Thin clients do far less work than regular PCs, and therefore, they need fewer resources. A thin client will not have a high-end graphics card, for example, or an expensive hard drive for storage. It will also have less memory than a PC. Each of these components comes with considerable cost.The thin client is simply a display terminal that connects to the server. This type of thin client computing is also known as a server-based computing model. In contrast, a rich client machine has most of its processing power locally.Thin clients are typically managed remotely with limited input from the end user. Thick clients can be customized by individual employees by installing the necessary local software and applications.
What is a thin client : A thin client is a device with limited computing capacity. Your users can use it to perform more complicated, compute-intensive tasks by exchanging data with a centralized server. Traditionally, organizations had to purchase expensive desktop machines for employees to perform business-related tasks.
Can I use a thin client as a normal PC
A thinclient is a normal computer, ok without a high end graphic card, it's got no DVD-/CD-ROM drive, but it's still a common computer.
Why use a thin client : Thin clients have a smaller carbon footprint than PCs because they have fewer moving parts. Hard drives are notoriously complex mechanical devices. With smaller processors and less memory, thin clients also generate less waste heat.
Thin clients are centrally controlled by a server. This means they are: More secure. Since users can't install programs or store files on their terminal, thin client devices are less vulnerable to malware. Choosing a thick client over a thin client can have several advantages. One of the primary reasons is improved performance since a significant portion of the processing is done locally. This reduces network traffic and response times.
Is a laptop a thin or thick client
Thick clients: Also called “rich” clients (or even “fat” clients), these are typically traditional PCs such as desktops and laptops, which provide a high level of functionality independent of a central server.Cons of thin clients
The greatest drawback of thin clients compared to PCs is the lack of power. Certain types of applications, such as computer-aided design programs, require more processing power and memory than a thin client can provide.Types of thin clients
Hardware thin clients: These are physical devices that resemble small desktop computers, often referred to as “thin clients.” They typically feature low-power processors, minimal storage, and no moving parts.
Hardware zero clients:
Software thin/zero clients:
The thin-client model is considered a perfect fit for online gaming for a number of reasons. Because modern games normally require tremendous computing and rendering power at the game client, deploying games with such models can transfer the burden of hardware upgrades from players to game operators.
How much RAM does a thin client have : True thin clients don't need very much RAM by their nature. Some thin client hardware includes as little as 512 MB, though others go up to 4 GB or even 8 GB. Regular PCs utilized as thin clients need enough RAM for their operating system to run easily. Minimal local storage is another hallmark of thin clients.
What is the disadvantage of a thin client : Cons of thin clients
The greatest drawback of thin clients compared to PCs is the lack of power. Certain types of applications, such as computer-aided design programs, require more processing power and memory than a thin client can provide.
Do companies still use thin clients
Cao notes that mobile workspace solutions from vendors such as Citrix enable workers to use thin clients for a wider range of tasks than in the past. However, he notes that thick clients are still needed for more processing-intensive use cases, such as when employees need to work on multiple high-resolution displays. Microsoft Office Suite: Microsoft Office applications like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint are examples of thick client software. These applications are installed directly on a user's computer and provide extensive functionality for creating, editing, and managing documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.Resource Usage: The thick client (Outlook) uses more of your computer's resources and works offline, whereas the thin client (Gmail on a browser) relies on server resources and requires an internet connection.
What are the problems with thin clients : Thin clients work with a few givens:
You have enough cash to maintain the infrastructure.
Even though the devices are just appliances, they have a shelf life and need to be replaced every so often.
They are not really flexible.
They may wind up obsolete, and not allowed to connect.
Antwort What is the difference between a thin client and a full client? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between a thin client and a full PC
Thin clients do far less work than regular PCs, and therefore, they need fewer resources. A thin client will not have a high-end graphics card, for example, or an expensive hard drive for storage. It will also have less memory than a PC. Each of these components comes with considerable cost.The thin client is simply a display terminal that connects to the server. This type of thin client computing is also known as a server-based computing model. In contrast, a rich client machine has most of its processing power locally.Thin clients are typically managed remotely with limited input from the end user. Thick clients can be customized by individual employees by installing the necessary local software and applications.
What is a thin client : A thin client is a device with limited computing capacity. Your users can use it to perform more complicated, compute-intensive tasks by exchanging data with a centralized server. Traditionally, organizations had to purchase expensive desktop machines for employees to perform business-related tasks.
Can I use a thin client as a normal PC
A thinclient is a normal computer, ok without a high end graphic card, it's got no DVD-/CD-ROM drive, but it's still a common computer.
Why use a thin client : Thin clients have a smaller carbon footprint than PCs because they have fewer moving parts. Hard drives are notoriously complex mechanical devices. With smaller processors and less memory, thin clients also generate less waste heat.
Thin clients are centrally controlled by a server. This means they are: More secure. Since users can't install programs or store files on their terminal, thin client devices are less vulnerable to malware.
