A chunk of China's debt is owed by its local governments. Their finances are under growing pressure now that revenue from selling land to property developers—a crucial source of income—has dried up. Real-estate firms account for another sizable chunk of China's debt.Local governments have amassed “hidden debt” (or off-budgetary borrowing) estimated by the IMF to be as much as over half of China's annual GDP. The “hidden debt” problem of local governments is a major source of concern for the Chinese leadership, and a policy priority.Tensions with the United States are the top external challenge for China's economic recovery in 2024, but not the only one. Complex global supply chain disruptions pose risks to Chinese exporters that are already operating on thin profit margins.
What is China’s most serious issue : No doubt China faces many structural and other challenges: slumping productivity, a shrinking labor force, restrictions on the transfer of technology imposed by the United States and other countries, an ongoing real estate bubble's correction, elevated unemployment among younger workers, and a leadership that seems to …
Is China good economically
It is the world's second largest economy by nominal GDP, behind the United States, and the world's largest economy since 2016 when measured by purchasing power parity (PPP). China accounted for 19% of the global economy in 2022 in PPP terms, and around 18% in nominal terms in 2022.
Is China’s economy falling : The Chinese economy is still growing, to the tune of 5.2% last year, according to official data. That compares with average annual growth of about 7% last decade and more than 10% in the 2000s. Some economists say this year's growth target of about 5% is overly ambitious.
A declining population has weakened the labour supply. And uncertainty surrounding China's economy and intensified geopolitical tensions have together driven foreign investment out of China.
Years of erratic and irresponsible policies, excessive Communist Party control and undelivered promises of reform have created a dead-end Chinese economy of weak domestic consumer demand and slowing growth.
Why is China economy weak
The current weak consumer demand in China's economy is closely related to the real estate crisis. The value of houses is much lower today than it was two years ago, creating fear about the future value of personal wealth.Significant property sector challenges and export weakness are major contributors to China's economic malaise. New home prices faced their steepest decline last year since early 2015. In April 2024, new home prices fell 3.5% compared to a year ago, with existing home prices down nearly 7% compared to year ago values.China's structural challenges — its paltry social security system, rigid household registration system, ageing population and rising labour costs — cannot be swiftly resolved. Three years of strict COVID-19 controls prevented unimaginable health and economic disaster but disrupted China's long-run growth trajectory.
According to official data, gross domestic product (GDP) expanded by 5.3% in the first three months of 2024, compared to a year earlier. That beat expectations the world's second largest economy could see growth slow to 4.6% in the first quarter.
Why is China in debt : Most of this debt came from building infrastructure, much of which is unlikely to generate revenues sufficient to pay off the obligations. With China's trend growth rate notably lower now than it was, it leaves a burden over the long haul.
Is China’s economy doing good : The Chinese economy is still growing, to the tune of 5.2% last year, according to official data. That compares with average annual growth of about 7% last decade and more than 10% in the 2000s. Some economists say this year's growth target of about 5% is overly ambitious.
Is China’s economy actually good
Since China began to open up and reform its economy in 1978, GDP growth has averaged over 9 percent a year, and more than 800 million people have lifted themselves out of poverty. There have also been significant improvements in access to health, education, and other services over the same period.
Many of the risks facing China's economy stem from its ailing real estate sector. For decades, China's economy was dependent on a booming property market driven by speculative investment returns. However, this growth was largely driven by debt.A declining population has weakened the labour supply. And uncertainty surrounding China's economy and intensified geopolitical tensions have together driven foreign investment out of China.
How is China’s economy right now : Economists at ANZ now see China's economy growing 4.9% this year, up from 4.2% previously, while economists at DBS Bank lifted their 2024 outlook to 5% from 4.5%.
Antwort What are the problems with China’s economy? Weitere Antworten – What is the problem with China’s economy
Debt: Tapped out
A chunk of China's debt is owed by its local governments. Their finances are under growing pressure now that revenue from selling land to property developers—a crucial source of income—has dried up. Real-estate firms account for another sizable chunk of China's debt.Local governments have amassed “hidden debt” (or off-budgetary borrowing) estimated by the IMF to be as much as over half of China's annual GDP. The “hidden debt” problem of local governments is a major source of concern for the Chinese leadership, and a policy priority.Tensions with the United States are the top external challenge for China's economic recovery in 2024, but not the only one. Complex global supply chain disruptions pose risks to Chinese exporters that are already operating on thin profit margins.
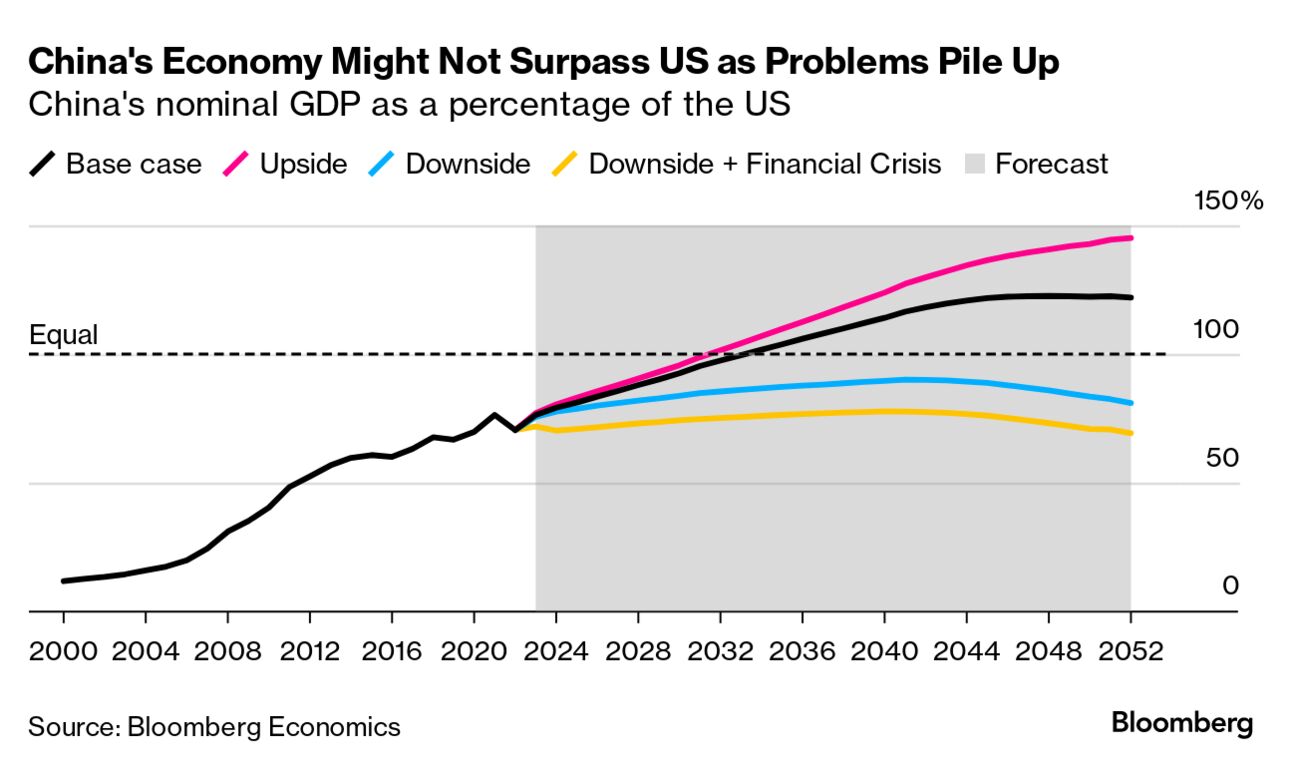
What is China’s most serious issue : No doubt China faces many structural and other challenges: slumping productivity, a shrinking labor force, restrictions on the transfer of technology imposed by the United States and other countries, an ongoing real estate bubble's correction, elevated unemployment among younger workers, and a leadership that seems to …
Is China good economically
It is the world's second largest economy by nominal GDP, behind the United States, and the world's largest economy since 2016 when measured by purchasing power parity (PPP). China accounted for 19% of the global economy in 2022 in PPP terms, and around 18% in nominal terms in 2022.
Is China’s economy falling : The Chinese economy is still growing, to the tune of 5.2% last year, according to official data. That compares with average annual growth of about 7% last decade and more than 10% in the 2000s. Some economists say this year's growth target of about 5% is overly ambitious.
A declining population has weakened the labour supply. And uncertainty surrounding China's economy and intensified geopolitical tensions have together driven foreign investment out of China.

