Two subjects that are joined by “and” usually take plural verbs. The word “and” connects the two subjects, making them plural. Therefore, do not add “s” to the verb. When two subjects are joined by these words, the subject is one or the other.Masculine inanimate nouns utilize endings such as '-y', '-e', or '-a' to create plurals. For instance, “stůl” (table) becomes “stoly” (tables). For feminine nouns, the plural formation typically involves replacing singular endings '+-a' or '+-e' with '-y'.In Czech, nouns and adjectives are declined into one of seven grammatical cases which indicate their function in a sentence, two numbers (singular and plural) and three genders (masculine, feminine and neuter). The masculine gender is further divided into animate and inanimate classes.
What is the locative case in Czech : The locative is the only Czech case that cannot be used without a preposition. The prepositions that take the locative include: na (on, at), v(e) (in, at), o (about), and po (after). Neznáte levné hotely v Praze a v Brně Byla jsem celý den na semináři.
Do plurals always end in s
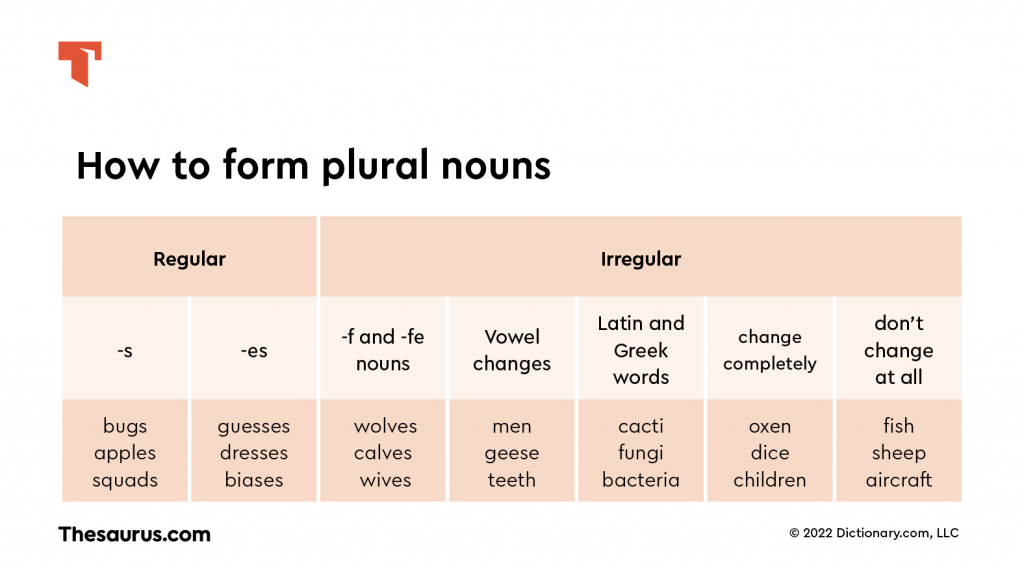
Plural nouns are normally formed by adding -s to the singular noun (e.g., the singular “cat” becomes the plural “cats”). With certain nouns, you need to add or change some of the other letters. The rules are explained in the table below. There are also some irregular plurals that don't end in -s at all.
What plural words don’t end in S : There are English words with irregular plural that doesn't end with an s. Examples are feet (plural of foot), oxen (plural of ox), geese (plural of goose). A number of English words are the same in singular and plural, and they don't end with an s. Examples are sheep, deer, fish, moose.
Czech (noun) Czech Republic (proper noun) In the Czech language, the concept of gender is of utmost importance when it comes to grammar rules. Nouns in this language are divided into three classes: masculine, feminine, and neuter.
Is Czech grammar hard
Czech Grammar
The bad news is that Czech is characterized by complicated declensions. There are seven cases. This means that in combination with singular and plural forms of nouns and adjectives you will have to memorize fourteen different forms for each noun and adjective.Polish, Czech and Slovak are similar languages that belong to the Western branch of Slavic languages. They are considerably mutually intelligible, especially in the case of Czech and Slovak. Their sound inventories are quite similar, but there are some sound changes that you might find confusing.Czech has seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative and instrumental, partly inherited from Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Slavic. 7 cases
The Czech language has 7 cases, and now we are going to take a look at how they work. The first case to be covered is the nominative.
Why do some plurals not have s : In most cases, irregular plurals exist because the noun has been adopted from a language with different ways to form the plural. In other cases, though, English has made these nouns regular by adding an -s that would seem strange in the original language.
