High risk: Tumor extends outside the prostate, the PSA >20, or grade group 4 or 5 (Gleason 8 to 10).Is prostate cancer very curable Yes, if it's caught early. In some cases, cancer grows so slowly that you may not need treatment right away. Treatment can often eliminate prostate cancers that haven't spread beyond the prostate gland.The PSA level is less than 10 and the Grade Group is 1; OR the cancer is felt during a digital rectal exam and is found in one-half or less of one side of the prostate. The PSA level is less than 10 and the Grade Group is 1.
Does a PSA of 30 mean cancer : CONCLUSIONS: Serum PSA >30 ng/ml is an almost certain predictor of the presence of prostate cancer. Aggressive prostate cancer education and screening programs are needed in our inner cities in order to detect prostate cancer at an earlier, treatable stage.
Can you live 20 years with stage 4 prostate cancer
When prostate cancer reaches stage 4 and has spread (metastasized) to other organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones, the five-year survival rate falls below 30%.
Is stage 4 cancer 100% death : Is stage 4 cancer always terminal Stage 4 cancer is not always terminal. It is usually advanced and requires more aggressive treatment. Terminal cancer refers to cancer that is not curable and eventually results in death.
Decoding a PSA Test
In general: For men in their 40s and 50s: A PSA score greater than 2.5 ng/ml is considered abnormal. The median PSA for this age range is 0.6 to 0.7 ng/ml. For men in their 60s: A PSA score greater than 4.0 ng/ml is considered abnormal. Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. In stage IIIA, cancer is found in one or both sides of the prostate. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level is at least 20 and the Grade Group is 1, 2, 3, or 4 (Gleason score is 8 or less).
Is a PSA of 50 high
Decoding a PSA Test
For men in their 40s and 50s: A PSA score greater than 2.5 ng/ml is considered abnormal. The median PSA for this age range is 0.6 to 0.7 ng/ml. For men in their 60s: A PSA score greater than 4.0 ng/ml is considered abnormal.10-year relative survival rate of 98 percent: Ten years after diagnosis, the average prostate cancer patient is just 2 percent less likely to survive than a man without prostate cancer.Although the overall prognosis may be poor based on cases with previous patients and older treatments, many patients with stage 4 cancer can live for years. Methods: Patients were divided into groups according to diagnostic PSA level: <20, 20-≤100, 100-≤200 ng/mL, 200-≤500 ng/mL, and >500 ng/mL. Outcomes measured include overall survival and prostate cancer-specific mortality.
What is the highest PSA can go : There is no limit to how high a PSA level may rise. But some men with prostate cancer will have a normal PSA level. For these reasons, researchers are still trying to find out the best way to use the PSA test to find prostate cancer.
Can you live 15 years with advanced prostate cancer : 15-year relative survival rate of 95 percent: Fifteen years after diagnosis, the average prostate cancer patient is 5 percent less likely to survive than a man without prostate cancer.
What PSA level is stage 4 prostate cancer
Similar to stage 3, stage 4 prostate cancer can involve any PSA levels and Gleason scores that range between two and 10. It may be almost all of the prostate biopsies in the patients with high PSA (>100ng/ml) are positive. Prostate cancer with high PSA may be adenocarcinoma. The prostate cancer with PSA greater than 100ng/ml may be advanced disease, and the treatment strategy would not changed according to pathological reports.What is an alarming PSA level A PSA level of 10 ng/ml or higher means you have a greater risk of prostate cancer.
How long can you live with a PSA of 100 : Results: Of this cohort, 241 patients (4.2%) had a diagnostic PSA level >100 ng/mL. Patients with PSA >100 ng/mL have a significant reduction in five (29.1% vs 62.5% vs 87%) and ten-year (18.2% vs 36.7% vs 70.7%) overall survival when compared to men with diagnostic PSA 20-100 and <20 ng/mL respectively.
Antwort What age is too high for PSA? Weitere Antworten – What PSA level is aggressive prostate cancer
High risk: Tumor extends outside the prostate, the PSA >20, or grade group 4 or 5 (Gleason 8 to 10).Is prostate cancer very curable Yes, if it's caught early. In some cases, cancer grows so slowly that you may not need treatment right away. Treatment can often eliminate prostate cancers that haven't spread beyond the prostate gland.The PSA level is less than 10 and the Grade Group is 1; OR the cancer is felt during a digital rectal exam and is found in one-half or less of one side of the prostate. The PSA level is less than 10 and the Grade Group is 1.
Does a PSA of 30 mean cancer : CONCLUSIONS: Serum PSA >30 ng/ml is an almost certain predictor of the presence of prostate cancer. Aggressive prostate cancer education and screening programs are needed in our inner cities in order to detect prostate cancer at an earlier, treatable stage.
Can you live 20 years with stage 4 prostate cancer
When prostate cancer reaches stage 4 and has spread (metastasized) to other organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones, the five-year survival rate falls below 30%.
Is stage 4 cancer 100% death : Is stage 4 cancer always terminal Stage 4 cancer is not always terminal. It is usually advanced and requires more aggressive treatment. Terminal cancer refers to cancer that is not curable and eventually results in death.
Decoding a PSA Test
In general: For men in their 40s and 50s: A PSA score greater than 2.5 ng/ml is considered abnormal. The median PSA for this age range is 0.6 to 0.7 ng/ml. For men in their 60s: A PSA score greater than 4.0 ng/ml is considered abnormal.

Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. In stage IIIA, cancer is found in one or both sides of the prostate. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level is at least 20 and the Grade Group is 1, 2, 3, or 4 (Gleason score is 8 or less).
Is a PSA of 50 high
Decoding a PSA Test
For men in their 40s and 50s: A PSA score greater than 2.5 ng/ml is considered abnormal. The median PSA for this age range is 0.6 to 0.7 ng/ml. For men in their 60s: A PSA score greater than 4.0 ng/ml is considered abnormal.10-year relative survival rate of 98 percent: Ten years after diagnosis, the average prostate cancer patient is just 2 percent less likely to survive than a man without prostate cancer.Although the overall prognosis may be poor based on cases with previous patients and older treatments, many patients with stage 4 cancer can live for years.
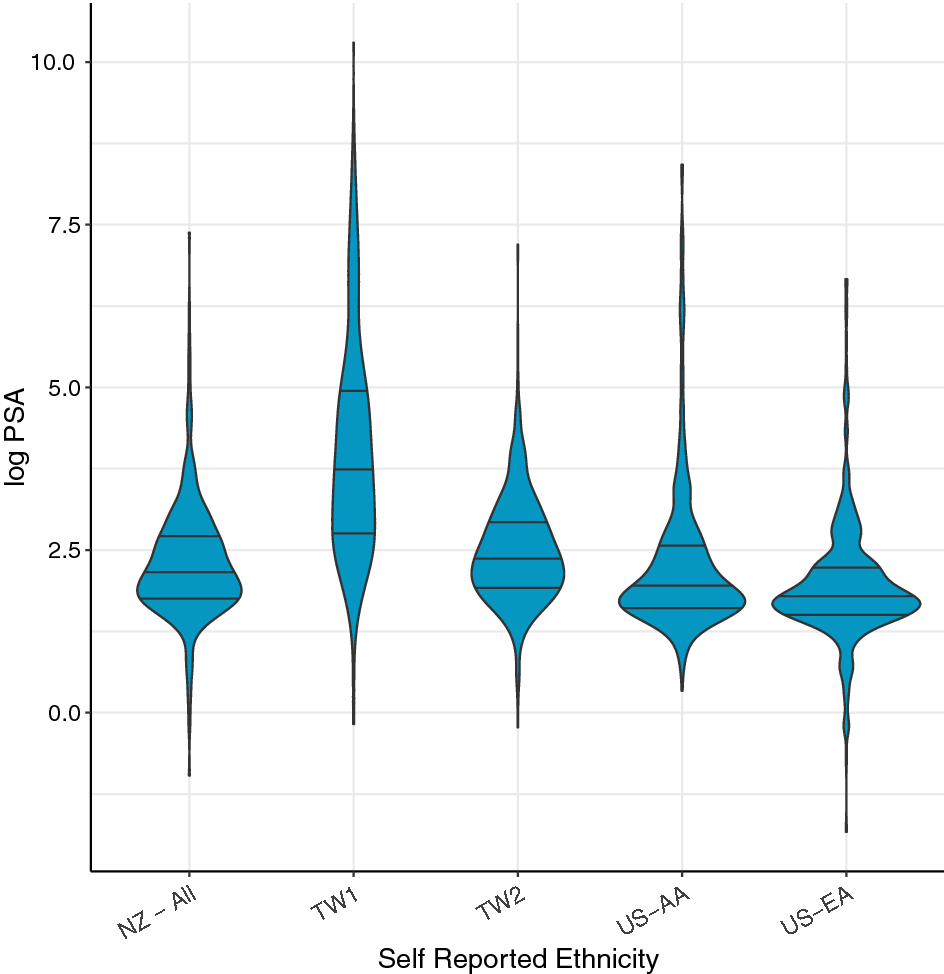
Methods: Patients were divided into groups according to diagnostic PSA level: <20, 20-≤100, 100-≤200 ng/mL, 200-≤500 ng/mL, and >500 ng/mL. Outcomes measured include overall survival and prostate cancer-specific mortality.
What is the highest PSA can go : There is no limit to how high a PSA level may rise. But some men with prostate cancer will have a normal PSA level. For these reasons, researchers are still trying to find out the best way to use the PSA test to find prostate cancer.
Can you live 15 years with advanced prostate cancer : 15-year relative survival rate of 95 percent: Fifteen years after diagnosis, the average prostate cancer patient is 5 percent less likely to survive than a man without prostate cancer.
What PSA level is stage 4 prostate cancer
Similar to stage 3, stage 4 prostate cancer can involve any PSA levels and Gleason scores that range between two and 10.
It may be almost all of the prostate biopsies in the patients with high PSA (>100ng/ml) are positive. Prostate cancer with high PSA may be adenocarcinoma. The prostate cancer with PSA greater than 100ng/ml may be advanced disease, and the treatment strategy would not changed according to pathological reports.What is an alarming PSA level A PSA level of 10 ng/ml or higher means you have a greater risk of prostate cancer.
How long can you live with a PSA of 100 : Results: Of this cohort, 241 patients (4.2%) had a diagnostic PSA level >100 ng/mL. Patients with PSA >100 ng/mL have a significant reduction in five (29.1% vs 62.5% vs 87%) and ten-year (18.2% vs 36.7% vs 70.7%) overall survival when compared to men with diagnostic PSA 20-100 and <20 ng/mL respectively.