Years of erratic and irresponsible policies, excessive Communist Party control and undelivered promises of reform have created a dead-end Chinese economy of weak domestic consumer demand and slowing growth.
Why is China economy weak
The current weak consumer demand in China's economy is closely related to the real estate crisis. The value of houses is much lower today than it was two years ago, creating fear about the future value of personal wealth.Significant property sector challenges and export weakness are major contributors to China's economic malaise. New home prices faced their steepest decline last year since early 2015. In April 2024, new home prices fell 3.5% compared to a year ago, with existing home prices down nearly 7% compared to year ago values.China's structural challenges — its paltry social security system, rigid household registration system, ageing population and rising labour costs — cannot be swiftly resolved. Three years of strict COVID-19 controls prevented unimaginable health and economic disaster but disrupted China's long-run growth trajectory.

According to official data, gross domestic product (GDP) expanded by 5.3% in the first three months of 2024, compared to a year earlier. That beat expectations the world's second largest economy could see growth slow to 4.6% in the first quarter.
Why is China in debt : Most of this debt came from building infrastructure, much of which is unlikely to generate revenues sufficient to pay off the obligations. With China's trend growth rate notably lower now than it was, it leaves a burden over the long haul.
Is China’s economy doing good : The Chinese economy is still growing, to the tune of 5.2% last year, according to official data. That compares with average annual growth of about 7% last decade and more than 10% in the 2000s. Some economists say this year's growth target of about 5% is overly ambitious.
Is China’s economy actually good
Since China began to open up and reform its economy in 1978, GDP growth has averaged over 9 percent a year, and more than 800 million people have lifted themselves out of poverty. There have also been significant improvements in access to health, education, and other services over the same period.

Many of the risks facing China's economy stem from its ailing real estate sector. For decades, China's economy was dependent on a booming property market driven by speculative investment returns. However, this growth was largely driven by debt.A declining population has weakened the labour supply. And uncertainty surrounding China's economy and intensified geopolitical tensions have together driven foreign investment out of China.
How is China’s economy right now : Economists at ANZ now see China's economy growing 4.9% this year, up from 4.2% previously, while economists at DBS Bank lifted their 2024 outlook to 5% from 4.5%.