Once the manuscript has been through peer review and revision, it will enter stage four, the editorial final decision . The editor will decide to accept or reject the manuscript on the basis of the comments from the reviewers and the quality of the revision.After peer review, the editor will consider feedback from the reviewers and then make a decision about the article. The decision letter is delivered to the author via email. There are three basic types of decisions: Accept, Revise, and Reject.If your manuscript passes peer review, the journal will give you an in-principle acceptance (IPA). This indicates that your article will be published as long as you successfully complete your study according to the pre-registered methods and submit an evidence-based interpretation of the results.
What are the outcomes of peer review : Possible outcomes of peer review
In addition to the comments received from the review, editors also base their decisions on: The journal's aims and audience. The state of knowledge in the field. The level of competition for acceptance and page space within the journal.
Does under review mean accepted
When the status of your manuscript changes to under review, this means that it has passed the initial editorial checks. The journal has confirmed that you've uploaded and submitted the correct documents and that the content of your paper is relevant to your journal.
How many rounds of peer review : This tends to depend on the paper and the journal. In my experience, it is fairly typical to expect at least 2 rounds of revision prior to acceptance, including some major revisions in the second round of reviews.
However, it's very common for papers to be rejected; studies have shown that around 21% of papers are rejected without review, while approximately 40% of papers are rejected after peer review. So, what are your options if your manuscript is rejected This article surveys available systematic information and studies of acceptance rates. The overall global average is around 35-40%. There are significant differences between fields of science, with biomedicine having higher acceptance rates compared to for instance the social sciences.
Does peer review mean anything
The peer-review process subjects an author's scholarly work, research, or ideas to the scrutiny of others who are experts in the same field (peers) and is considered necessary to ensure academic scientific quality.The primary goals of a peer review are to determine whether a scholarly work falls within the journal's scope, to check whether the research topic has been clearly formulated, and to decide if a suitable approach has been taken to address the scientific issues involved.Peer review provides informed considerations of a candidate's teaching that student ratings cannot address: breadth, depth, and rigor of course objectives and materials; patterns of and procedures for course management; and a contextualized sense of the interactions between teacher and students as a whole. Here's a general understanding of what these status changes could imply: Under Review: This status indicates that your paper is currently being evaluated by peer reviewers. Peer review involves experts in the field assessing the quality, validity, and significance of your work.
Does under review mean denied : Until the review is complete, your application might say it's pending or under review. This isn't necessarily bad news, and it doesn't automatically mean your application will be denied.
What is the rejection rate for peer review : For every research paper that is successfully published, there are thousands more that get left behind and there are many reasons for rejection. In fact, manuscript rejection rates can be as high as 97% in some reputed international journal publications.
What are the negative effects of peer review
Con: Peer reviews can create confusion
People may get clashing feedback. After all, one colleague may give their coworker a couple examples of where they need to improve in communicating—while another colleague may praise that same person for their prompt communication. Reviewers often find themselves swamped with multiple review requests at a time. While accepting peer review requests can boost a researcher's reputation and career progress, it is important to understand that, at times, turning down a request may be a better decision.Peer review is designed to assess the validity, quality and often the originality of articles for publication. Its ultimate purpose is to maintain the integrity of science by filtering out invalid or poor quality articles.
What are three benefits of peer review : Being part of a Peer-Review Group will not only help you keep your writing progress on track, but also allows you to workshop ideas, improve your written communication, and receive constructive feedback from an interdisciplinary audience, something which you possibly do not receive from your advisor or committee.
Antwort What happens after peer review? Weitere Antworten – What is the next step after peer review
Once the manuscript has been through peer review and revision, it will enter stage four, the editorial final decision . The editor will decide to accept or reject the manuscript on the basis of the comments from the reviewers and the quality of the revision.After peer review, the editor will consider feedback from the reviewers and then make a decision about the article. The decision letter is delivered to the author via email. There are three basic types of decisions: Accept, Revise, and Reject.If your manuscript passes peer review, the journal will give you an in-principle acceptance (IPA). This indicates that your article will be published as long as you successfully complete your study according to the pre-registered methods and submit an evidence-based interpretation of the results.
What are the outcomes of peer review : Possible outcomes of peer review
In addition to the comments received from the review, editors also base their decisions on: The journal's aims and audience. The state of knowledge in the field. The level of competition for acceptance and page space within the journal.
Does under review mean accepted
When the status of your manuscript changes to under review, this means that it has passed the initial editorial checks. The journal has confirmed that you've uploaded and submitted the correct documents and that the content of your paper is relevant to your journal.
How many rounds of peer review : This tends to depend on the paper and the journal. In my experience, it is fairly typical to expect at least 2 rounds of revision prior to acceptance, including some major revisions in the second round of reviews.
