The amendments James Madison proposed were designed to win support in both houses of Congress and the states. He focused on rights-related amendments, ignoring suggestions that would have structurally changed the government.On June 8, 1789, Representative James Madison introduced a series of proposed amendments to the newly ratified U.S. Constitution. That summer the House of Representatives debated Madison's proposal, and on August 24 the House passed 17 amendments to be added to the Constitution.James Madison James Madison, America's fourth President (1809-1817), made a major contribution to the ratification of the Constitution by writing The Federalist Papers, along with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In later years, he was referred to as the “Father of the Constitution.”
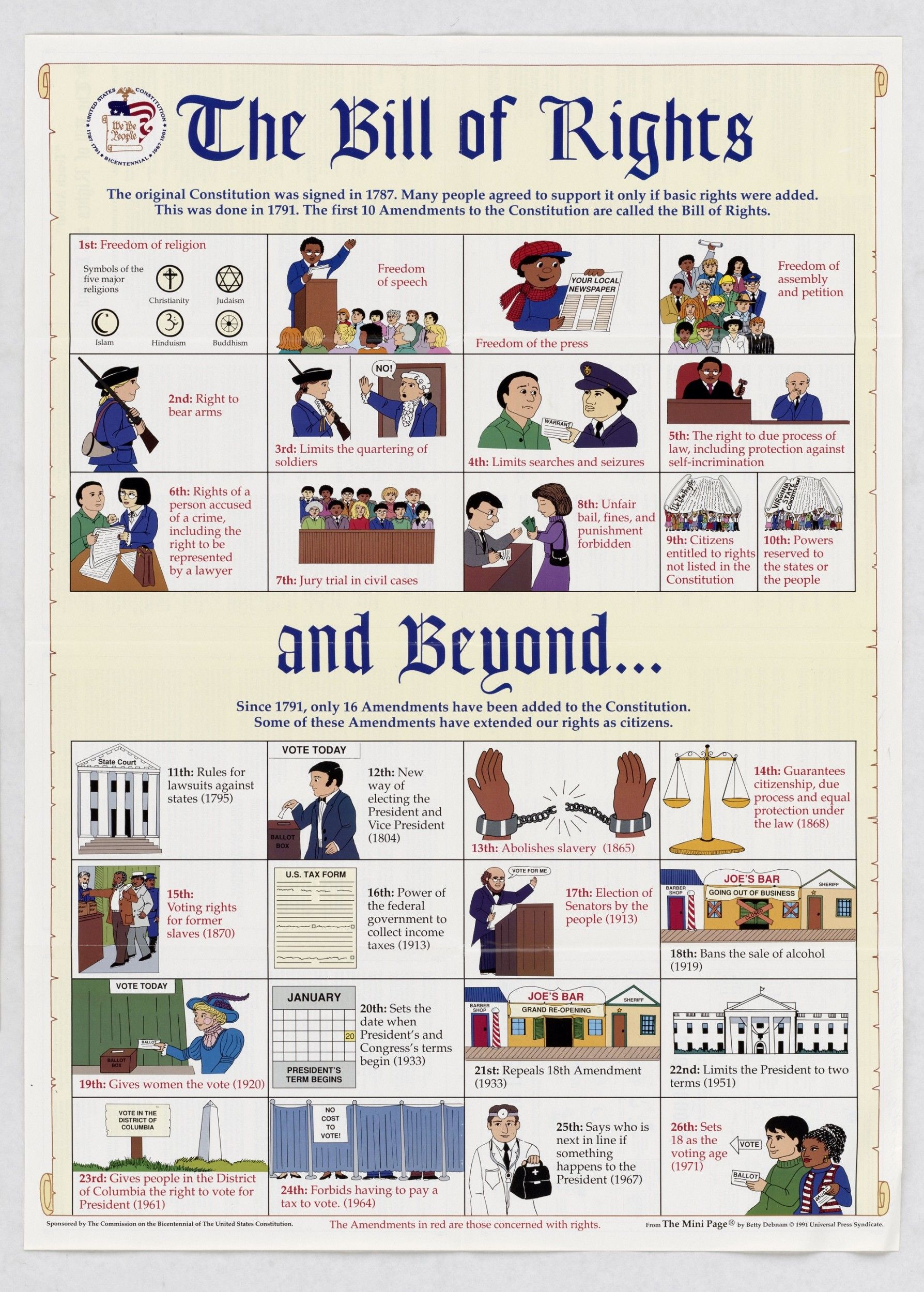
How many amendments make up the Bill of Rights : ten amendments The first ten amendments to the Constitution are called the Bill of Rights.
