Metadata simplifies Big Data collection, analysis, and integration. It also manages the data lifecycle and maintains an audit trail to comply with regulatory requirements. Big data can be defined as data with greater variety, arriving at increasing volumes and speed.Kind of. There are some other key distinctions, but this is a good starting point. Big Data is a collection of data so large (and moving so fast) that it can't be examined with standard technology tools. Metadata refers to descriptive details about an individual digital asset.Big data and artificial intelligence can improve how we respond to real world crises. Over three billion people use Meta services. Leveraging insights from this global community can help organizations better deliver services.
Is data and metadata the same : The main difference between data and metadata lies in how we use the two pieces of information. Data is a set of raw facts that help identify useful information when they are cleaned, processed, and organized. Metadata, on the other hand, is data about data. If data is the new oil, metadata is the refinery.
Does meta use big data
Big data and artificial intelligence can improve how we respond to real world crises. Over three billion people use Meta services. Leveraging insights from this global community can help organizations better deliver services.
Is data also called metadata : Metadata means "data about data". Metadata is defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data; it is used to summarize basic information about data that can make tracking and working with specific data easier. Some examples include: Means of creation of the data.
Big data refers to data that is so large, fast or complex that it's difficult or impossible to process using traditional methods. The act of accessing and storing large amounts of information for analytics has been around for a long time. Google generally uses Big data from its Web index to initially match the queries with potentially useful results. It uses machine-learning algorithms to assess the reliability of data and then ranks the sites accordingly.
What is an example of data and metadata
The table row and column headers in a spreadsheet are examples of metadata as they offer context to the data. Other metadata examples include: Number of rows and columns. Source descriptions and relationships.Master data is usually structured and it is often used as a reference or lookup data. Metadata, on the other hand, is data that provides information about other data. It describes the characteristics, structure and context of the data.Metadata tells you things about the data without giving any actual data. Master data tells you everything about the data and includes metadata as a matter of form. In terms of variety, big data encompasses several data types, including the following: Structured data, such as transactions and financial records. Unstructured data, such as text, documents and multimedia files. Semi-structured data, such as web server logs and streaming data from sensors.
What are the three types of big data : What are the main types of big data Big data can be classified into structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Is master data big data : Big data encompasses enormous amounts of data while Master Data governs a smaller universe. A large portion of big data is unstructured, whereas Master Data revolves around structured data.
What are the 3 types of big data
What are the main types of big data Big data can be classified into structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. These data, essentially termed as 'big data', typically encompasses large volumes of texts and other forms of unstructured behavioral data from a variety of sources. Master data management (MDM) primarily revolves around the creation of a trusted source of highly structured data throughout an enterprise.Unlike traditional data management solutions, big data technologies and tools are made to help you deal with large and complex datasets to extract value from them.
What is the difference between big data and information : Data is an individual unit that contains raw materials which do not carry any specific meaning. Information is a group of data that collectively carries a logical meaning.
Antwort What is difference between big data and metadata? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between metadata and Big Data
Metadata simplifies Big Data collection, analysis, and integration. It also manages the data lifecycle and maintains an audit trail to comply with regulatory requirements. Big data can be defined as data with greater variety, arriving at increasing volumes and speed.Kind of. There are some other key distinctions, but this is a good starting point. Big Data is a collection of data so large (and moving so fast) that it can't be examined with standard technology tools. Metadata refers to descriptive details about an individual digital asset.Big data and artificial intelligence can improve how we respond to real world crises. Over three billion people use Meta services. Leveraging insights from this global community can help organizations better deliver services.
Is data and metadata the same : The main difference between data and metadata lies in how we use the two pieces of information. Data is a set of raw facts that help identify useful information when they are cleaned, processed, and organized. Metadata, on the other hand, is data about data. If data is the new oil, metadata is the refinery.
Does meta use big data
Big data and artificial intelligence can improve how we respond to real world crises. Over three billion people use Meta services. Leveraging insights from this global community can help organizations better deliver services.
Is data also called metadata : Metadata means "data about data". Metadata is defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data; it is used to summarize basic information about data that can make tracking and working with specific data easier. Some examples include: Means of creation of the data.
Big data refers to data that is so large, fast or complex that it's difficult or impossible to process using traditional methods. The act of accessing and storing large amounts of information for analytics has been around for a long time.

Google generally uses Big data from its Web index to initially match the queries with potentially useful results. It uses machine-learning algorithms to assess the reliability of data and then ranks the sites accordingly.
What is an example of data and metadata
The table row and column headers in a spreadsheet are examples of metadata as they offer context to the data. Other metadata examples include: Number of rows and columns. Source descriptions and relationships.Master data is usually structured and it is often used as a reference or lookup data. Metadata, on the other hand, is data that provides information about other data. It describes the characteristics, structure and context of the data.Metadata tells you things about the data without giving any actual data. Master data tells you everything about the data and includes metadata as a matter of form.
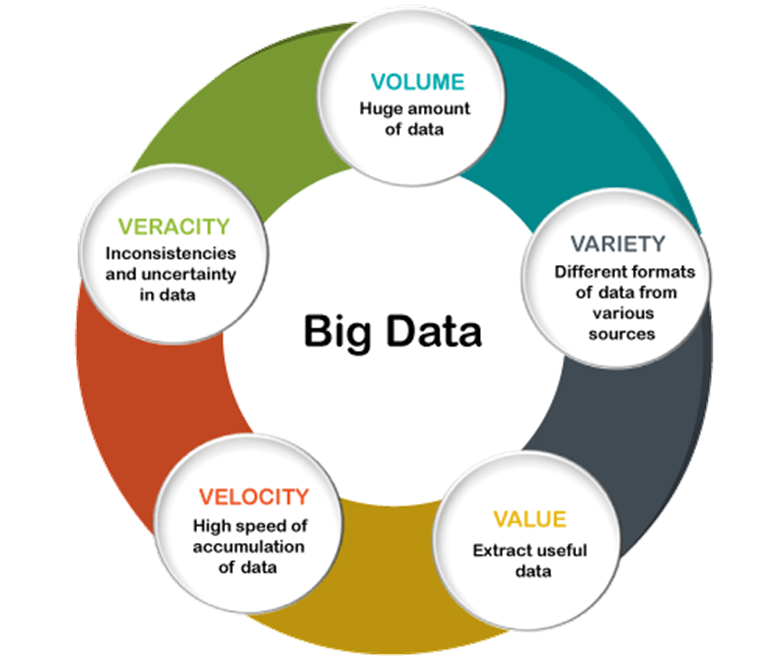
In terms of variety, big data encompasses several data types, including the following: Structured data, such as transactions and financial records. Unstructured data, such as text, documents and multimedia files. Semi-structured data, such as web server logs and streaming data from sensors.
What are the three types of big data : What are the main types of big data Big data can be classified into structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Is master data big data : Big data encompasses enormous amounts of data while Master Data governs a smaller universe. A large portion of big data is unstructured, whereas Master Data revolves around structured data.
What are the 3 types of big data
What are the main types of big data Big data can be classified into structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.

These data, essentially termed as 'big data', typically encompasses large volumes of texts and other forms of unstructured behavioral data from a variety of sources. Master data management (MDM) primarily revolves around the creation of a trusted source of highly structured data throughout an enterprise.Unlike traditional data management solutions, big data technologies and tools are made to help you deal with large and complex datasets to extract value from them.
What is the difference between big data and information : Data is an individual unit that contains raw materials which do not carry any specific meaning. Information is a group of data that collectively carries a logical meaning.