The two major causes of stent failure are stent thrombosis (ST) and in-stent restenosis (ISR).As demonstrated in the Global Journal for Research Analysis the most common symptoms of stent failure include: Chest pain and/or discomfort (usually similar pain that is experienced during a heart attack. Pain may be during physical activity or while resting)Ever since the wire-mesh tubes known as stents were first used to prop open arteries after they were cleared of cholesterol-filled plaque, doctors have had to figure out how to open clogged stents. The most common method is to maneuver a drug-coated stent wrapped around a balloon into the middle of the closed-up stent.
What is the difference between stent thrombosis and restenosis : Stent Thrombosis vs Restenosis
While stent thrombosis is an acute occlusion that causes an acute coronary syndrome, restenosis is a slow and progressive process that involves the narrowing of the stent lumen due to the growth of biologically fibrous neointima around the stem, resulting in anginal symptoms.
What percentage of blockage requires a stent
Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
Can arteries be too small for stents : Some patients have coronary plaques that are not amenable to balloon angioplasty or stenting because 1) the coronary artery is too small or 2) there is a complete blockage that cannot be crossed with the balloon.
Age or other risk factors may lead your provider to recommend a different treatment instead of a carotid stent, especially if you are over age 70 or you have a high risk of stroke. Stent grafts may be riskier for older people and those with conditions such as kidney or heart failure. Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
What percent of blockage requires a stent
An artery should be clogged at least 70% before a stent should be placed in it.The strongest predictor for the development of early stent thrombosis is premature discontinuation of DAPT in the first 30 days following stent implantation (7, 22).Stents are made to be permanent and will continue to keep your artery open once they've been placed. However, stents don't cure the underlying condition that caused the buildup in your artery (atherosclerosis). You'll still need treatment to prevent future artery narrowing. A mild blockage is one that's less than 50%. This means that less than half of your artery is blocked. A moderate blockage is between 50% and 79%. The most severe classification involves having the majority of your artery blocked — from 80% to 99%.
Is 50% blockage normal : Normal levels of arterial blockage can vary, but up to 50% blockage may be considered within a typical range. However, individual health conditions and risk factors should be assessed by an experienced cardiologist for accurate evaluation.
Do you need a stent at 50% blockage : Any amount of blockage in the LMCA, such as from plaque buildup or a clot, is referred to as “LMCA disease.” However, treatment is only needed when there is a blockage of 50% or more. At that level, there is an increased risk of death, a major heart attack, or a life-threatening arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat).
Can you stent a 70 blocked artery
At 70% blockage, your heart disease is likely to be causing symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath. In some cases, a blockage may be so serious that you have a heart attack and need emergency placement of one or more stents to restore healthy blood flow. It provides oxygenated blood to most of the left ventricle, which is the main pumping chamber of the heart. Any amount of blockage in the LMCA, such as from plaque buildup or a clot, is referred to as “LMCA disease.” However, treatment is only needed when there is a blockage of 50% or more.Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
Does 50% blockage require a stent : An artery should be clogged at least 70% before a stent should be placed in it.
Antwort Why do they not stent a 50 blockage? Weitere Antworten – What causes stent failure
The two major causes of stent failure are stent thrombosis (ST) and in-stent restenosis (ISR).As demonstrated in the Global Journal for Research Analysis the most common symptoms of stent failure include: Chest pain and/or discomfort (usually similar pain that is experienced during a heart attack. Pain may be during physical activity or while resting)Ever since the wire-mesh tubes known as stents were first used to prop open arteries after they were cleared of cholesterol-filled plaque, doctors have had to figure out how to open clogged stents. The most common method is to maneuver a drug-coated stent wrapped around a balloon into the middle of the closed-up stent.
What is the difference between stent thrombosis and restenosis : Stent Thrombosis vs Restenosis
While stent thrombosis is an acute occlusion that causes an acute coronary syndrome, restenosis is a slow and progressive process that involves the narrowing of the stent lumen due to the growth of biologically fibrous neointima around the stem, resulting in anginal symptoms.
What percentage of blockage requires a stent
Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
Can arteries be too small for stents : Some patients have coronary plaques that are not amenable to balloon angioplasty or stenting because 1) the coronary artery is too small or 2) there is a complete blockage that cannot be crossed with the balloon.
Age or other risk factors may lead your provider to recommend a different treatment instead of a carotid stent, especially if you are over age 70 or you have a high risk of stroke. Stent grafts may be riskier for older people and those with conditions such as kidney or heart failure.

Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
What percent of blockage requires a stent
An artery should be clogged at least 70% before a stent should be placed in it.The strongest predictor for the development of early stent thrombosis is premature discontinuation of DAPT in the first 30 days following stent implantation (7, 22).Stents are made to be permanent and will continue to keep your artery open once they've been placed. However, stents don't cure the underlying condition that caused the buildup in your artery (atherosclerosis). You'll still need treatment to prevent future artery narrowing.
