They mostly settled in the Danelaw, to the north and east of England. Some Norwegian Vikings or 'Norse' sailed to Scotland. They made settlements in the north, and on the Shetland and Orkney Islands.Then most of Anglia became the Danelaw as Danegeld. And as a response, West Saxon Alfred began calling the people Anglo-Saxon and the language English around 900CE. After that the Danelaw was defeated there were kings of the English or of a united land called England (Angleland), but not before that…Lindisfarne Priory, Northumberland
For this reason, the Lindisfarne raid is often cited as the beginning of the Viking Age in Europe. During a visit to Lindisfarne, you can follow in the footsteps of the ancient monks who built their priory here almost 1,400 years ago.
Who defeated the Vikings in England : King Harold
The last serious Viking invasion was led by a Norwegian king called Harald Hardrada in 1066, but he was defeated by the English King Harold at the battle of Stamford Bridge just two weeks before the famous Battle of Hastings.
What language did the Vikings speak
Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.
Who wiped out the Vikings : Led by King Alfred, the armies of Wessex defeated half of the Viking forces in the Battle of Edington in 878, forever crushing their hopes of dominating all of the Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms.
The 4 Kingdoms of England were in place for around 100 years, from 829 AD to 929 AD, when England was united as one. The 4 Kingdoms were East Anglia, Mercia, Northumbria, and Wessex. York
Alice visits York where she provides evidence to show it is Britain's most Viking town.
Is London in Wessex and Mercia
It appears from maps that the River Thames was the border between Wessex and Mercia. Since ancient London was on the North side of the Thames, so until about Alfred's time, when it became part the Kingdom of the Viking Guthrum, it was in Mercia.Norman, member of those Vikings, or Norsemen, who settled in northern France (or the Frankish kingdom), together with their descendants. The Normans founded the duchy of Normandy and sent out expeditions of conquest and colonization to southern Italy and Sicily and to England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.Scandinavian and Nordic Greetings & Useful Phrases
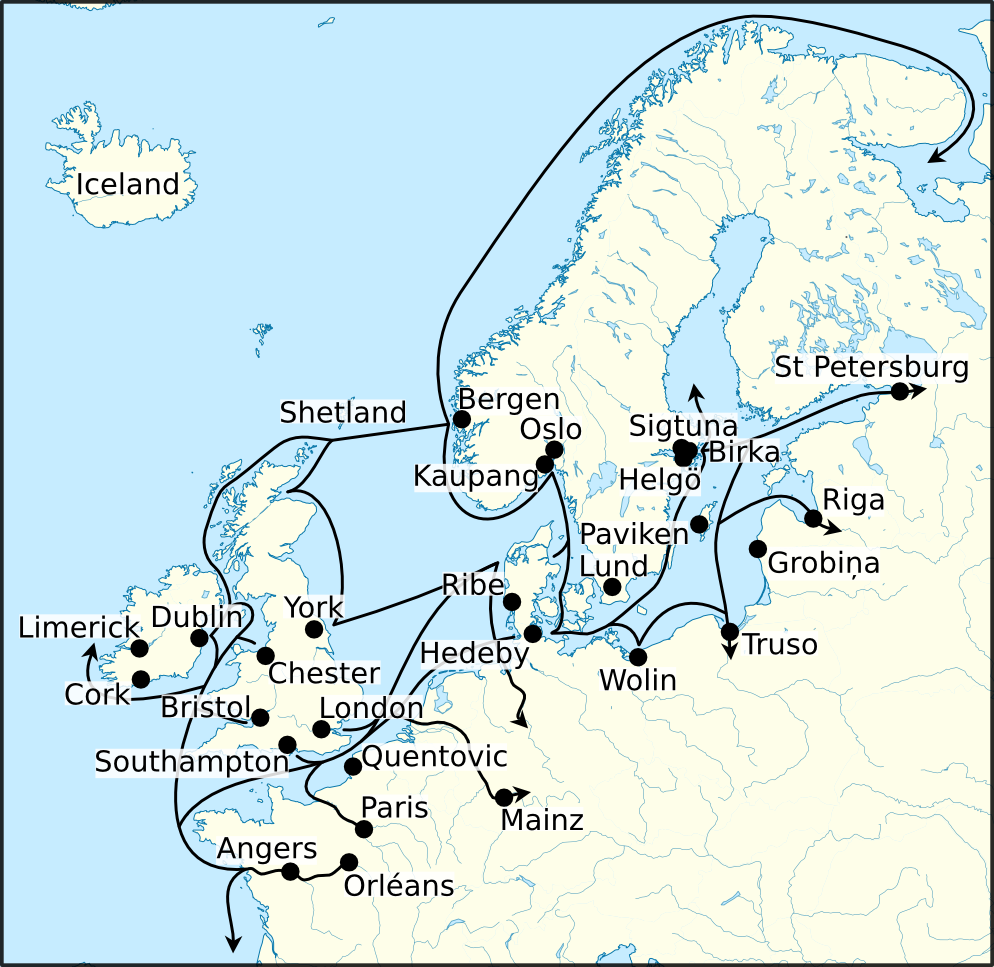
Hello – Hej! Good morning/day/evening/night – God morgon! / Goddag! / God kväll! / God natt! Over the centuries, Old Norse continued to fragment into more regionally-specific languages, and by the early modern era, it had been transformed into Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Faroese.
