Modes of transport such as air, sea, rail and road form the main channels for the transfer of goods and ensure accessibility to even the most remote areas. Warehouses and distribution centres are the central hubs where goods are stored and streamline their distribution to the different sectors.The Role of Logistics Infrastructure: Logistics infrastructure serves to support production activities and fulfills the essential requirements of goods and service supply chains across all businesses, making a significant contribution to economic development.The four types of logistics are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, reverse logistics, and third-party logistics (3PL) or fourth-party logistics (4PL).
Which is an example of infrastructure : Examples include roads, highways, and bridges, as well as the assets required to make them operational such as transit buses, vehicles, and oil refineries. Technical systems such as networking equipment and cabling are considered hard infrastructure and provide a critical function to support business operations.
What is the international logistics infrastructure
International logistics is a process that involves the transportation offinished goods through an international supply chain. It consists of cross-border shipping and international distribution to efficiently deliver goods to end users across the globe.
What is transportation infrastructure in logistics : Transport infrastructure is the fixed installations, structures, and networks that provide a framework for the movement of people and goods. Urban transport infrastructure can be collated under five broad headings: Roads. Bridges and tunnels. Rail and trams.
We identify, based on the literature, the '7 Cs of supply chain management': Connect, Create, Customise, Coordinate, Consolidate, Collaborate and Contribute. Types of Logistics
Inbound Logistics. Inbound logistics comprises the transportation, storage, and receiving of goods into a business.
Outbound Logistics.
Reverse Logistics.
Green Logistics.
Third-party Logistics.
Fourth-party Logistics.
Fifth-party Logistics.
Digital Logistics.
What are the four types of infrastructure
Types of Infrastructure
Soft Infrastructure. Soft infrastructure refers to all the institutions that help maintain a healthy economy.
Hard Infrastructure.
Critical Infrastructure.
Taxation.
Investments.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
11 Types of Infrastructure Construction Projects in 2024
Aviation Infrastructure.
Bridge Infrastructure.
Communications Infrastructure.
Power and Energy Infrastructure.
Railroad Infrastructure.
Road Infrastructure.
Water Infrastructure.
Waste Management.
Maritime “infrastructure” is generally thought of as cranes, wharves, dredged channels, locks, dams and other tangible structures. These are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, and reverse logistics. The information about these three supply chain directions is essential, especially for people in the logistics industry in the Philippines.
What are the 4 types of transportation in logistics : Air, Road, Sea and Rail. These are the four major modes of transport (or types) in the logistics industry. Which method you use will depend on what you're shipping, where you're shipping from and where you're shipping to. Even then, more than one method may be suitable.
Is infrastructure the same as transportation : Transportation system refers to the overall network and operations of moving people and goods, while transportation infrastructure specifically refers to the physical facilities and structures that support transportation.
What are the 5 P’s of logistics
The 5 P's of logistics are an essential framework for logistics management. Your shipping and logistics company follows these 5 basic principles in order to provide you with the best service possible. The 5 P's include people, products, processes, partnerships, and performance. Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The perfect product must provide value for the customer. customer what they want, not what we think they want.Examples include roads, highways, and bridges, as well as the assets required to make them operational such as transit buses, vehicles, and oil refineries.
What are the 5 infrastructure : Core infrastructure incorporates all the main types of infrastructure, such as roads, highways, railways, public transportation, water, and gas supply.
Antwort What is an example of logistics infrastructure? Weitere Antworten – What are the examples of logistics infrastructure
Modes of transport such as air, sea, rail and road form the main channels for the transfer of goods and ensure accessibility to even the most remote areas. Warehouses and distribution centres are the central hubs where goods are stored and streamline their distribution to the different sectors.The Role of Logistics Infrastructure: Logistics infrastructure serves to support production activities and fulfills the essential requirements of goods and service supply chains across all businesses, making a significant contribution to economic development.The four types of logistics are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, reverse logistics, and third-party logistics (3PL) or fourth-party logistics (4PL).
Which is an example of infrastructure : Examples include roads, highways, and bridges, as well as the assets required to make them operational such as transit buses, vehicles, and oil refineries. Technical systems such as networking equipment and cabling are considered hard infrastructure and provide a critical function to support business operations.
What is the international logistics infrastructure
International logistics is a process that involves the transportation offinished goods through an international supply chain. It consists of cross-border shipping and international distribution to efficiently deliver goods to end users across the globe.
