Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.If the independent and dependent variables are numeric, use line diagrams or scattergrams; if only the dependent variable is numeric, use bar graphs; for proportions, use bar graphs or pie charts.Graphs and charts are effective visual tools because they present information quickly and easily. It is not surprising then, that graphs are commonly used by print and electronic media. Sometimes, data can be better understood when presented by a graph than by a table because the graph can reveal a trend or comparison.
What are the 3 main types of graphs used for : Comparing Line Graphs, Pie Charts, and Bar Graphs
Pie graphs are often better than line graphs at showing how an overall group is divided. However, if a pie graph has too many slices, it can become difficult to interpret. Bar graphs are especially useful when comparing quantities.
How to pick a visualization
How to Choose the Right Visualizations
Tabular format is best used when exact quantities of numbers must be known.
Line charts are best used when trying to visualize continuous data over time.
Bar charts are best used when showing comparisons between categories.
Pie charts are best used to compare parts to the whole.
Why use a bar graph : A bar chart is used when you want to show a distribution of data points or perform a comparison of metric values across different subgroups of your data. From a bar chart, we can see which groups are highest or most common, and how other groups compare against the others.
A line chart, area chart, and column chart are the most common chart types used to visualize change over time. In most cases, they can be used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between them. Line charts and area charts are the best tools to visualize data that goes up and down from day to day. Types of Graphs in Statistics. The four basic graphs used in statistics include bar, line, histogram and pie charts.
How to know which graph to use in science
A line graph should be used when the independent and dependent variables are continuous close continuousA variable that has values that can be any number.. A bar chart should be used if the independent variable is categoric. Examples include gender, hair colour and the name of your school..A graph with a simple design strives for a clean, uncluttered look. Simplicity in design does not mean simplicity in data however; well-designed graphs can represent rich data. Avoid distortions, shading, perspective, volume, unnecessary colour, decoration or pictograms, and 3D.Bar graphs are used to compare things between different groups or to track changes over time. Most Common Types of Data Visualization
Column Chart. They are a straightforward, time-tested method of comparing several collections of data.
Line Graph. A line graph is used to show trends, development, or changes through time.
Pie Chart.
Bar Chart.
Heat Maps.
Scatter Plot.
Bubble Chart.
Funnel Chart.
How do you know what to visualize : Here are some steps to help you visualize and accurately manifest the life you want:
Step 1: Know what you want.
Step 2 : Describe your vision in detail.
Step 3: Start visualizing and create the emotions.
Step 4: Take daily actions.
Step 5: Have grit and persevere.
Why use histograms : The histogram is a popular graphing tool. It is used to summarize discrete or continuous data that are measured on an interval scale. It is often used to illustrate the major features of the distribution of the data in a convenient form.
When not to use bar graph
Avoid using bar graphs overlayed on a map to show geospatial information, unless the chart has enough space to show the entire bar for all bars. Otherwise, this can lead to occlusion, where some bars hide shorter bars behind them, like in this chart showing the populations of the 100 biggest cities in the world. How to Choose the Right Visualizations
Tabular format is best used when exact quantities of numbers must be known.
Line charts are best used when trying to visualize continuous data over time.
Bar charts are best used when showing comparisons between categories.
Pie charts are best used to compare parts to the whole.
If you have nominal data, use bar charts or histograms if your data is discrete, or line/ area charts if it is continuous. If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts.
What graphs are best for what data : Donut and pie charts are great choices to show composition when simple proportions are useful. Area charts put the composition of data within the context of trends over time. Stacked bar, percent, and column charts show an overview of the data's composition.
Antwort What graph to use and why? Weitere Antworten – How do you decide which graph to use
Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.If the independent and dependent variables are numeric, use line diagrams or scattergrams; if only the dependent variable is numeric, use bar graphs; for proportions, use bar graphs or pie charts.Graphs and charts are effective visual tools because they present information quickly and easily. It is not surprising then, that graphs are commonly used by print and electronic media. Sometimes, data can be better understood when presented by a graph than by a table because the graph can reveal a trend or comparison.