Who actually wrote the US Constitution
The main authors of the Constitution were James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay. These three men were all delegates to the Constitutional Convention, and they played a leading role in drafting the document.
Why did they create the English Bill of Rights : The Bill limits the power of the monarchy by creating a separation of powers, therefore enhancing and protecting the rights of citizens. After the Glorious Revolution, William and Mary had to agree to accept the Bill of Rights before they were able to be sworn in as king and queen in February 1689.
James Madison The American Bill of Rights, inspired by Jefferson and drafted by James Madison, was adopted, and in 1791 the Constitution's first ten amendments became the law of the land. The first 10 amendments to the Constitution make up the Bill of Rights. James Madison wrote the amendments, which list specific prohibitions on governmental power, in response to calls from several states for greater constitutional protection for individual liberties.
Is Thomas Jefferson the father of the Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights was proposed by the Congress that met in Federal Hall in New York City in 1789. Thomas Jefferson was the principal drafter of the Declaration and James Madison of the Bill of Rights; Madison, along with Gouverneur Morris and James Wilson, was also one of the principal architects of the Constitution.Thomas Jefferson, a spokesman for democracy, was an American Founding Father, the principal author of the Declaration of Independence (1776), and the third President of the United States (1801–1809).There are 27 ratified, or officially binding, amendments that have been added to the U.S. Constitution. Passed by the Senate on June 8, 1866, and ratified two years later, on July 9, 1868, the Fourteenth Amendment granted citizenship to all persons "born or naturalized in the United States," including formerly enslaved people, and provided all citizens with “equal protection under the laws,” extending the provisions of …
Who literally wrote the Constitution : Jacob Shallus or Shalus (1750–April 18, 1796) was the engrosser or penman of the original copy of the United States Constitution.
Who are the 12 founding fathers :
Founding Fathers of the United States
Leader(s)
John Adams Samuel Adams Benjamin Franklin Alexander Hamilton John Hancock John Jay Thomas Jefferson Richard Henry Lee Robert R. Livingston James Madison George Mason Robert Morris Peyton Randolph Roger Sherman George Washington
Who signed the English Bill of Rights
William III and Mary II The English Bill of Rights was an act signed into law in 1689 by William III and Mary II, who became co-rulers in England after the overthrow of King James II. The bill outlined specific constitutional and civil rights and ultimately gave Parliament power over the monarchy. noun phrase. variants or Bill of Rights. : a document containing a formal statement of rights. a patients' bill of rights. specifically : a summary of fundamental rights and privileges guaranteed to a people against violation by the state.So while we all as individuals, organisations or businesses, have a clear responsibility to respect and not to violate human rights, our governments have that same duty but also a further obligation to ensure human rights are both protected and fulfilled.
Who can use the Bill of Rights : (1) The Bill of Rights applies to all law, and binds the legislature, the executive, the judiciary and all organs of state.
