Bar graphs are used to compare things between different groups or to track changes over time.Bar graphs can help you compare data between different groups or to track changes over time. Bar graphs are most useful when there are big changes or to show how one group compares against other groups.A bar graph is composed of discrete bars that represent different categories of data. The length or height of the bar is equal to the quantity within that category of data. Bar graphs are best used to compare values across categories.
Which type of chart will be most effective : Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.
Which chart is used for comparison
Bar Chart. The bar chart is a widely used graphical representation for comparing different elements. One axis of the chart shows the items being compared, and the other axis represents the measured value.
When to use bar vs line chart :
Bar graphs are typically used to compare quantities of different categories in data. They are great for comparing categorical or nominal data where the categories are distinct and don't overlap.
Line graphs, on the other hand, are used to show a trend over time, also known as a time series.
One of the most common ways to measure similarity of two sets is to compare their data summary via mean and median. Figure 1 shows two graphs that compare the means and medians of the three pairs of data sets respectively. A line chart can be used to compare values between groups across time by plotting one line per group. A grouped bar chart allows for comparison of data across two different grouping variables by plotting multiple bars at each location, not just one.
What is the best graph to use for quantitative data
The type of graph or chart used to visualize data is determined by the type of data being represented. A pie chart or bar chart is typically used for nominal data and a bar chart for ordinal data. For quantitative data, we typically use a histogram for discrete data and a line graph for continuous data.You should choose a bar chart when you want to compare different categories or types of data. But if you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single set of data, go with a histogram.Graphs represent data with trends or patterns on two axes. It's a good way of showing the relationship between data sets and making sense of such data. When handling well-categorized data like age buckets, then charts are the best fit. On the other hand, graphs are ideal for showing patterns or trends in a data set. A line chart can be used to compare values between groups across time by plotting one line per group. A grouped bar chart allows for comparison of data across two different grouping variables by plotting multiple bars at each location, not just one.
Which chart type is used to compare two variables : A scatter plot displays values on two numeric variables using points positioned on two axes: one for each variable. Scatter plots are a versatile demonstration of the relationship between the plotted variables—whether that correlation is strong or weak, positive or negative, linear or non-linear.
Why are line graphs better than bar charts : Line charts are ideal for showing changing time series as well as trends and developments over time. Bar charts are good for comparing size, especially on small screens. They are a good alternative to column charts when the data are not time series, or axis labels are long.
When not to use line graph
Sometimes a line chart just won't be the best way to visualize the data. If you are working with data that is not numeric, you will probably want to use a bar chart instead. If you want to look at categories of any kind, even if the data is numeric, a bar chart is a great solution. It may be useful to compare two sets of data using the mean, mode or median in order to draw conclusions about the information presented. You may be choosing one measure over another for its accuracy or choosing the one that best backs up what you want to show.A bar chart is especially useful with comparing two sets of data.
Which of the graphs is analyzed by using comparison : Bar chart. A bar chart is often used to compare values of items at a certain point of time. It uses rectangles (bars) to visualise information. It is used mostly to show proportions, trends, comparisons or contrasts.
Antwort Which type of chart or graph is best when comparing data? Weitere Antworten – What kind of graph is best for comparing data
Bar graphs are used to compare things between different groups or to track changes over time.Bar graphs can help you compare data between different groups or to track changes over time. Bar graphs are most useful when there are big changes or to show how one group compares against other groups.A bar graph is composed of discrete bars that represent different categories of data. The length or height of the bar is equal to the quantity within that category of data. Bar graphs are best used to compare values across categories.
Which type of chart will be most effective : Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.
Which chart is used for comparison
Bar Chart. The bar chart is a widely used graphical representation for comparing different elements. One axis of the chart shows the items being compared, and the other axis represents the measured value.
When to use bar vs line chart :
One of the most common ways to measure similarity of two sets is to compare their data summary via mean and median. Figure 1 shows two graphs that compare the means and medians of the three pairs of data sets respectively.

A line chart can be used to compare values between groups across time by plotting one line per group. A grouped bar chart allows for comparison of data across two different grouping variables by plotting multiple bars at each location, not just one.
What is the best graph to use for quantitative data
The type of graph or chart used to visualize data is determined by the type of data being represented. A pie chart or bar chart is typically used for nominal data and a bar chart for ordinal data. For quantitative data, we typically use a histogram for discrete data and a line graph for continuous data.You should choose a bar chart when you want to compare different categories or types of data. But if you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single set of data, go with a histogram.Graphs represent data with trends or patterns on two axes. It's a good way of showing the relationship between data sets and making sense of such data. When handling well-categorized data like age buckets, then charts are the best fit. On the other hand, graphs are ideal for showing patterns or trends in a data set.