What are the 3 main types of graphs used for : Comparing Line Graphs, Pie Charts, and Bar Graphs
Pie graphs are often better than line graphs at showing how an overall group is divided. However, if a pie graph has too many slices, it can become difficult to interpret. Bar graphs are especially useful when comparing quantities.
How to pick a visualization
How to Choose the Right Visualizations
Why use a bar graph : A bar chart is used when you want to show a distribution of data points or perform a comparison of metric values across different subgroups of your data. From a bar chart, we can see which groups are highest or most common, and how other groups compare against the others.
A line chart, area chart, and column chart are the most common chart types used to visualize change over time. In most cases, they can be used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between them. Line charts and area charts are the best tools to visualize data that goes up and down from day to day.
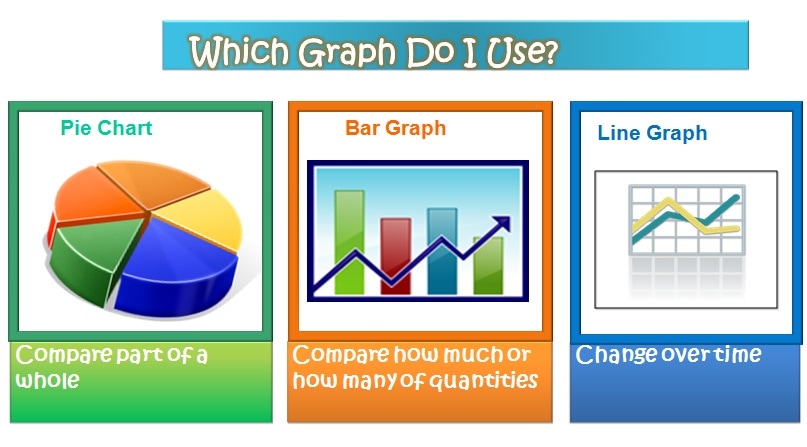
Types of Graphs in Statistics. The four basic graphs used in statistics include bar, line, histogram and pie charts.
How to know which graph to use in science
A line graph should be used when the independent and dependent variables are continuous close continuousA variable that has values that can be any number.. A bar chart should be used if the independent variable is categoric. Examples include gender, hair colour and the name of your school..A graph with a simple design strives for a clean, uncluttered look. Simplicity in design does not mean simplicity in