Is it Czech or Czechia : In 2022, the American AP Stylebook stated in its entry on the country that "Czechia, the Czech Republic. Both are acceptable. The shorter name Czechia is preferred by the Czech government. If using Czechia, clarify in the story that the country is more widely known in English as the Czech Republic."
Why is it spelled Czech
The current English ethnonym "Czech" comes from the Czech ethnonym associated with the area spelled historically as "Cžech" until the reform of 1842, possibly influenced by Latin "Czechus", or the Polish spelling "Czech". Czech has seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative and instrumental, partly inherited from Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Slavic. Some forms of words match in more than one place in each paradigm.a) Gender: There are four grammatical genders in Slovak: animate masculine, inanimate masculine, feminine, and neuter. In popular description, the first two genders are often covered under common masculine gender.
Is Czech or Russian harder : I would agree with others that Czech grammar is more difficult than Russian, and Polish even more complicated. I dabbled in Croatian a couple of years ago and found it really easy to pick up, at least up to A2 level. It was a lot of fun.
Antwort What if a plural noun doesn’t end in s? Weitere Antworten – Why do plural verbs not end in s
Two subjects that are joined by “and” usually take plural verbs. The word “and” connects the two subjects, making them plural. Therefore, do not add “s” to the verb. When two subjects are joined by these words, the subject is one or the other.Masculine inanimate nouns utilize endings such as '-y', '-e', or '-a' to create plurals. For instance, “stůl” (table) becomes “stoly” (tables). For feminine nouns, the plural formation typically involves replacing singular endings '+-a' or '+-e' with '-y'.In Czech, nouns and adjectives are declined into one of seven grammatical cases which indicate their function in a sentence, two numbers (singular and plural) and three genders (masculine, feminine and neuter). The masculine gender is further divided into animate and inanimate classes.
What is the locative case in Czech : The locative is the only Czech case that cannot be used without a preposition. The prepositions that take the locative include: na (on, at), v(e) (in, at), o (about), and po (after). Neznáte levné hotely v Praze a v Brně Byla jsem celý den na semináři.
Do plurals always end in s
Plural nouns are normally formed by adding -s to the singular noun (e.g., the singular “cat” becomes the plural “cats”). With certain nouns, you need to add or change some of the other letters. The rules are explained in the table below. There are also some irregular plurals that don't end in -s at all.
What plural words don’t end in S : There are English words with irregular plural that doesn't end with an s. Examples are feet (plural of foot), oxen (plural of ox), geese (plural of goose). A number of English words are the same in singular and plural, and they don't end with an s. Examples are sheep, deer, fish, moose.
Czech (noun) Czech Republic (proper noun)

In the Czech language, the concept of gender is of utmost importance when it comes to grammar rules. Nouns in this language are divided into three classes: masculine, feminine, and neuter.
Is Czech grammar hard
Czech Grammar
The bad news is that Czech is characterized by complicated declensions. There are seven cases. This means that in combination with singular and plural forms of nouns and adjectives you will have to memorize fourteen different forms for each noun and adjective.Polish, Czech and Slovak are similar languages that belong to the Western branch of Slavic languages. They are considerably mutually intelligible, especially in the case of Czech and Slovak. Their sound inventories are quite similar, but there are some sound changes that you might find confusing.Czech has seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative and instrumental, partly inherited from Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Slavic.
7 cases
The Czech language has 7 cases, and now we are going to take a look at how they work. The first case to be covered is the nominative.
Why do some plurals not have s : In most cases, irregular plurals exist because the noun has been adopted from a language with different ways to form the plural. In other cases, though, English has made these nouns regular by adding an -s that would seem strange in the original language.
Is it Czech or Czechia : In 2022, the American AP Stylebook stated in its entry on the country that "Czechia, the Czech Republic. Both are acceptable. The shorter name Czechia is preferred by the Czech government. If using Czechia, clarify in the story that the country is more widely known in English as the Czech Republic."
Why is it spelled Czech
The current English ethnonym "Czech" comes from the Czech ethnonym associated with the area spelled historically as "Cžech" until the reform of 1842, possibly influenced by Latin "Czechus", or the Polish spelling "Czech".

Czech has seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative and instrumental, partly inherited from Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Slavic. Some forms of words match in more than one place in each paradigm.a) Gender: There are four grammatical genders in Slovak: animate masculine, inanimate masculine, feminine, and neuter. In popular description, the first two genders are often covered under common masculine gender.
Is Czech or Russian harder : I would agree with others that Czech grammar is more difficult than Russian, and Polish even more complicated. I dabbled in Croatian a couple of years ago and found it really easy to pick up, at least up to A2 level. It was a lot of fun.