Antwort Who made the Bill of Rights? Weitere Antworten – Who wrote the Bill of Rights
James Madison
Writing the Bill of Rights
The amendments James Madison proposed were designed to win support in both houses of Congress and the states. He focused on rights-related amendments, ignoring suggestions that would have structurally changed the government.On June 8, 1789, Representative James Madison introduced a series of proposed amendments to the newly ratified U.S. Constitution. That summer the House of Representatives debated Madison's proposal, and on August 24 the House passed 17 amendments to be added to the Constitution.James Madison
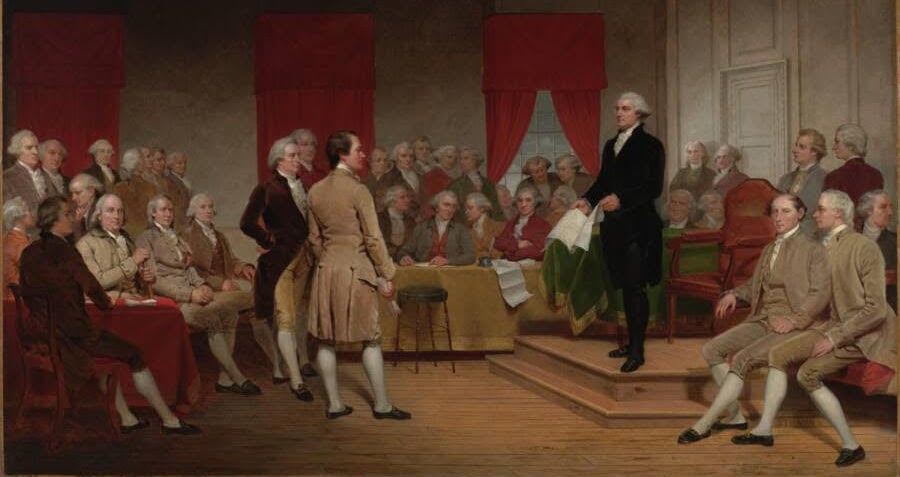

James Madison, America's fourth President (1809-1817), made a major contribution to the ratification of the Constitution by writing The Federalist Papers, along with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In later years, he was referred to as the “Father of the Constitution.”
How many amendments make up the Bill of Rights : ten amendments
The first ten amendments to the Constitution are called the Bill of Rights.
Who actually wrote the US Constitution
The main authors of the Constitution were James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay. These three men were all delegates to the Constitutional Convention, and they played a leading role in drafting the document.
Why did they create the English Bill of Rights : The Bill limits the power of the monarchy by creating a separation of powers, therefore enhancing and protecting the rights of citizens. After the Glorious Revolution, William and Mary had to agree to accept the Bill of Rights before they were able to be sworn in as king and queen in February 1689.
James Madison

The American Bill of Rights, inspired by Jefferson and drafted by James Madison, was adopted, and in 1791 the Constitution's first ten amendments became the law of the land.
The first 10 amendments to the Constitution make up the Bill of Rights. James Madison wrote the amendments, which list specific prohibitions on governmental power, in response to calls from several states for greater constitutional protection for individual liberties.
Is Thomas Jefferson the father of the Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights was proposed by the Congress that met in Federal Hall in New York City in 1789. Thomas Jefferson was the principal drafter of the Declaration and James Madison of the Bill of Rights; Madison, along with Gouverneur Morris and James Wilson, was also one of the principal architects of the Constitution.Thomas Jefferson, a spokesman for democracy, was an American Founding Father, the principal author of the Declaration of Independence (1776), and the third President of the United States (1801–1809).There are 27 ratified, or officially binding, amendments that have been added to the U.S. Constitution.
Passed by the Senate on June 8, 1866, and ratified two years later, on July 9, 1868, the Fourteenth Amendment granted citizenship to all persons "born or naturalized in the United States," including formerly enslaved people, and provided all citizens with “equal protection under the laws,” extending the provisions of …
Who literally wrote the Constitution : Jacob Shallus or Shalus (1750–April 18, 1796) was the engrosser or penman of the original copy of the United States Constitution.
Who are the 12 founding fathers :
Who signed the English Bill of Rights
William III and Mary II

The English Bill of Rights was an act signed into law in 1689 by William III and Mary II, who became co-rulers in England after the overthrow of King James II. The bill outlined specific constitutional and civil rights and ultimately gave Parliament power over the monarchy.
noun phrase. variants or Bill of Rights. : a document containing a formal statement of rights. a patients' bill of rights. specifically : a summary of fundamental rights and privileges guaranteed to a people against violation by the state.So while we all as individuals, organisations or businesses, have a clear responsibility to respect and not to violate human rights, our governments have that same duty but also a further obligation to ensure human rights are both protected and fulfilled.
Who can use the Bill of Rights : (1) The Bill of Rights applies to all law, and binds the legislature, the executive, the judiciary and all organs of state.