data however; well-designed graphs can represent rich data. Avoid distortions, shading, perspective, volume, unnecessary colour, decoration or pictograms, and 3D.Bar graphs are used to compare things between different groups or to track changes over time.
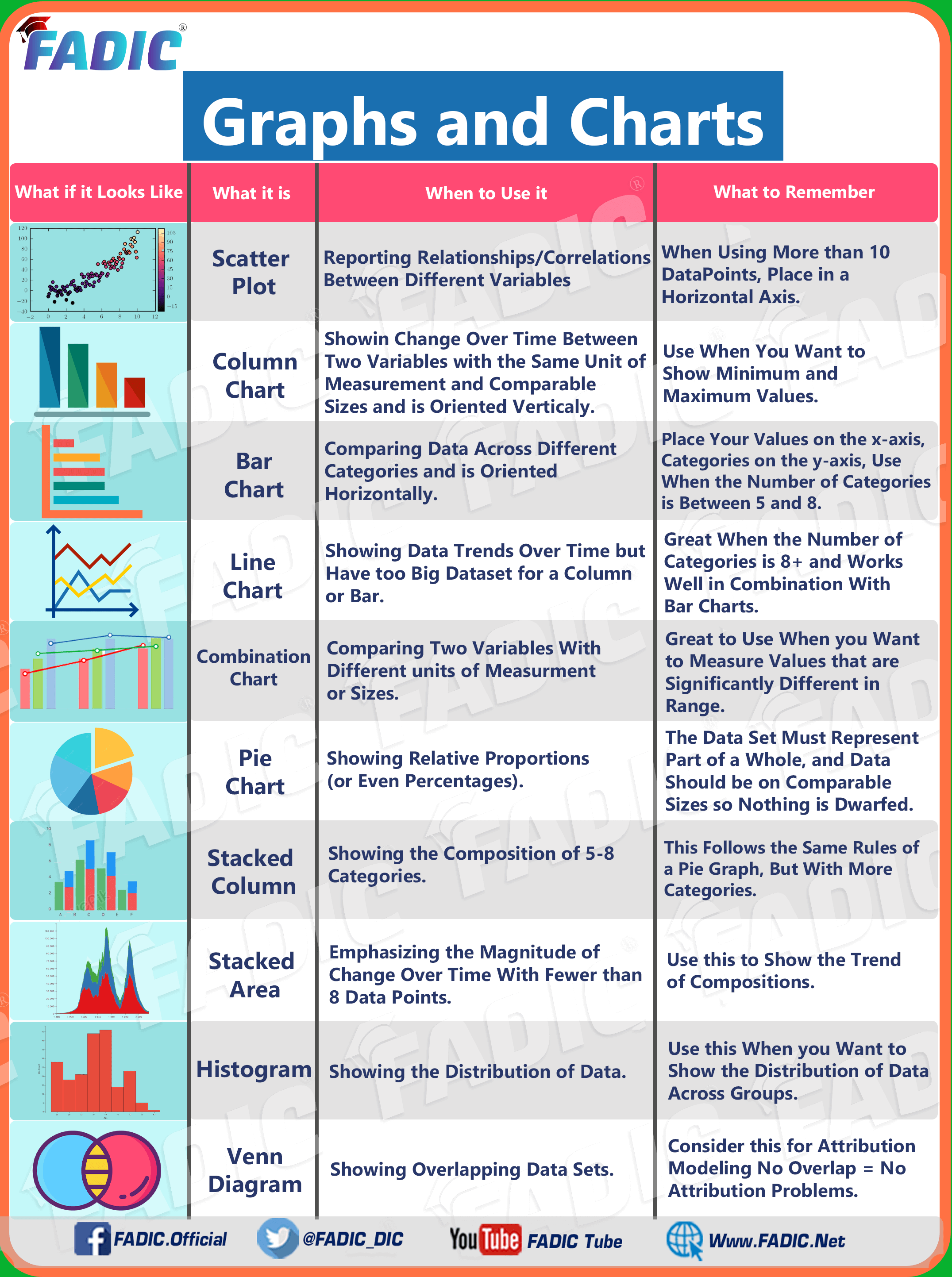
Most Common Types of Data Visualization
How do you know what to visualize : Here are some steps to help you visualize and accurately manifest the life you want:
Why use histograms : The histogram is a popular graphing tool. It is used to summarize discrete or continuous data that are measured on an interval scale. It is often used to illustrate the major features of the distribution of the data in a convenient form.
When not to use bar graph
Avoid using bar graphs overlayed on a map to show geospatial information, unless the chart has enough space to show the entire bar for all bars. Otherwise, this can lead to occlusion, where some bars hide shorter bars behind them, like in this chart showing the populations of the 100 biggest cities in the world.
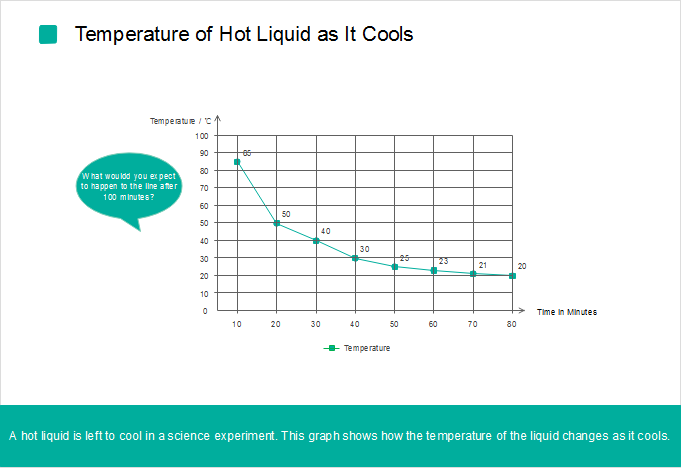
How to Choose the Right Visualizations
If you have nominal data, use bar charts or histograms if your data is discrete, or line/ area charts if it is continuous. If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts.
What graphs are best for what data : Donut and pie charts are great choices to show composition when simple proportions are useful. Area charts put the composition of data within the context of trends over time. Stacked bar, percent, and column charts show an overview of the data's composition.