Your stomach sits in your upper abdomen on the left side of your body. The top of your stomach connects to a valve called the esophageal sphincter (a muscle at the end of your esophagus). The bottom of your stomach connects to your small intestine.Areas of the stomach
The cardia is the first part of the stomach, which is connected to the esophagus.
The fundus is the top, rounded area that lies to the left of the cardia.
The body is the largest and main part of the stomach.
The antrum is the lower part of the stomach.
As a component of the alimentary canal (i.e., the tubal passageway for ingested food to be digested, absorbed, then excreted as waste), the stomach's physiological function is structured around creating an environment where the food ingested can be safely acted on by proteolytic enzymes and acidic solutions.
What is the anatomy of the Git : The GI tract consists of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anal canal. The accessory organs include the teeth, tongue, and glandular organs such as salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What are the layers of the stomach called
Layers of the stomach wall. The wall of the stomach is made up of the mucosa (innermost layer), submucosa, muscle layer, subserosa, and serosa (outermost layer). The stomach is an organ in the upper abdomen.
What are the 4 main functions of the stomach : The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir, acid secretion, enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility.
Gastric pits.
Secretion of gastric juice.
Protein digestion.
Fat digestion.
Formation of chyme.
Passage of chyme into the duodenum.
Food absorption.
Hunger and satiety.
The duodenum is the initial C-shaped segment of the small intestine and is a continuation of the pylorus. Distally, it is in continuation with the jejunum and ileum, with the proximal segment being the shortest and widest. Positioned inferiorly to the stomach, the duodenum is approximately 25 to 30 cm long.
What is the term anatomy
(uh-NA-toh-mee) The study of the structure of a plant or animal. Human anatomy includes the cells, tissues, and organs that make up the body and how they are organized in the body.Layers of the stomach wall. The wall of the stomach is made up of the mucosa (innermost layer), submucosa, muscle layer, subserosa, and serosa (outermost layer). The stomach is an organ in the upper abdomen.four parts
The stomach has four parts, the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus. The cardia is the point where the oesophagus enters the stomach and pylorus is the part that connects the stomach to the small intestine. There are four main regions in the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The cardia (or cardiac region) is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach and through which food passes into the stomach. Located inferior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, is the dome-shaped fundus.
What are four 4 key functions of the stomach : The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir, acid secretion, enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility.
What is the Anatomy of duodenum and stomach : The stomach is a J-shaped sac connecting the esophagus above and the small intestine below. The first part of the small intestine is known as the duodenum. The stomach varies considerably in size, shape and position but lies in the upper central part of the abdomen behind the lower ribs.
What are the 4 parts of the duodenum Anatomy
It may be subdivided into four sections: superior part, descending part, horizontal part and ascending part. The superior part (first part, D1) lies intraperitoneally and is enlarged proximally (duodenal bulb). Anatomy is the study of the physical structure and parts of organisms. Examples of anatomy include body parts such as muscles, heart, brain, bladder, and kidneys.Types of Anatomy
It focuses on numerous systems, including circulatory, digestive, endocrine, skeletal, lymphatic, nervous, respiratory, urinary, reproductive and muscular systems. Plant Anatomy – Also called the phytotomy.
Antwort What is the anatomy of the stomach? Weitere Antworten – What is the anatomy of the stomach in the body
Your stomach sits in your upper abdomen on the left side of your body. The top of your stomach connects to a valve called the esophageal sphincter (a muscle at the end of your esophagus). The bottom of your stomach connects to your small intestine.Areas of the stomach
As a component of the alimentary canal (i.e., the tubal passageway for ingested food to be digested, absorbed, then excreted as waste), the stomach's physiological function is structured around creating an environment where the food ingested can be safely acted on by proteolytic enzymes and acidic solutions.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1081/eLC5cjsJfDdUq5JVtvH14w_arteries-of-stomach-liver-and-gallbladder_english.jpg)
What is the anatomy of the Git : The GI tract consists of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anal canal. The accessory organs include the teeth, tongue, and glandular organs such as salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What are the layers of the stomach called
Layers of the stomach wall. The wall of the stomach is made up of the mucosa (innermost layer), submucosa, muscle layer, subserosa, and serosa (outermost layer). The stomach is an organ in the upper abdomen.
What are the 4 main functions of the stomach : The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir, acid secretion, enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility.
The duodenum is the initial C-shaped segment of the small intestine and is a continuation of the pylorus. Distally, it is in continuation with the jejunum and ileum, with the proximal segment being the shortest and widest. Positioned inferiorly to the stomach, the duodenum is approximately 25 to 30 cm long.
What is the term anatomy
(uh-NA-toh-mee) The study of the structure of a plant or animal. Human anatomy includes the cells, tissues, and organs that make up the body and how they are organized in the body.Layers of the stomach wall. The wall of the stomach is made up of the mucosa (innermost layer), submucosa, muscle layer, subserosa, and serosa (outermost layer). The stomach is an organ in the upper abdomen.four parts
The stomach has four parts, the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus. The cardia is the point where the oesophagus enters the stomach and pylorus is the part that connects the stomach to the small intestine.
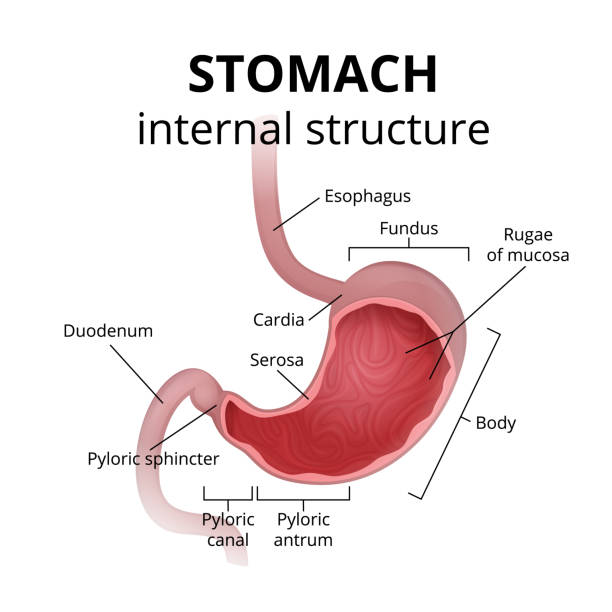
There are four main regions in the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The cardia (or cardiac region) is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach and through which food passes into the stomach. Located inferior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, is the dome-shaped fundus.
What are four 4 key functions of the stomach : The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir, acid secretion, enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility.
What is the Anatomy of duodenum and stomach : The stomach is a J-shaped sac connecting the esophagus above and the small intestine below. The first part of the small intestine is known as the duodenum. The stomach varies considerably in size, shape and position but lies in the upper central part of the abdomen behind the lower ribs.
What are the 4 parts of the duodenum Anatomy
It may be subdivided into four sections: superior part, descending part, horizontal part and ascending part. The superior part (first part, D1) lies intraperitoneally and is enlarged proximally (duodenal bulb).

Anatomy is the study of the physical structure and parts of organisms. Examples of anatomy include body parts such as muscles, heart, brain, bladder, and kidneys.Types of Anatomy
It focuses on numerous systems, including circulatory, digestive, endocrine, skeletal, lymphatic, nervous, respiratory, urinary, reproductive and muscular systems. Plant Anatomy – Also called the phytotomy.
What cells make up the stomach : Stomach