Xeon processors are ideal for servers and workstations as they have a little bit more processing capability. Core processors are ideal for laptops, desktops and particularly for gaming PCs. We can provide you with a Xeon or Core processor depending on your needs.They lack Xeon's support for error-correcting memory (see below), but for advanced users, Core i7 CPUs can be overclocked to temporarily work at higher-than-rated speeds, whereas Xeon models cannot. Intel Xeon CPUs offer similar frequencies and cache sizes as the Core i7 series and higher maximum core counts.Generally, Xeon CPUs offer a few advantages over Core CPUs that military, industrial and commercial customers find valuable, including: Support for ECC RAM. Support for larger amounts of RAM in general. More cache memory.
How many cores are in a Xeon processor : Xeon
General information
Physical specifications
Cores
Up to 64 cores per socket (up to 128 threads per socket)
Memory (RAM)
Up to 4 TB and 8 channels per socket Up to DDR5-5600 with ECC support
GPU(s)
Intel Graphics Technology (some models only)
Why use Xeon instead of i7
Longevity (under heavy load) – Xeon processors are qualified to handle heavier, more intensive loads day in and day out. For the serious workstation user, this can translate to better longevity over i7 counterparts.
What is the disadvantage of Xeon CPU : Disadvantages of using an Intel Xeon CPU: Cost: Xeon CPUs are generally more expensive than desktop or laptop CPUs. They are designed for professional and enterprise use, which often comes with a higher price tag [2]. Power consumption: Xeon CPUs tend to have higher power consumption compared to desktop or laptop CPUs.
Longevity (under heavy load) – Xeon processors are qualified to handle heavier, more intensive loads day in and day out. For the serious workstation user, this can translate to better longevity over i7 counterparts. Numerous Cores
In addition to the potential of multiple CPU benefits, Xeons can feature multiple cores. In general Xeon processors can have a maximum of 48 cores whereas core I7 processors can possess a maximum of 8 cores. Due to the complexity of increasing the core count, Xeon processors are quite expensive.
Why Xeon is better
Numerous Cores
In addition to the potential of multiple CPU benefits, Xeons can feature multiple cores. In general Xeon processors can have a maximum of 48 cores whereas core I7 processors can possess a maximum of 8 cores. Due to the complexity of increasing the core count, Xeon processors are quite expensive.While Xeon CPUs offer impressive multi-threaded performance and reliability, they are typically tailored for tasks such as data processing, virtualization, and high-performance computing rather than gaming. Xeon CPUs often feature lower base and boost clock speeds compared to consumer-oriented CPUs.LONG STORY SHORT, for gaming, Xeons are fine for most games but will bottleneck high-end GPU cards due to their lower single-thread speed. Xeons are generally outperformed by core i5 and i7 counterparts because they were designed for servers: More cores/threads, but at lower processing speed. LONG STORY SHORT, for gaming, Xeons are fine for most games but will bottleneck high-end GPU cards due to their lower single-thread speed. Xeons are generally outperformed by core i5 and i7 counterparts because they were designed for servers: More cores/threads, but at lower processing speed.
Antwort What is the difference between Core processor and Xeon processor? Weitere Antworten – Which is better Xeon or Core
Xeon processors are ideal for servers and workstations as they have a little bit more processing capability. Core processors are ideal for laptops, desktops and particularly for gaming PCs. We can provide you with a Xeon or Core processor depending on your needs.They lack Xeon's support for error-correcting memory (see below), but for advanced users, Core i7 CPUs can be overclocked to temporarily work at higher-than-rated speeds, whereas Xeon models cannot. Intel Xeon CPUs offer similar frequencies and cache sizes as the Core i7 series and higher maximum core counts.Generally, Xeon CPUs offer a few advantages over Core CPUs that military, industrial and commercial customers find valuable, including: Support for ECC RAM. Support for larger amounts of RAM in general. More cache memory.
How many cores are in a Xeon processor : Xeon
Why use Xeon instead of i7
Longevity (under heavy load) – Xeon processors are qualified to handle heavier, more intensive loads day in and day out. For the serious workstation user, this can translate to better longevity over i7 counterparts.
What is the disadvantage of Xeon CPU : Disadvantages of using an Intel Xeon CPU: Cost: Xeon CPUs are generally more expensive than desktop or laptop CPUs. They are designed for professional and enterprise use, which often comes with a higher price tag [2]. Power consumption: Xeon CPUs tend to have higher power consumption compared to desktop or laptop CPUs.
Longevity (under heavy load) – Xeon processors are qualified to handle heavier, more intensive loads day in and day out. For the serious workstation user, this can translate to better longevity over i7 counterparts.