What is transportation infrastructure in logistics : Transport infrastructure is the fixed installations, structures, and networks that provide a framework for the movement of people and goods. Urban transport infrastructure can be collated under five broad headings: Roads. Bridges and tunnels. Rail and trams.
We identify, based on the literature, the '7 Cs of supply chain management': Connect, Create, Customise, Coordinate, Consolidate, Collaborate and Contribute.
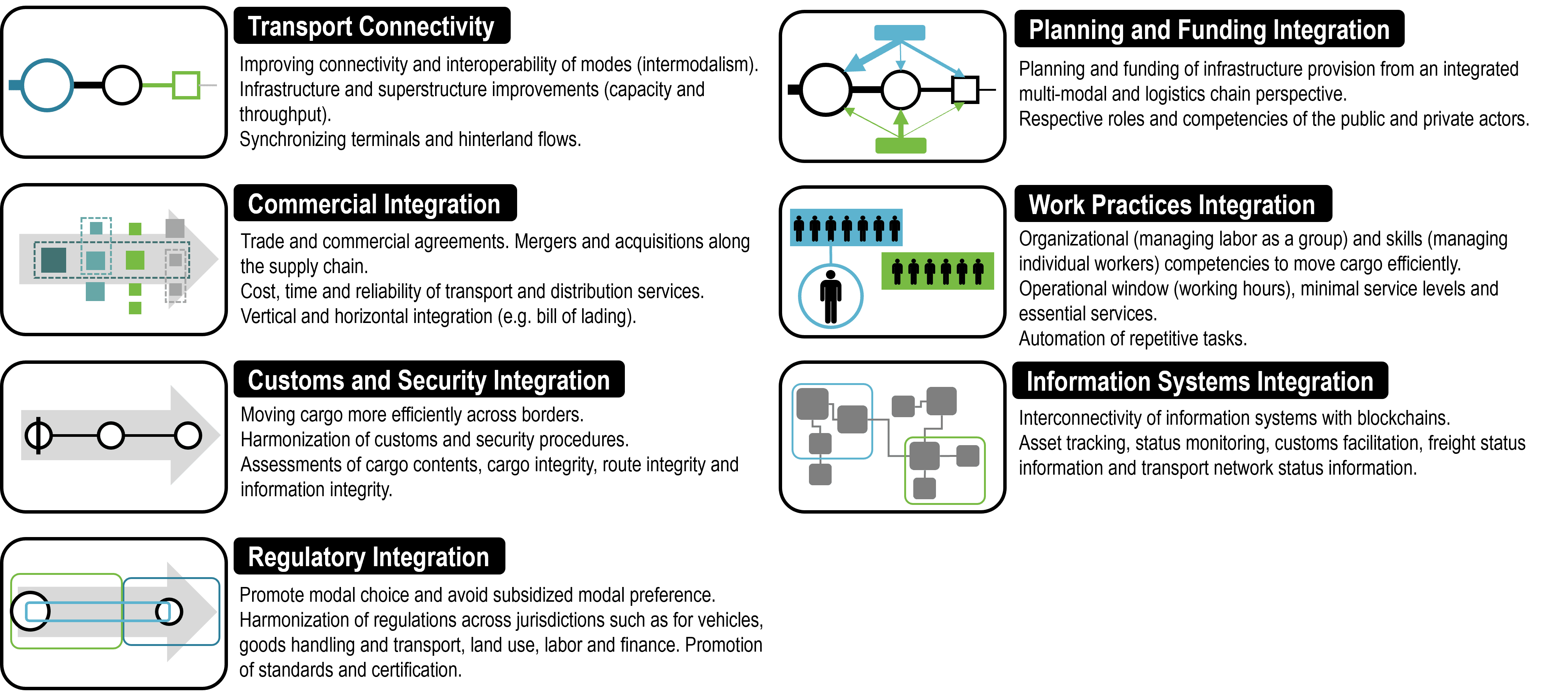
Types of Logistics
What are the four types of infrastructure
Types of Infrastructure
11 Types of Infrastructure Construction Projects in 2024
Maritime “infrastructure” is generally thought of as cranes, wharves, dredged channels, locks, dams and other tangible structures.