However, it's very common for papers to be rejected; studies have shown that around 21% of papers are rejected without review, while approximately 40% of papers are rejected after peer review. So, what are your options if your manuscript is rejected
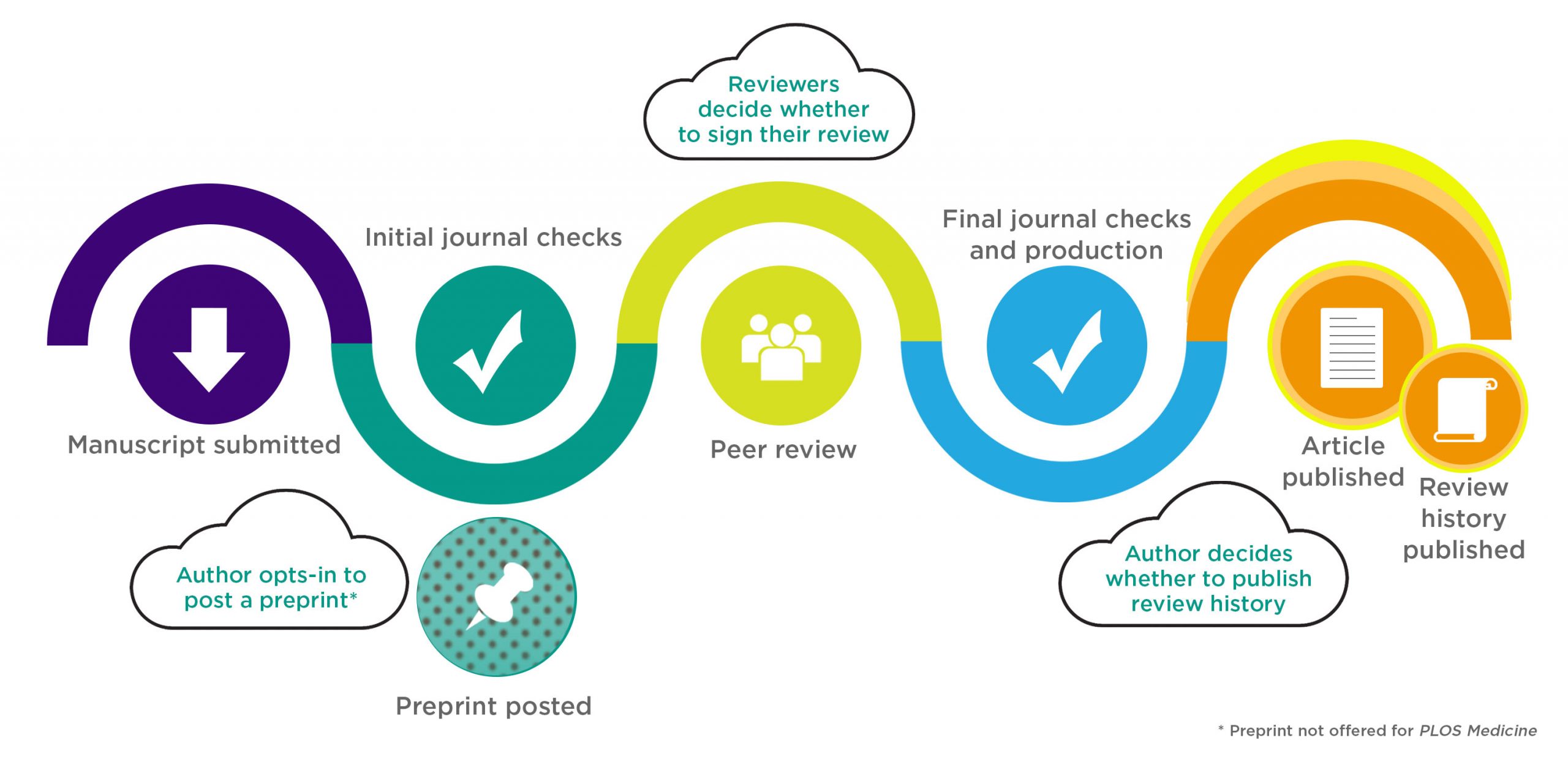
This article surveys available systematic information and studies of acceptance rates. The overall global average is around 35-40%. There are significant differences between fields of science, with biomedicine having higher acceptance rates compared to for instance the social sciences.
Does peer review mean anything
The peer-review process subjects an author's scholarly work, research, or ideas to the scrutiny of others who are experts in the same field (peers) and is considered necessary to ensure academic scientific quality.The primary goals of a peer review are to determine whether a scholarly work falls within the journal's scope, to check whether the research topic has been clearly formulated, and to decide if a suitable approach has been taken to address the scientific issues involved.Peer review provides informed considerations of a candidate's teaching that student ratings cannot address: breadth, depth, and rigor of course objectives and materials; patterns of and procedures for course management; and a contextualized sense of the interactions between teacher and students as a whole.