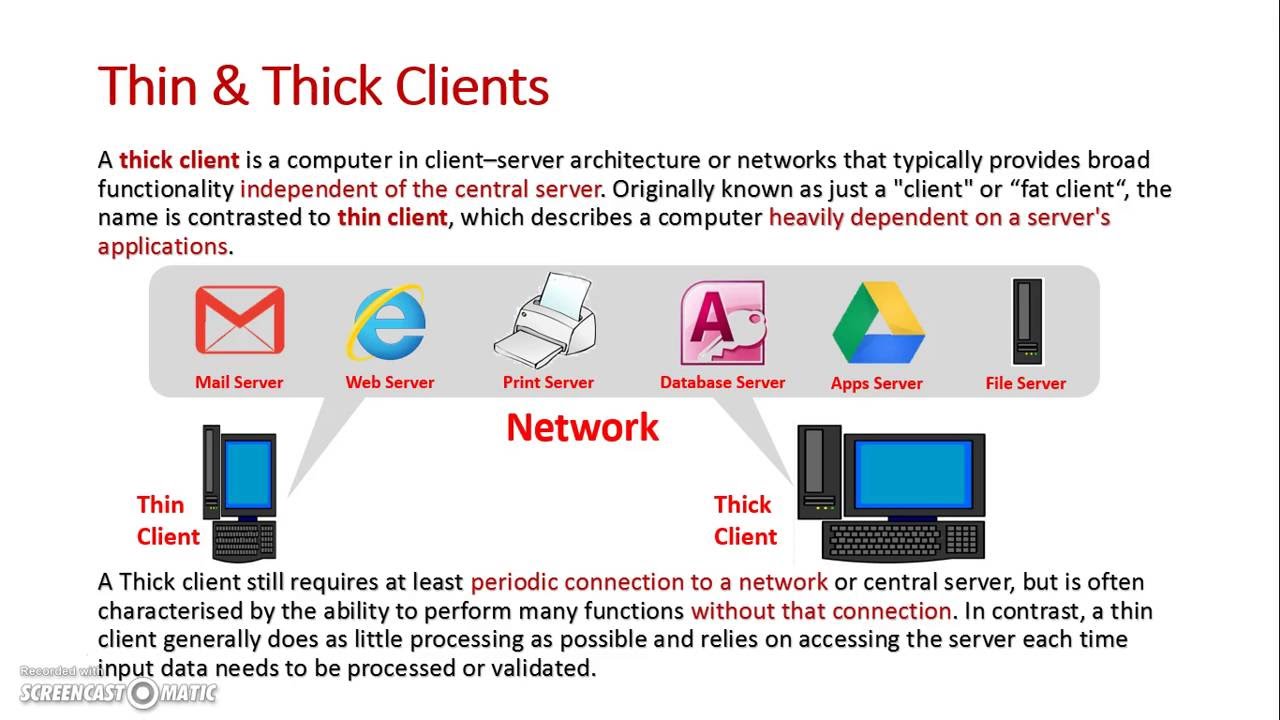
Choosing a thick client over a thin client can have several advantages. One of the primary reasons is improved performance since a significant portion of the processing is done locally. This reduces network traffic and response times.
Is a laptop a thin or thick client
Thick clients: Also called “rich” clients (or even “fat” clients), these are typically traditional PCs such as desktops and laptops, which provide a high level of functionality independent of a central server.Cons of thin clients
The greatest drawback of thin clients compared to PCs is the lack of power. Certain types of applications, such as computer-aided design programs, require more processing power and memory than a thin client can provide.Types of thin clients
The thin-client model is considered a perfect fit for online gaming for a number of reasons. Because modern games normally require tremendous computing and rendering power at the game client, deploying games with such models can transfer the burden of hardware upgrades from players to game operators.
How much RAM does a thin client have : True thin clients don't need very much RAM by their nature. Some thin client hardware includes as little as 512 MB, though others go up to 4 GB or even 8 GB. Regular PCs utilized as thin clients need enough RAM for their operating system to run easily. Minimal local storage is another hallmark of thin clients.
What is the disadvantage of a thin client : Cons of thin clients
The greatest drawback of thin clients compared to PCs is the lack of power. Certain types of applications, such as computer-aided design programs, require more processing power and memory than a thin client can provide.
Do companies still use thin clients
Cao notes that mobile workspace solutions from vendors such as Citrix enable workers to use thin clients for a wider range of tasks than in the past. However, he notes that thick clients are still needed for more processing-intensive use cases, such as when employees need to work on multiple high-resolution displays.

Microsoft Office Suite: Microsoft Office applications like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint are examples of thick client software. These applications are installed directly on a user's computer and provide extensive functionality for creating, editing, and managing documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.Resource Usage: The thick client (Outlook) uses more of your computer's resources and works offline, whereas the thin client (Gmail on a browser) relies on server resources and requires an internet connection.
What are the problems with thin clients : Thin clients work with a few givens: