European leaders met in the Congress of Vienna in 1814 and 1815 to redraw Europe's boundaries after Napoleon's fall and ensure stability in Europe. They returned the old royal family of France to power and acknowledged Finland, which was taken over by Russia during the wars, as Russian territory.The coalition invaded France and captured Paris, forcing Napoleon to abdicate in April 1814. He was exiled to the island of Elba, between Corsica and Italy. In France, the Bourbons were restored to power. Napoleon escaped in February 1815 and took control of France.After Napoleon's defeat, the power of Europe was captured by conservatives. After Napoleon was defeated in 1815, conservatism became the driving force behind European governments.
What was the role of Napoleon in the unification of Europe : Through his conquests he brought the scattered areas of Europe together under the first French Empire. The End of Feudalism- Together the French Revolution and Napoleon's rule brought an end to Feudalism in France. Lands belonging Church and nobles were confiscated and privileges were abolished.
What was France like after Napoleon
Following his defeat in the Napoleonic Wars, France went through regime changes, being ruled as a monarchy, then Second Republic, then Second Empire, until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. France was one of the Triple Entente powers in World War I against Germany and the Central Powers.
What changes did Napoleon introduce in Europe : It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. In towns too, guild systems were removed. Transport and communication systems were improved.
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today. His last words were 'France, the Army, the Head of the Army, Josephine'. Napoleon's body was returned to France and in 1840 was interred in Les Invalides along with the bodies of his brothers and son.
Who saved Europe from Napoleon
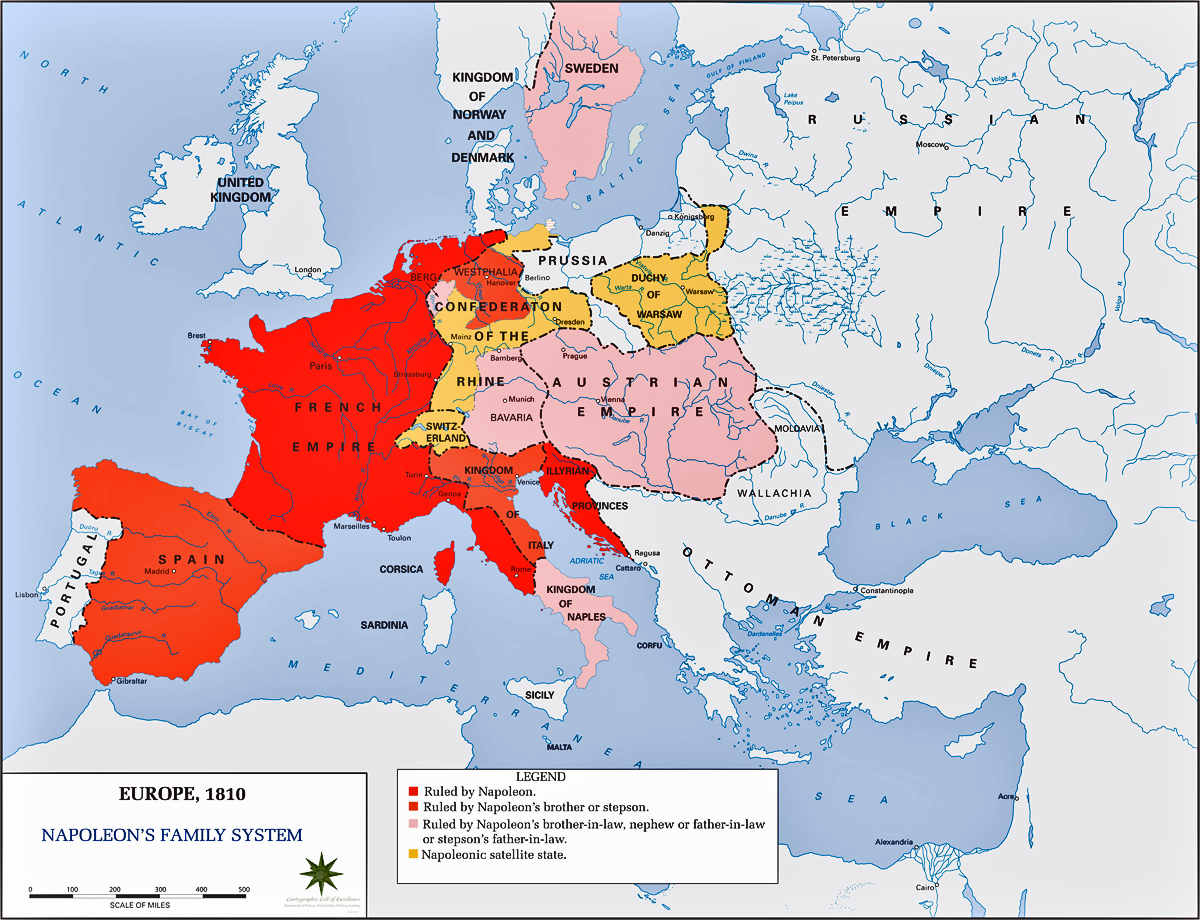
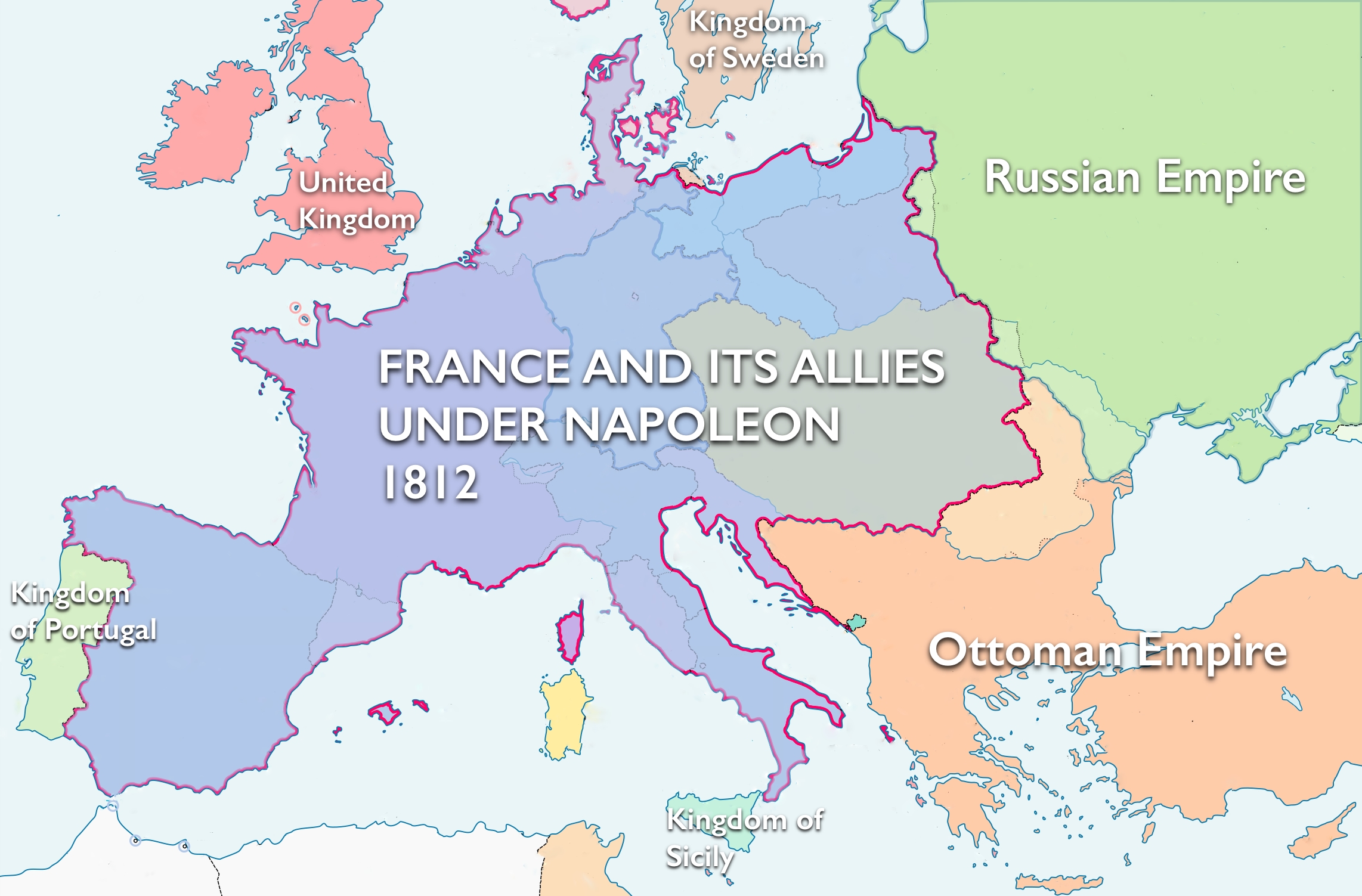
Clemens Lothar Metternich: The Man Who Saved “Old Europe” From Napoleon. Clemens Lothar Metternich was a symbol of old Europe in the 19th century. He protected this Europe from Napoleon and from nationalists and revolutionaries in 1848.The European map changed a lot, Poland went to Russia, Holland and Belgium were united, and a loose confederation of states was drawn up for Germany. Q. Napoleon Bonaparte was defeated in the Battle of Waterloo by Britain, Denmark, Prussia and Austria.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie. His victory over the royalists made him an immediate hero. He was sent to lead French forces in Italy, fighting the Austrian (Habsburg) Empire. There, he won a number of huge victories and by 1797 had invaded Austria itself.