A line chart can be used to compare values between groups across time by plotting one line per group. A grouped bar chart allows for comparison of data across two different grouping variables by plotting multiple bars at each location, not just one.
Which chart type is used to compare two variables : A scatter plot displays values on two numeric variables using points positioned on two axes: one for each variable. Scatter plots are a versatile demonstration of the relationship between the plotted variables—whether that correlation is strong or weak, positive or negative, linear or non-linear.
Why are line graphs better than bar charts : Line charts are ideal for showing changing time series as well as trends and developments over time. Bar charts are good for comparing size, especially on small screens. They are a good alternative to column charts when the data are not time series, or axis labels are long.
When not to use line graph
Sometimes a line chart just won't be the best way to visualize the data. If you are working with data that is not numeric, you will probably want to use a bar chart instead. If you want to look at categories of any kind, even if the data is numeric, a bar chart is a great solution.
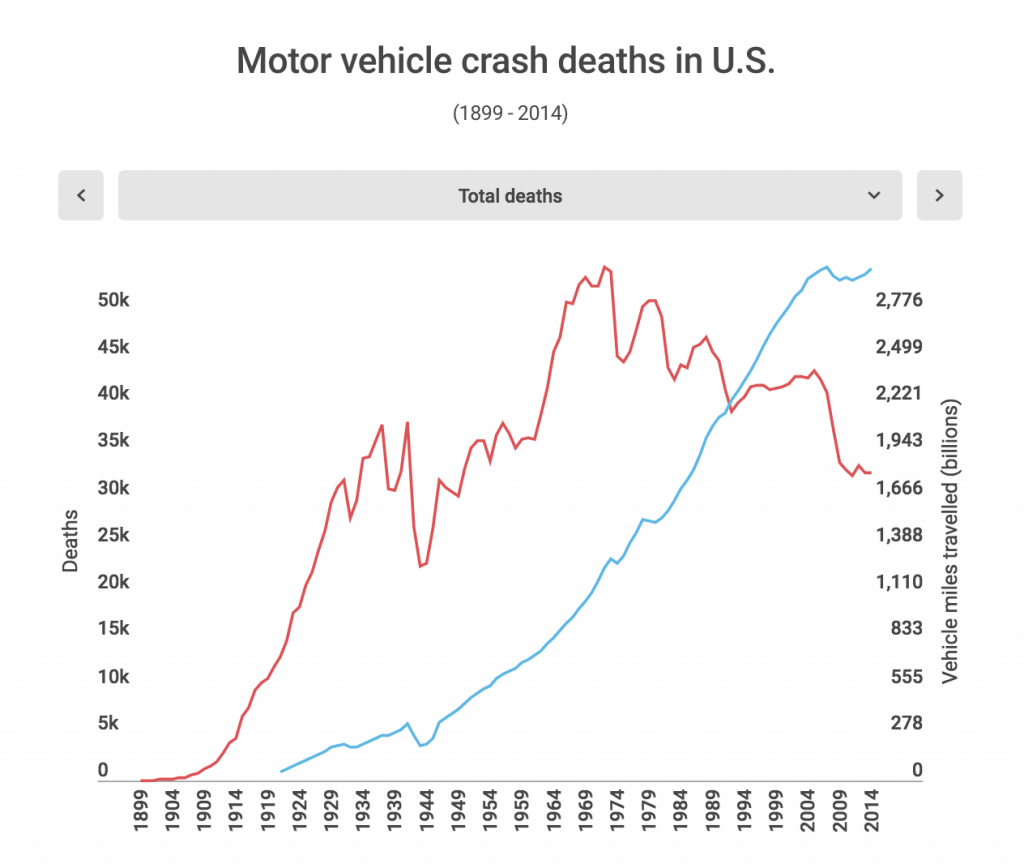
It may be useful to compare two sets of data using the mean, mode or median in order to draw conclusions about the information presented. You may be choosing one measure over another for its accuracy or choosing the one that best backs up what you want to show.A bar chart is especially useful with comparing two sets of data.
Which of the graphs is analyzed by using comparison : Bar chart. A bar chart is often used to compare values of items at a certain point of time. It uses rectangles (bars) to visualise information. It is used mostly to show proportions, trends, comparisons or contrasts.