Who was the last real Viking : Harald Hardrada
Harald Hardrada (Harald III Sigurdsson) is often known as "the last real Viking," and maybe he was what many understood by a real Viking king.
What language did Vikings speak : Old Norse
The Vikings spoke Old Norse, also known as Dǫnsk Tunga/Norrœnt mál. Old Norse was a North Germanic language spoken by the Vikings in Scandinavia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and in parts of Russia, France, the British Isles where Vikings had settled.
Was Mercia Angle or Saxon
Mercia was one of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of the Heptarchy. It was in the region now known as the English Midlands now East Midlands & West Midlands. Mercia was centered on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries. Settled by Angles, their name is the root of the name 'England'. The Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon Britain were as follows:
East Anglia.
Mercia.
Northumbria.
Wessex.
Essex.
Kent.
Sussex.
6%
From this, it was calculated that the modern English population has approximately 6% Danish Viking ancestry, with Scottish and Irish populations having up to 16%. Additionally, populations from all areas of Britain and Ireland were found to have 3–4% Norwegian Viking ancestry.
What is Mercia now called : the English Midlands
Mercia was one of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of the Heptarchy. It was in the region now known as the English Midlands now East Midlands & West Midlands.
Antwort What regions of England were in Viking times? Weitere Antworten – What part of England did the Vikings settle in
Danelaw
They mostly settled in the Danelaw, to the north and east of England. Some Norwegian Vikings or 'Norse' sailed to Scotland. They made settlements in the north, and on the Shetland and Orkney Islands.Then most of Anglia became the Danelaw as Danegeld. And as a response, West Saxon Alfred began calling the people Anglo-Saxon and the language English around 900CE. After that the Danelaw was defeated there were kings of the English or of a united land called England (Angleland), but not before that…Lindisfarne Priory, Northumberland
For this reason, the Lindisfarne raid is often cited as the beginning of the Viking Age in Europe. During a visit to Lindisfarne, you can follow in the footsteps of the ancient monks who built their priory here almost 1,400 years ago.

Who defeated the Vikings in England : King Harold
The last serious Viking invasion was led by a Norwegian king called Harald Hardrada in 1066, but he was defeated by the English King Harold at the battle of Stamford Bridge just two weeks before the famous Battle of Hastings.
What language did the Vikings speak
Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.
Who wiped out the Vikings : Led by King Alfred, the armies of Wessex defeated half of the Viking forces in the Battle of Edington in 878, forever crushing their hopes of dominating all of the Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms.
The 4 Kingdoms of England were in place for around 100 years, from 829 AD to 929 AD, when England was united as one. The 4 Kingdoms were East Anglia, Mercia, Northumbria, and Wessex.

York
Alice visits York where she provides evidence to show it is Britain's most Viking town.
Is London in Wessex and Mercia
It appears from maps that the River Thames was the border between Wessex and Mercia. Since ancient London was on the North side of the Thames, so until about Alfred's time, when it became part the Kingdom of the Viking Guthrum, it was in Mercia.Norman, member of those Vikings, or Norsemen, who settled in northern France (or the Frankish kingdom), together with their descendants. The Normans founded the duchy of Normandy and sent out expeditions of conquest and colonization to southern Italy and Sicily and to England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.Scandinavian and Nordic Greetings & Useful Phrases
Hello – Hej! Good morning/day/evening/night – God morgon! / Goddag! / God kväll! / God natt!
Over the centuries, Old Norse continued to fragment into more regionally-specific languages, and by the early modern era, it had been transformed into Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Faroese.
Who was the last real Viking : Harald Hardrada
Harald Hardrada (Harald III Sigurdsson) is often known as "the last real Viking," and maybe he was what many understood by a real Viking king.
What language did Vikings speak : Old Norse
The Vikings spoke Old Norse, also known as Dǫnsk Tunga/Norrœnt mál. Old Norse was a North Germanic language spoken by the Vikings in Scandinavia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and in parts of Russia, France, the British Isles where Vikings had settled.
Was Mercia Angle or Saxon
Mercia was one of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of the Heptarchy. It was in the region now known as the English Midlands now East Midlands & West Midlands. Mercia was centered on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries. Settled by Angles, their name is the root of the name 'England'.
The Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon Britain were as follows:
6%
From this, it was calculated that the modern English population has approximately 6% Danish Viking ancestry, with Scottish and Irish populations having up to 16%. Additionally, populations from all areas of Britain and Ireland were found to have 3–4% Norwegian Viking ancestry.
What is Mercia now called : the English Midlands
Mercia was one of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of the Heptarchy. It was in the region now known as the English Midlands now East Midlands & West Midlands.