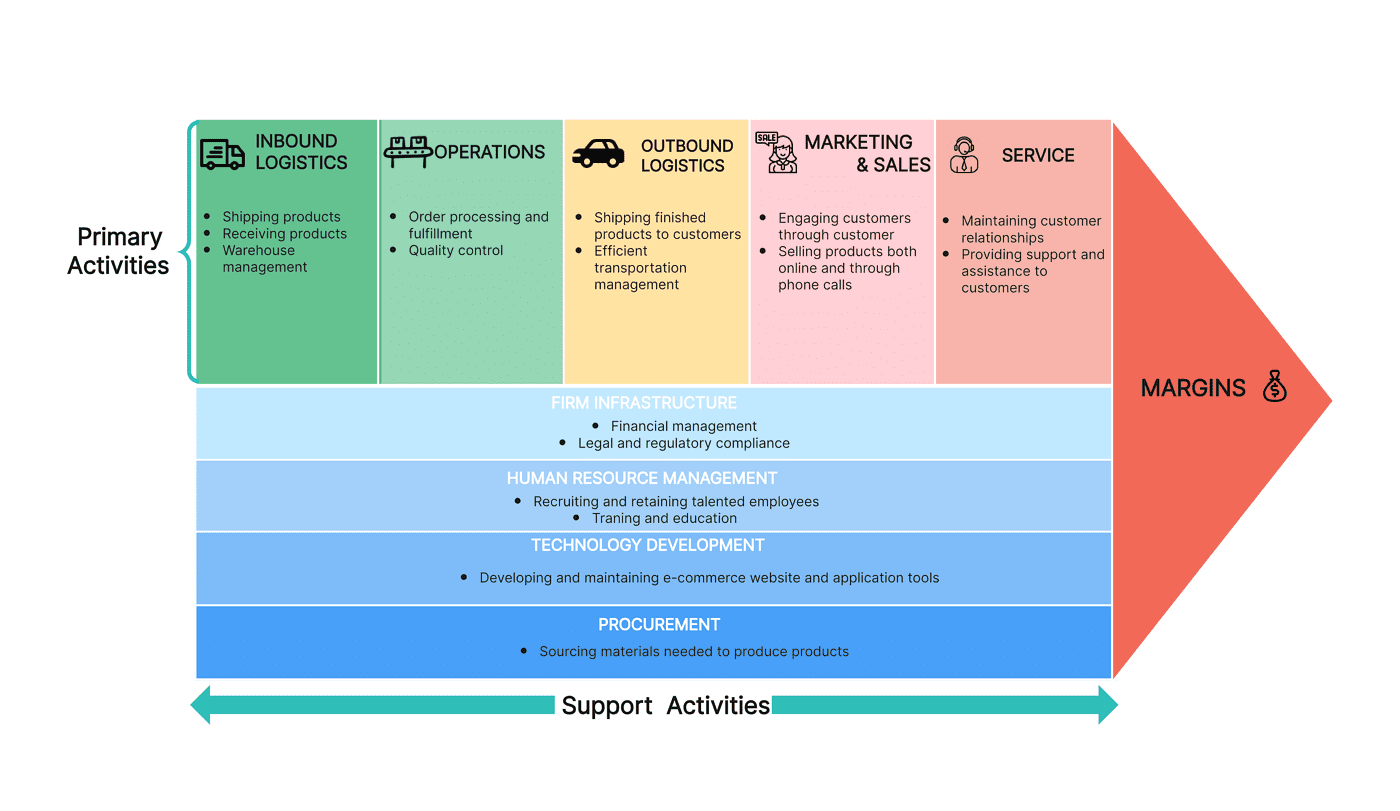
These are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, and reverse logistics. The information about these three supply chain directions is essential, especially for people in the logistics industry in the Philippines.
What are the 4 types of transportation in logistics : Air, Road, Sea and Rail. These are the four major modes of transport (or types) in the logistics industry. Which method you use will depend on what you're shipping, where you're shipping from and where you're shipping to. Even then, more than one method may be suitable.
Is infrastructure the same as transportation : Transportation system refers to the overall network and operations of moving people and goods, while transportation infrastructure specifically refers to the physical facilities and structures that support transportation.
What are the 5 P’s of logistics
The 5 P's of logistics are an essential framework for logistics management. Your shipping and logistics company follows these 5 basic principles in order to provide you with the best service possible. The 5 P's include people, products, processes, partnerships, and performance.

Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The perfect product must provide value for the customer. customer what they want, not what we think they want.Examples include roads, highways, and bridges, as well as the assets required to make them operational such as transit buses, vehicles, and oil refineries.
What are the 5 infrastructure : Core infrastructure incorporates all the main types of infrastructure, such as roads, highways, railways, public transportation, water, and gas supply.