 large U.S. companies, offers a more comprehensive market view, weighted by market capitalization.The S&P500 is considered less volatile than the DJIA.Answer & Explanation
The S&P 500 covers a broader spectrum of industries, offering better diversification compared to the DJIA, which is more concentrated in industrial companies.

What are the key differences between the S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average Chegg : The S&P 500 represents a much fewer number of companies and is weighted based on company stock prices, while the DJIA represents a much larger number of companies and its index is market cap weighted.
Why is S&P 500 so successful
The S&P is a float-weighted index, meaning the market capitalizations of the companies in the index are adjusted by the number of shares available for public trading. Because of its depth and diversity, the S&P 500 is widely considered one of the best gauges of large U.S. stocks, and even the entire equities market.
Is the S&P 500 the best index : Bottom line. S&P 500 index funds are some of the best investments for investors of all skill levels, but they can be especially beneficial for newer investors, who can enjoy solid returns without needing extensive expertise. Investors have a variety of cheap options to attain those tasty returns.
The key advantage of using the S&P 500 as a benchmark is the wide market breadth of the large-cap companies included in the index. The index can provide a broad view of the economic health of the U.S. because it covers so many companies in so many different sectors.
In the Nasdaq vs Dow Jones consideration, investors weigh the Nasdaq's growth potential against the Dow's stability. The S&P 500: This index tracks 500 large US companies listed on stock exchanges. It offers a wider view of the stock market's performance than the Dow.
Why is the S&P 500 so successful
The S&P is a float-weighted index, meaning the market capitalizations of the companies in the index are adjusted by the number of shares available for public trading. Because of its depth and diversity, the S&P 500 is widely considered one of the best gauges of large U.S. stocks, and even the entire equities market.Because the S&P 5 0 0 has a greater number of companies and covers a wider range of industries, providing a more diverse and representative sample of the market.Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general.

Several factors influence the index's value besides a company's share price. Instead of adding the constituents' stock prices, the S&P 500 adds the companies' float-adjusted market capitalization. Also, the index does not include gains from cash dividends paid by the companies that comprise the index.
Is S and P 500 overvalued : The S&P 500 is now 20% overvalued based on calculations comparing the stock market with the bond market, says Jack Ablin, chief investment officer at Cresset Capital Management. That's a scary pronouncement as it means a 20% crash is needed just to make the S&P 500 fairly priced.
What is the 20 year return of the S&P 500 : Stock Market Average Yearly Return for the Last 20 Years
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 9.88% over the last 20 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 20-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 7.13%.
Why is the S&P 500 a leading indicator
The variable that is used to measure movements in stock prices is the quarterly percent change in the Standard and Poor's Composite Index of 500 stocks (SP500). The reason for choosing the S&P500 rather than other stock indexes is because it is a fairly representative measure of the stock market.
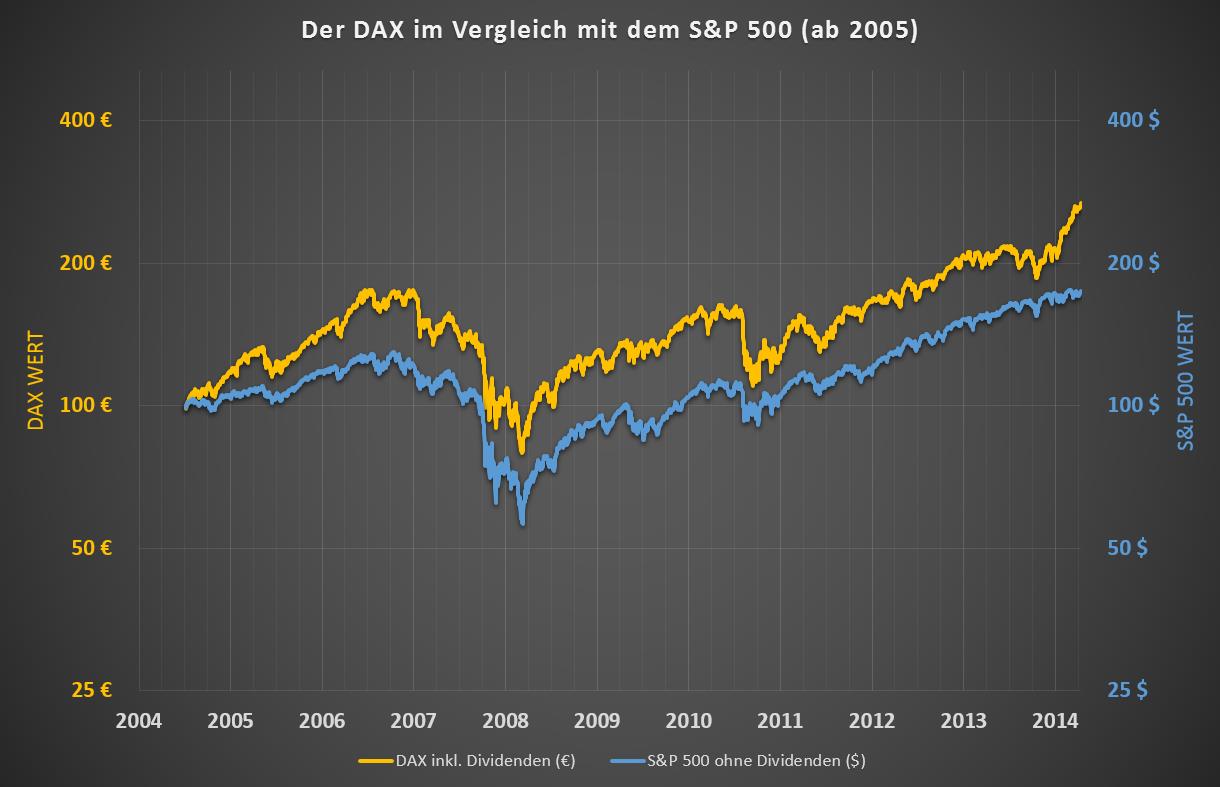
Nasdaq 100 has outperformed S&P by a wide margin. The average 10-year return of Nasdaq 100 over these 15 years was around 9%, while that of S&P 500 was about 5%.The DJIA is based on the price of stocks for 30 large companies; the S&P 500 is based on the price of stocks for 500 companies.
What is the downside of S&P : The main drawback to the S&P 500 is that the index gives higher weights to companies with more market capitalization. The stock prices for Apple and Microsoft have a much greater influence on the index than a company with a lower market cap.