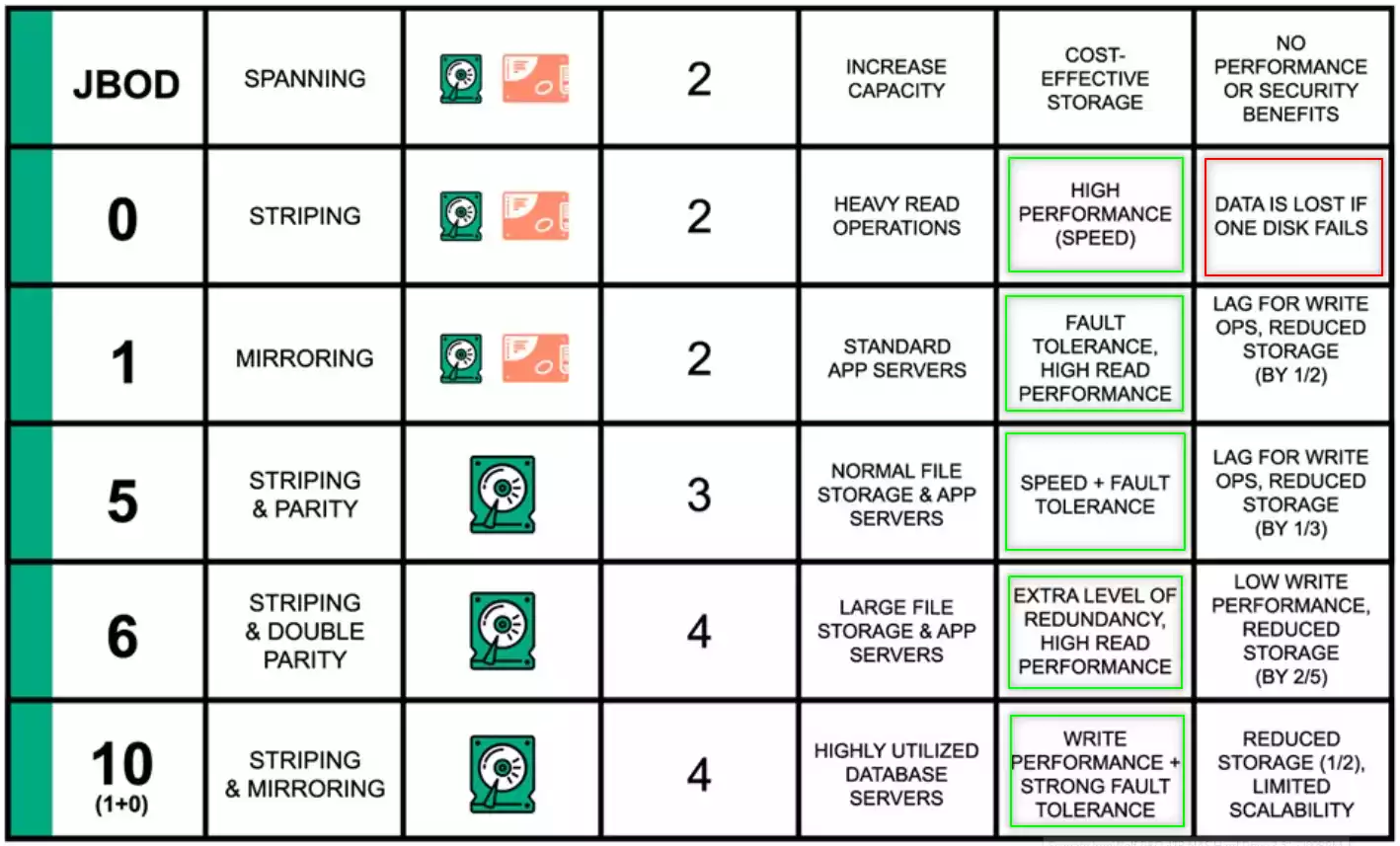
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple drives to be combined into a single storage space. There are different types of RAID, each providing different levels of performance, storage capacity, and reliability.Efficient Storage Utilization: Compared to RAID 1, RAID 5 provides a more efficient use of disk space. While it still offers data protection through parity checks, it doesn't require a complete copy of all data, thereby using storage capacity more effectively.
Is RAID 5 still useful : RAID 5 evenly balances reads and writes, and is currently one of the most commonly used RAID methods. It has more usable storage than RAID 1 and RAID 10 configurations and provides performance equivalent to RAID 0. RAID 5 groups have a minimum of three HDDs and no maximum.
Should a NAS use RAID
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
Why should I use RAID : A RAID controller is a device used to manage hard disk drives in a storage array. It can be used as a level of abstraction between the OS and the physical disks, presenting groups of disks as logical units. Using a RAID controller can improve performance and help protect data in case of a crash.
RAID 1 offers higher fault tolerance compared to RAID 5. In RAID 1, a single disk failure does not result in data loss or downtime, as the mirrored disk contains an exact copy. RAID 5 can tolerate the failure of a single disk but is vulnerable to data loss if multiple disks fail simultaneously. typically, a RAID 5 rebuild on large disks (2TB+) can be measured in days. During this time your data is at risk as the server is calculating the missing data and as such, it's painfully slow. In some cases it may not even be usable. URE – Uncorrectable read error.
