PSA tests aren't foolproof. It's possible for your PSA levels to be elevated when cancer isn't present, and to not be elevated when cancer is present.Because prostate cancer often grows slowly, men without symptoms of prostate cancer who have less than a 10-year life expectancy should not be offered prostate cancer screening, because they aren't likely to benefit from it. Overall health status, and not age alone, is important when making decisions about screening.
it can miss cancer and provide false reassurance.
it may lead to unnecessary worry and medical tests when there's no cancer.
it cannot tell the difference between slow-growing and fast-growing cancers.
it may make you worry by finding a slow-growing cancer that may never cause any problems.
What are the potential downsides to PSA screening : The risks include:
Biopsy issues. A biopsy is a procedure that carries its own risks, including pain, bleeding and infection.
Psychological effects. False-positive test results — high PSA levels but no cancer found with biopsy — can cause anxiety or distress.
Is PSA more harm than good
“However, this research highlights that a PSA test for early detection can do more harm than good – it's simply not accurate enough and can lead to some men having tests and treatment that they don't need.
What is the truth about PSA levels : The PSA level in blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the PSA level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesn't have prostate cancer.
The task force recommends that men ages 55 to 69 make a shared decision with their doctors regarding routine prostate cancer screening, which usually means periodic blood tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA). The task force advises men to stop screening once they reach age 70. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that men ages 55 to 69 years discuss the possible benefits and harms of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening with their health care provider and make an individualized decision about whether to get screened.
Is it worth having a PSA test
Some studies have found that screening with the PSA test could mean fewer men die from prostate cancer. But it would also mean that: some men would have a biopsy, which could cause side effects. a large number of men would be diagnosed with a slow-growing cancer that wouldn't cause any symptoms or shorten their life.Absolute and relative change in serum PSA concentration, as well as the time to return to baseline PSA concentration following ejaculation, were assessed. Results: The serum PSA concentration increased following ejaculation in 87% of the subjects.The PSA test may give false-positive results.
A false-positive test result occurs when the PSA level is elevated but no cancer is actually present. A false-positive test result may create anxiety and lead to additional medical procedures, such as a prostate biopsy, that can be harmful. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening is not the panacea that enthusiasts hoped for, but it is not worthless. Men who have elevated PSA need to be aware that a prostate biopsy can identify both clinically significant and insignificant cancers and that intervention can affect quality of life.
What age are PSA no longer recommended : Before deciding, men should talk to their doctor about the benefits and harms of screening for prostate cancer, including the benefits and harms of other tests and treatment. Men who are 70 years old and older should not be screened for prostate cancer routinely.
Should a 72 year old get a PSA test : The US Preventive Services Task Force advises against PSA screening in men older than 69 years due to the risk of false-positive results and overdiagnosis of indolent disease. The American Urological Association (AUA) recommends against routine PSA screening of men older than 70 years.
Why no PSA test after 75
We are living longer, and 75 is not the ripe old age it used to be. But it's a cutoff age for PSA screening — and this is missing cancer in men who really need to be treated, say Brady investigators. "There is increasing evidence that this age-based approach is significantly flawed," says Patrick C. New Prostate Cancer Blood Test
If you have an abnormal PSA score, your doctor may recommend another newer test that gives a better sense of your prostate cancer risk . The prostate health index (PHI) is one such test that is a more accurate blood test and measures your risk for having prostate cancer.What happens after 7 days of not ejaculating If a person does not ejaculate, the unreleased sperm breaks down and absorbs back into the body. Not releasing sperm should not cause any health problems. However, if a person tries to ejaculate and is unable to, this could be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
How many times should a man release sperm in a week : Some studies suggest that moderate ejaculation (2–4 times per week) is associated with a lower prostate cancer risk. However, ejaculating more often doesn't mean your cancer risk drops even more.
Antwort Why is PSA screening no longer recommended? Weitere Antworten – Why are PSA tests not recommended
PSA tests aren't foolproof. It's possible for your PSA levels to be elevated when cancer isn't present, and to not be elevated when cancer is present.Because prostate cancer often grows slowly, men without symptoms of prostate cancer who have less than a 10-year life expectancy should not be offered prostate cancer screening, because they aren't likely to benefit from it. Overall health status, and not age alone, is important when making decisions about screening.
What are the potential downsides to PSA screening : The risks include:
Is PSA more harm than good
“However, this research highlights that a PSA test for early detection can do more harm than good – it's simply not accurate enough and can lead to some men having tests and treatment that they don't need.
What is the truth about PSA levels : The PSA level in blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the PSA level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesn't have prostate cancer.
The task force recommends that men ages 55 to 69 make a shared decision with their doctors regarding routine prostate cancer screening, which usually means periodic blood tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA). The task force advises men to stop screening once they reach age 70.
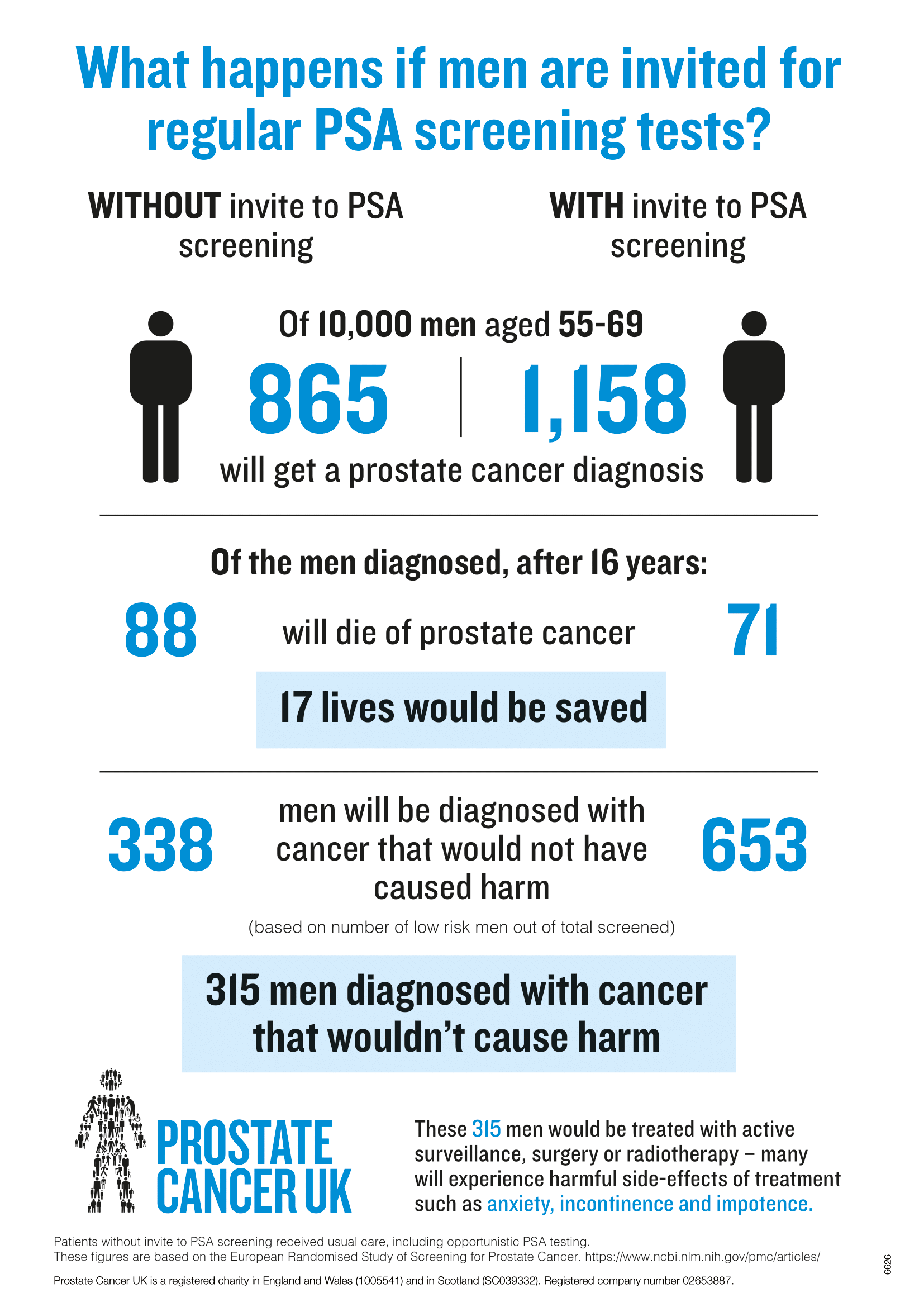
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that men ages 55 to 69 years discuss the possible benefits and harms of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening with their health care provider and make an individualized decision about whether to get screened.
Is it worth having a PSA test
Some studies have found that screening with the PSA test could mean fewer men die from prostate cancer. But it would also mean that: some men would have a biopsy, which could cause side effects. a large number of men would be diagnosed with a slow-growing cancer that wouldn't cause any symptoms or shorten their life.Absolute and relative change in serum PSA concentration, as well as the time to return to baseline PSA concentration following ejaculation, were assessed. Results: The serum PSA concentration increased following ejaculation in 87% of the subjects.The PSA test may give false-positive results.
A false-positive test result occurs when the PSA level is elevated but no cancer is actually present. A false-positive test result may create anxiety and lead to additional medical procedures, such as a prostate biopsy, that can be harmful.

Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening is not the panacea that enthusiasts hoped for, but it is not worthless. Men who have elevated PSA need to be aware that a prostate biopsy can identify both clinically significant and insignificant cancers and that intervention can affect quality of life.
What age are PSA no longer recommended : Before deciding, men should talk to their doctor about the benefits and harms of screening for prostate cancer, including the benefits and harms of other tests and treatment. Men who are 70 years old and older should not be screened for prostate cancer routinely.
Should a 72 year old get a PSA test : The US Preventive Services Task Force advises against PSA screening in men older than 69 years due to the risk of false-positive results and overdiagnosis of indolent disease. The American Urological Association (AUA) recommends against routine PSA screening of men older than 70 years.
Why no PSA test after 75
We are living longer, and 75 is not the ripe old age it used to be. But it's a cutoff age for PSA screening — and this is missing cancer in men who really need to be treated, say Brady investigators. "There is increasing evidence that this age-based approach is significantly flawed," says Patrick C.
New Prostate Cancer Blood Test
If you have an abnormal PSA score, your doctor may recommend another newer test that gives a better sense of your prostate cancer risk . The prostate health index (PHI) is one such test that is a more accurate blood test and measures your risk for having prostate cancer.What happens after 7 days of not ejaculating If a person does not ejaculate, the unreleased sperm breaks down and absorbs back into the body. Not releasing sperm should not cause any health problems. However, if a person tries to ejaculate and is unable to, this could be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
How many times should a man release sperm in a week : Some studies suggest that moderate ejaculation (2–4 times per week) is associated with a lower prostate cancer risk. However, ejaculating more often doesn't mean your cancer risk drops even more.