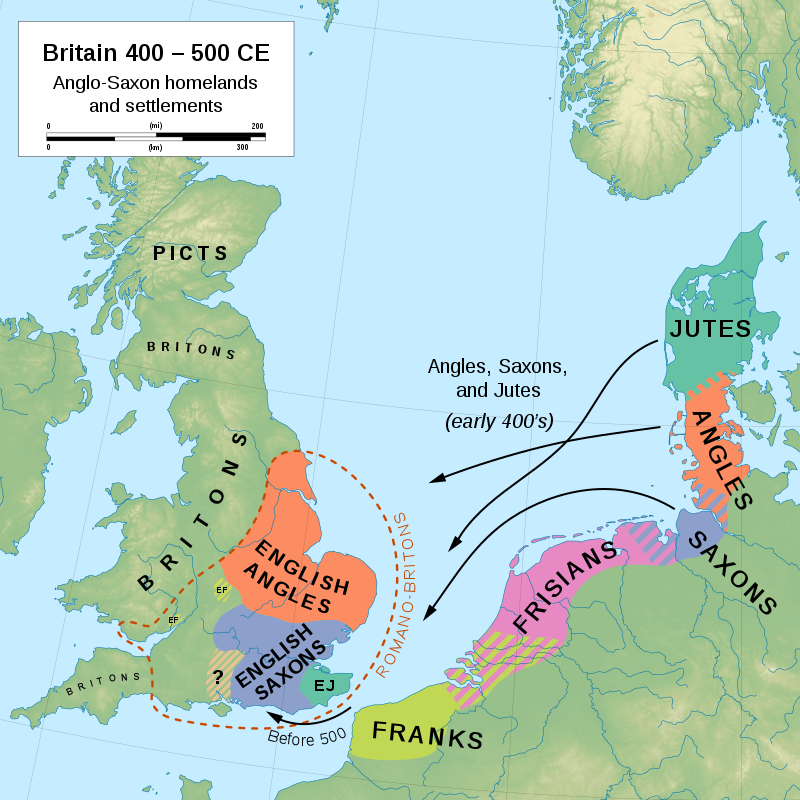
The most significant of them were Wessex in the south west, Mercia in the Midlands, Northumbria in the north of England (extending into southern Scotland) and East Anglia (covering the present-day counties of Norfolk and Suffolk).By Vikings, we mean groups of raiders and settlers originally from what are now the Scandinavian countries of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. It was most often people from the first two places that were involved with England from about AD 789 to 1066.Tarkhan. (which is what England is called in both English and old Norse or at least 13th century Icelandic. England was called "Englaland" until Old English was replaced by Middle English.
Who defeated the Vikings in England : King Harold
The last serious Viking invasion was led by a Norwegian king called Harald Hardrada in 1066, but he was defeated by the English King Harold at the battle of Stamford Bridge just two weeks before the famous Battle of Hastings.
Did any Vikings stay in England
Anglo-Saxon writers called them Danes, Norsemen, Northmen, the Great Army, sea rovers, sea wolves, or the heathen. From around 860AD onwards, Vikings stayed, settled and prospered in Britain, becoming part of the mix of people who today make up the British nation.
What language did the Vikings speak : Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.
Old Norse
The Vikings spoke Old Norse, also known as Dǫnsk Tunga/Norrœnt mál. Old Norse was a North Germanic language spoken by the Vikings in Scandinavia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and in parts of Russia, France, the British Isles where Vikings had settled. Alfred
At the battle of Ashdown in 871, Alfred routed the Viking army in a fiercely fought uphill assault. However, further defeats followed for Wessex and Alfred's brother died.
Did a Viking ever rule England
Although Danelaw was no more in England, the Vikings were far from done on English soil. They retreated, consolidated and successfully conquered the country in the early 11th century. In 1013, Sweyn Forkbeard became the first Danish King of England. His son, Cnut the Great, held the throne until he died in 1035.Norman, member of those Vikings, or Norsemen, who settled in northern France (or the Frankish kingdom), together with their descendants. The Normans founded the duchy of Normandy and sent out expeditions of conquest and colonization to southern Italy and Sicily and to England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.The 4 Kingdoms of England were in place for around 100 years, from 829 AD to 929 AD, when England was united as one. The 4 Kingdoms were East Anglia, Mercia, Northumbria, and Wessex. Scandinavian and Nordic Greetings & Useful Phrases
Hello – Hej! Good morning/day/evening/night – God morgon! / Goddag! / God kväll! / God natt!