Is RAID 50 faster than RAID 5
RAID 50 is capable of faster rebuilds, a necessity when downtime is considered unacceptable. Although performance inevitably degrades in the event of a disk failure, it degrades less than it does in a RAID 5 array. This is because a single failure only affects one of the arrays, leaving the other fully functional.Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.Having all the drives in one box that is being served by one power supply and controller has its problems too. A bad enough power surge will probably fry all disks in the RAID. If your house burns down… well, you get the point. A RAID is still a single device and because of that, also a single point of failure. However, they still may be currently used to prevent data loss. Hyperscale computing also removes the need for RAID by using redundant servers instead of redundant drives. Still, RAID remains an ingrained part of data storage and major technology vendors continue to release RAID products.
Is RAID 5 still recommended : RAID 5 is deprecated and not recommended for new arrays due to its vulnerability during rebuilds with large-capacity drives.
Why is RAID 0 risky : Since the data is split evenly between all the drives on the array, there is absolutely no redundancy. Because of this zero-fault tolerance, if one drive fails, all the data on the array is lost. That means RAID 0 is actually less reliable than using a single disk. RAID 0 failure is a real possibility.
Why never use raid 5
This four step read-read-write-write operation is known as the RAID5 write penalty since these two writes are sequential and synchronous the write system call cannot return until the reread and both writes complete, for safety, so writing to RAID5 is up to 50% slower than RAID0 for an array of the same capacity. SSD RAID is widely recommended for its fast data read and write ability, where SSD RAID is superior to a single SSD. The RAID array configured with multiple SSDs can greatly impact the reading and writing of data.If performance needs are paramount, you will certainly benefit from using a RAID 10 setup. The RAID controller can perform disk reads and writes across multiple drives simultaneously giving your server (and users) helpful performance enhancements!
Should you raid a NAS : While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
Antwort Which is better NAS or RAID? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between Synology RAID 5 and RAID 6
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple drives to be combined into a single storage space. There are different types of RAID, each providing different levels of performance, storage capacity, and reliability.Efficient Storage Utilization: Compared to RAID 1, RAID 5 provides a more efficient use of disk space. While it still offers data protection through parity checks, it doesn't require a complete copy of all data, thereby using storage capacity more effectively.
Is RAID 5 still useful : RAID 5 evenly balances reads and writes, and is currently one of the most commonly used RAID methods. It has more usable storage than RAID 1 and RAID 10 configurations and provides performance equivalent to RAID 0. RAID 5 groups have a minimum of three HDDs and no maximum.
Should a NAS use RAID
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.
Why should I use RAID : A RAID controller is a device used to manage hard disk drives in a storage array. It can be used as a level of abstraction between the OS and the physical disks, presenting groups of disks as logical units. Using a RAID controller can improve performance and help protect data in case of a crash.
RAID 1 offers higher fault tolerance compared to RAID 5. In RAID 1, a single disk failure does not result in data loss or downtime, as the mirrored disk contains an exact copy. RAID 5 can tolerate the failure of a single disk but is vulnerable to data loss if multiple disks fail simultaneously.

typically, a RAID 5 rebuild on large disks (2TB+) can be measured in days. During this time your data is at risk as the server is calculating the missing data and as such, it's painfully slow. In some cases it may not even be usable. URE – Uncorrectable read error.
Is RAID 50 faster than RAID 5
RAID 50 is capable of faster rebuilds, a necessity when downtime is considered unacceptable. Although performance inevitably degrades in the event of a disk failure, it degrades less than it does in a RAID 5 array. This is because a single failure only affects one of the arrays, leaving the other fully functional.Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.Having all the drives in one box that is being served by one power supply and controller has its problems too. A bad enough power surge will probably fry all disks in the RAID. If your house burns down… well, you get the point. A RAID is still a single device and because of that, also a single point of failure.
However, they still may be currently used to prevent data loss. Hyperscale computing also removes the need for RAID by using redundant servers instead of redundant drives. Still, RAID remains an ingrained part of data storage and major technology vendors continue to release RAID products.
Is RAID 5 still recommended : RAID 5 is deprecated and not recommended for new arrays due to its vulnerability during rebuilds with large-capacity drives.
Why is RAID 0 risky : Since the data is split evenly between all the drives on the array, there is absolutely no redundancy. Because of this zero-fault tolerance, if one drive fails, all the data on the array is lost. That means RAID 0 is actually less reliable than using a single disk. RAID 0 failure is a real possibility.
Why never use raid 5
This four step read-read-write-write operation is known as the RAID5 write penalty since these two writes are sequential and synchronous the write system call cannot return until the reread and both writes complete, for safety, so writing to RAID5 is up to 50% slower than RAID0 for an array of the same capacity.
SSD RAID is widely recommended for its fast data read and write ability, where SSD RAID is superior to a single SSD. The RAID array configured with multiple SSDs can greatly impact the reading and writing of data.If performance needs are paramount, you will certainly benefit from using a RAID 10 setup. The RAID controller can perform disk reads and writes across multiple drives simultaneously giving your server (and users) helpful performance enhancements!
Should you raid a NAS : While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.