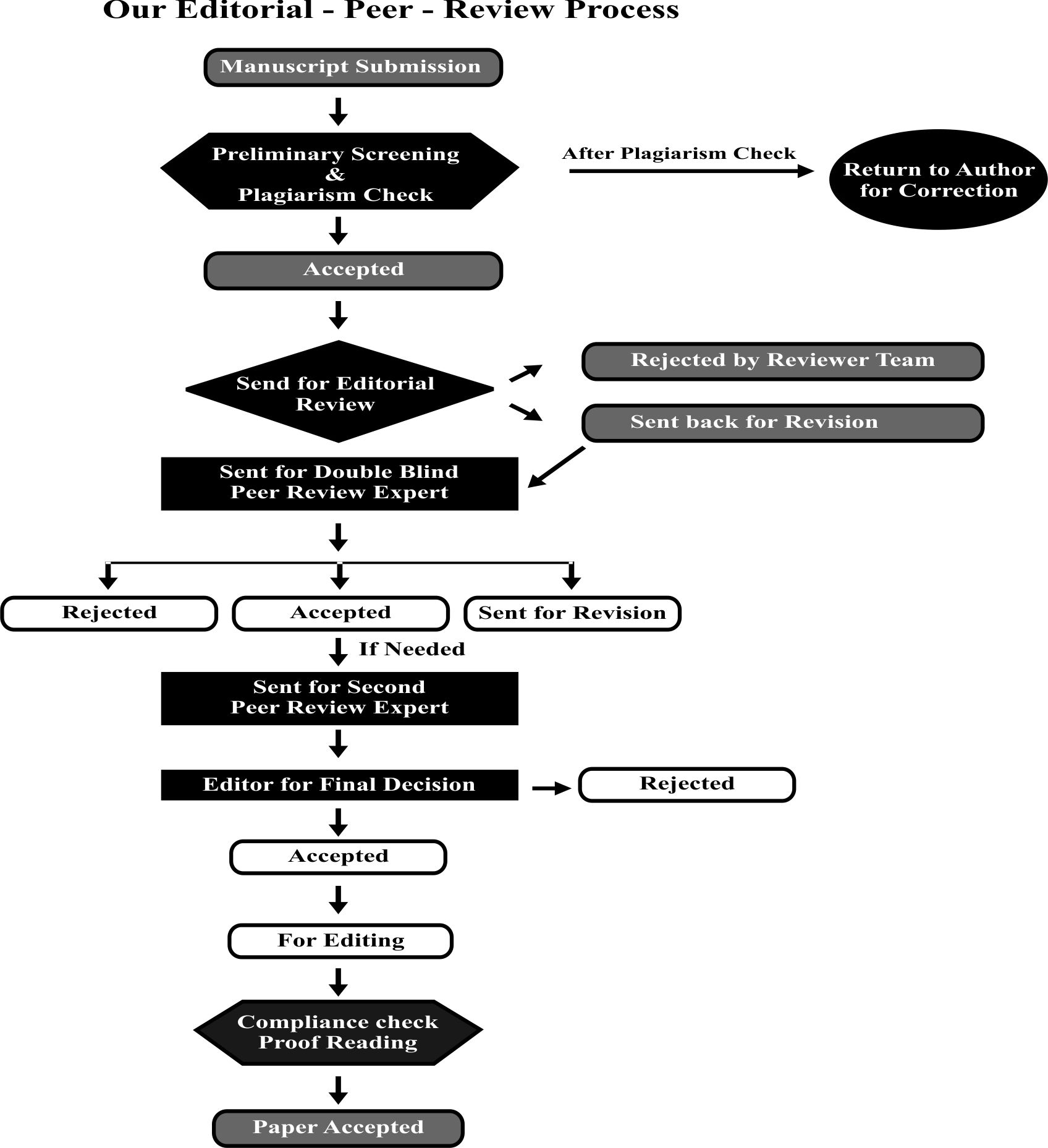
Here's a general understanding of what these status changes could imply: Under Review: This status indicates that your paper is currently being evaluated by peer reviewers. Peer review involves experts in the field assessing the quality, validity, and significance of your work.
Does under review mean denied : Until the review is complete, your application might say it's pending or under review. This isn't necessarily bad news, and it doesn't automatically mean your application will be denied.
What is the rejection rate for peer review : For every research paper that is successfully published, there are thousands more that get left behind and there are many reasons for rejection. In fact, manuscript rejection rates can be as high as 97% in some reputed international journal publications.
What are the negative effects of peer review
Con: Peer reviews can create confusion
People may get clashing feedback. After all, one colleague may give their coworker a couple examples of where they need to improve in communicating—while another colleague may praise that same person for their prompt communication.

Reviewers often find themselves swamped with multiple review requests at a time. While accepting peer review requests can boost a researcher's reputation and career progress, it is important to understand that, at times, turning down a request may be a better decision.Peer review is designed to assess the validity, quality and often the originality of articles for publication. Its ultimate purpose is to maintain the integrity of science by filtering out invalid or poor quality articles.
What are three benefits of peer review : Being part of a Peer-Review Group will not only help you keep your writing progress on track, but also allows you to workshop ideas, improve your written communication, and receive constructive feedback from an interdisciplinary audience, something which you possibly do not receive from your advisor or committee.