Can you still speak Old Norse : Over the centuries, Old Norse continued to fragment into more regionally-specific languages, and by the early modern era, it had been transformed into Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Faroese.
Are there any Vikings left : ' or 'do Vikings still exist ', the answer is no. The Viking Age ended at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, although the influence of the Vikings still lives on across Europe, particularly in the Scandinavian nations.
Who are the Normans today
Normans are still there. The word meant simply “northern men”. It referred to Scandinavians. Today as well, most of Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, Faroese and Icelandic population descends from Normans aka Vikings. Norman French
Norman or Norman French (Normaund, French: Normand [nɔʁmɑ̃], Guernésiais: Normand, Jèrriais: Nouormand) is a Romance language which can be classified as a langue d'oïl, which also includes French, Picard and Walloon.The Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon Britain were as follows:
East Anglia.
Mercia.
Northumbria.
Wessex.
Essex.
Kent.
Sussex.
What is Mercia known as today : Mercia (pron.: / ˈ m ɜr s i ə /, / ˈ m ɜr ʃ ə /) was one of the kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was centred on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries in the region now known as the English Midlands.
Antwort Where did the Vikings settle in England? Weitere Antworten – Where was the Viking settlement in England
The most significant of them were Wessex in the south west, Mercia in the Midlands, Northumbria in the north of England (extending into southern Scotland) and East Anglia (covering the present-day counties of Norfolk and Suffolk).By Vikings, we mean groups of raiders and settlers originally from what are now the Scandinavian countries of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. It was most often people from the first two places that were involved with England from about AD 789 to 1066.Tarkhan. (which is what England is called in both English and old Norse or at least 13th century Icelandic. England was called "Englaland" until Old English was replaced by Middle English.
Who defeated the Vikings in England : King Harold
The last serious Viking invasion was led by a Norwegian king called Harald Hardrada in 1066, but he was defeated by the English King Harold at the battle of Stamford Bridge just two weeks before the famous Battle of Hastings.
Did any Vikings stay in England
Anglo-Saxon writers called them Danes, Norsemen, Northmen, the Great Army, sea rovers, sea wolves, or the heathen. From around 860AD onwards, Vikings stayed, settled and prospered in Britain, becoming part of the mix of people who today make up the British nation.
What language did the Vikings speak : Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.
Old Norse
The Vikings spoke Old Norse, also known as Dǫnsk Tunga/Norrœnt mál. Old Norse was a North Germanic language spoken by the Vikings in Scandinavia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and in parts of Russia, France, the British Isles where Vikings had settled.
Alfred
At the battle of Ashdown in 871, Alfred routed the Viking army in a fiercely fought uphill assault. However, further defeats followed for Wessex and Alfred's brother died.
Did a Viking ever rule England
Although Danelaw was no more in England, the Vikings were far from done on English soil. They retreated, consolidated and successfully conquered the country in the early 11th century. In 1013, Sweyn Forkbeard became the first Danish King of England. His son, Cnut the Great, held the throne until he died in 1035.Norman, member of those Vikings, or Norsemen, who settled in northern France (or the Frankish kingdom), together with their descendants. The Normans founded the duchy of Normandy and sent out expeditions of conquest and colonization to southern Italy and Sicily and to England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.The 4 Kingdoms of England were in place for around 100 years, from 829 AD to 929 AD, when England was united as one. The 4 Kingdoms were East Anglia, Mercia, Northumbria, and Wessex.

Scandinavian and Nordic Greetings & Useful Phrases
Hello – Hej! Good morning/day/evening/night – God morgon! / Goddag! / God kväll! / God natt!
Can you still speak Old Norse : Over the centuries, Old Norse continued to fragment into more regionally-specific languages, and by the early modern era, it had been transformed into Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Faroese.
Are there any Vikings left : ' or 'do Vikings still exist ', the answer is no. The Viking Age ended at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, although the influence of the Vikings still lives on across Europe, particularly in the Scandinavian nations.
Who are the Normans today
Normans are still there. The word meant simply “northern men”. It referred to Scandinavians. Today as well, most of Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, Faroese and Icelandic population descends from Normans aka Vikings.

Norman French
Norman or Norman French (Normaund, French: Normand [nɔʁmɑ̃], Guernésiais: Normand, Jèrriais: Nouormand) is a Romance language which can be classified as a langue d'oïl, which also includes French, Picard and Walloon.The Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon Britain were as follows:
What is Mercia known as today : Mercia (pron.: / ˈ m ɜr s i ə /, / ˈ m ɜr ʃ ə /) was one of the kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was centred on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries in the region now known as the English Midlands.