What was Napoleon’s influence on the rest of Europe : Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy.
How did France react to Napoleon : The people of France loved Napoleon. He had defended France against invasion, won her glory in battle, and had restored relative order to a country wracked by strife and political division. Support for his coronation was mixed. Not much changed in the short term, he was an autocratic ruler before and after.
How did Napoleon impact Europe
Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy. The Civil Code of 1804 or Napoleonic Code abolished privileges by birth, introduced equality before law and incorporated right to property. He also abolished feudal systems in other parts of Europe and liberated the peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. The traditional guild system was also abolished.After the defeat of Napoleon, European rulers moved to restore the old order. This was the goal of the victors—Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, and Russia. They met at the Congress of Vienna in September 1814 to arrange a final peace settlement.
What was Napoleon’s IQ : 145Estimated IQs of 301 Geniuses of the 15th – 19th Centuries by Catharine Morris Cox, PhD
Antwort What was Europe like after Napoleon? Weitere Antworten – What happened to Europe after Napoleon
European leaders met in the Congress of Vienna in 1814 and 1815 to redraw Europe's boundaries after Napoleon's fall and ensure stability in Europe. They returned the old royal family of France to power and acknowledged Finland, which was taken over by Russia during the wars, as Russian territory.The coalition invaded France and captured Paris, forcing Napoleon to abdicate in April 1814. He was exiled to the island of Elba, between Corsica and Italy. In France, the Bourbons were restored to power. Napoleon escaped in February 1815 and took control of France.After Napoleon's defeat, the power of Europe was captured by conservatives. After Napoleon was defeated in 1815, conservatism became the driving force behind European governments.
What was the role of Napoleon in the unification of Europe : Through his conquests he brought the scattered areas of Europe together under the first French Empire. The End of Feudalism- Together the French Revolution and Napoleon's rule brought an end to Feudalism in France. Lands belonging Church and nobles were confiscated and privileges were abolished.
What was France like after Napoleon
Following his defeat in the Napoleonic Wars, France went through regime changes, being ruled as a monarchy, then Second Republic, then Second Empire, until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. France was one of the Triple Entente powers in World War I against Germany and the Central Powers.
What changes did Napoleon introduce in Europe : It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. In towns too, guild systems were removed. Transport and communication systems were improved.
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.
His last words were 'France, the Army, the Head of the Army, Josephine'. Napoleon's body was returned to France and in 1840 was interred in Les Invalides along with the bodies of his brothers and son.
Who saved Europe from Napoleon
Clemens Lothar Metternich: The Man Who Saved “Old Europe” From Napoleon. Clemens Lothar Metternich was a symbol of old Europe in the 19th century. He protected this Europe from Napoleon and from nationalists and revolutionaries in 1848.The European map changed a lot, Poland went to Russia, Holland and Belgium were united, and a loose confederation of states was drawn up for Germany. Q. Napoleon Bonaparte was defeated in the Battle of Waterloo by Britain, Denmark, Prussia and Austria.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.
His victory over the royalists made him an immediate hero. He was sent to lead French forces in Italy, fighting the Austrian (Habsburg) Empire. There, he won a number of huge victories and by 1797 had invaded Austria itself.
What was Napoleon’s influence on the rest of Europe : Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy.
How did France react to Napoleon : The people of France loved Napoleon. He had defended France against invasion, won her glory in battle, and had restored relative order to a country wracked by strife and political division. Support for his coronation was mixed. Not much changed in the short term, he was an autocratic ruler before and after.
How did Napoleon impact Europe
Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy.
/https%3A%2F%2Fengelsbergideas.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2022%2F08%2FMy-Post-2-3.jpeg)
The Civil Code of 1804 or Napoleonic Code abolished privileges by birth, introduced equality before law and incorporated right to property. He also abolished feudal systems in other parts of Europe and liberated the peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. The traditional guild system was also abolished.After the defeat of Napoleon, European rulers moved to restore the old order. This was the goal of the victors—Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, and Russia. They met at the Congress of Vienna in September 1814 to arrange a final peace settlement.
What was Napoleon’s IQ : 145Estimated IQs of 301 Geniuses of the 15th – 19th Centuries by Catharine Morris Cox, PhD