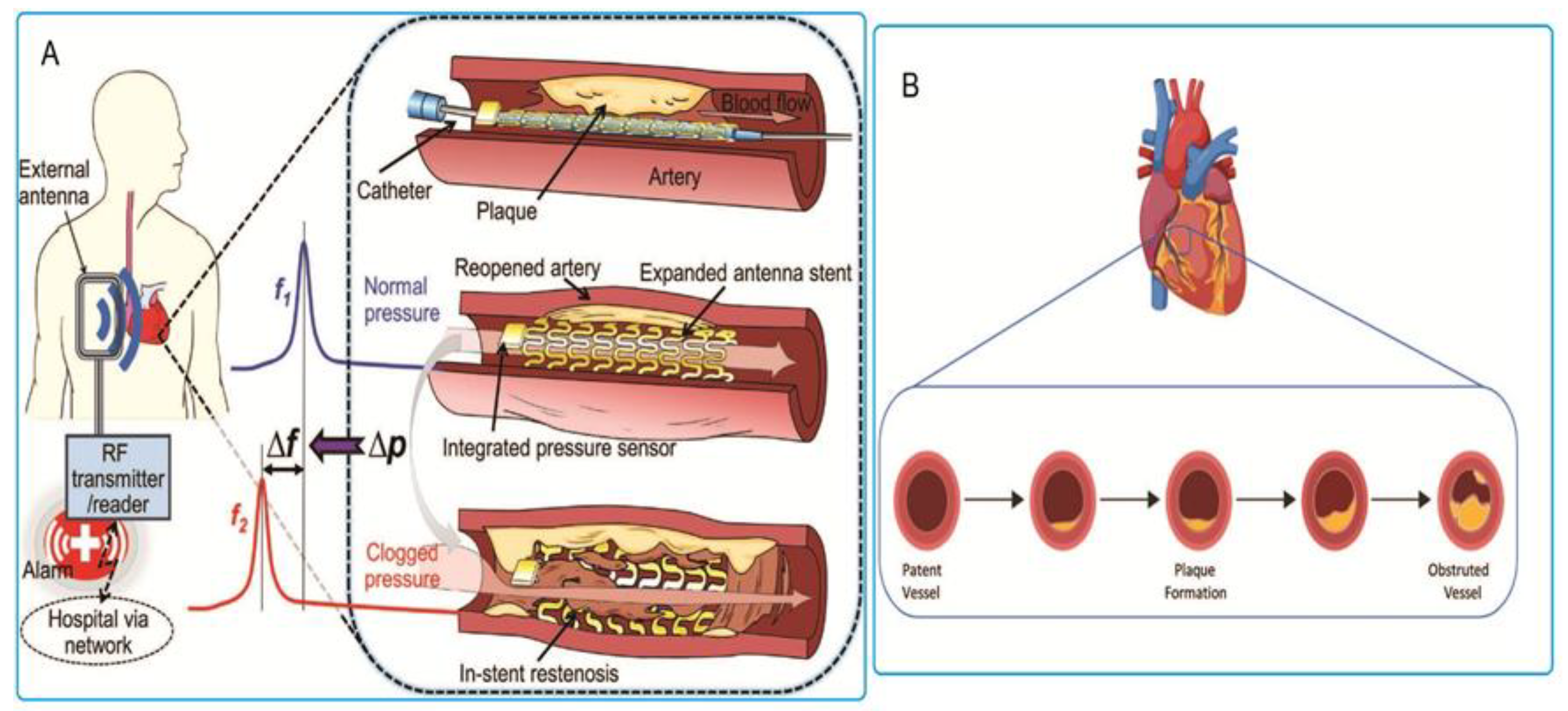
A mild blockage is one that's less than 50%. This means that less than half of your artery is blocked. A moderate blockage is between 50% and 79%. The most severe classification involves having the majority of your artery blocked — from 80% to 99%.
Is 50% blockage normal : Normal levels of arterial blockage can vary, but up to 50% blockage may be considered within a typical range. However, individual health conditions and risk factors should be assessed by an experienced cardiologist for accurate evaluation.
Do you need a stent at 50% blockage : Any amount of blockage in the LMCA, such as from plaque buildup or a clot, is referred to as “LMCA disease.” However, treatment is only needed when there is a blockage of 50% or more. At that level, there is an increased risk of death, a major heart attack, or a life-threatening arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat).
Can you stent a 70 blocked artery
At 70% blockage, your heart disease is likely to be causing symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath. In some cases, a blockage may be so serious that you have a heart attack and need emergency placement of one or more stents to restore healthy blood flow.
It provides oxygenated blood to most of the left ventricle, which is the main pumping chamber of the heart. Any amount of blockage in the LMCA, such as from plaque buildup or a clot, is referred to as “LMCA disease.” However, treatment is only needed when there is a blockage of 50% or more.Many people are told that a 70 percent blockage of the coronary artery will require a stent, but ultimately, it depends on the individual, their current health status, and the likelihood that the stent will improve the overall quality of life.
Does 50% blockage require a stent : An artery should be clogged at least 70% before a stent should be placed in it.