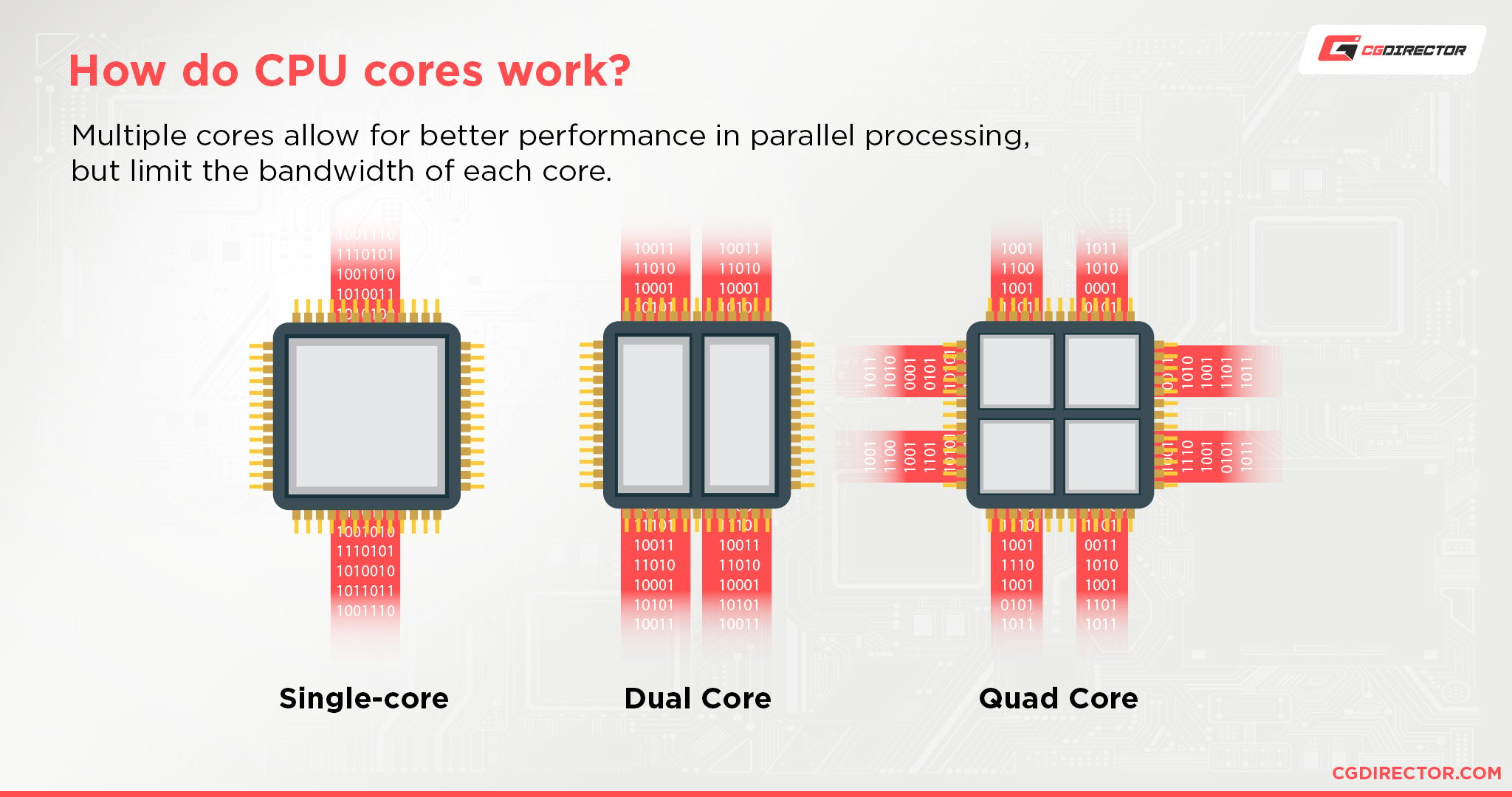
Numerous Cores
In addition to the potential of multiple CPU benefits, Xeons can feature multiple cores. In general Xeon processors can have a maximum of 48 cores whereas core I7 processors can possess a maximum of 8 cores. Due to the complexity of increasing the core count, Xeon processors are quite expensive.
Why Xeon is better
Numerous Cores
In addition to the potential of multiple CPU benefits, Xeons can feature multiple cores. In general Xeon processors can have a maximum of 48 cores whereas core I7 processors can possess a maximum of 8 cores. Due to the complexity of increasing the core count, Xeon processors are quite expensive.While Xeon CPUs offer impressive multi-threaded performance and reliability, they are typically tailored for tasks such as data processing, virtualization, and high-performance computing rather than gaming. Xeon CPUs often feature lower base and boost clock speeds compared to consumer-oriented CPUs.LONG STORY SHORT, for gaming, Xeons are fine for most games but will bottleneck high-end GPU cards due to their lower single-thread speed. Xeons are generally outperformed by core i5 and i7 counterparts because they were designed for servers: More cores/threads, but at lower processing speed.

LONG STORY SHORT, for gaming, Xeons are fine for most games but will bottleneck high-end GPU cards due to their lower single-thread speed. Xeons are generally outperformed by core i5 and i7 counterparts because they were designed for servers: More cores/threads, but at lower processing speed.