While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.RAID 5's distributed parity provides the most reliable and cost-effective data protection, with an additional disk holding the parity bits for automatically recreating the data in the event of a drive failure. As a result, a minimum of three drives with a capacity utilization of 75% are required.From a software perspective, RAID is a low-level function that operates at the disk level, while NAS is a high-level function that operates at the file level. From a network perspective, RAID is usually internal to a computer or a server, while NAS is external and accessible by multiple clients.
What is the difference between Synology RAID 5 and RAID 6 : RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.
Should I shut down my NAS every night
Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.
Should I use RAID 1 or 5 for NAS : Efficient Storage Utilization: Compared to RAID 1, RAID 5 provides a more efficient use of disk space. While it still offers data protection through parity checks, it doesn't require a complete copy of all data, thereby using storage capacity more effectively.
RAID 0 is more cost-effective in terms of raw storage space since all the space on the drives is usable. For instance, if you use two 1TB drives in RAID 0, you'll have 2TB of usable space. In contrast, RAID 1 mirrors data, so with two 1TB drives, you'd only have 1TB of usable space due to redundancy. NAS can offer more flexibility and convenience than RAID or SAN, but it also has more overhead and latency in terms of network traffic, bandwidth, and security. SAN can offer more speed and efficiency than RAID or NAS, but it also has more complexity and cost in terms of infrastructure, configuration, and maintenance.
Is RAID 5 still useful
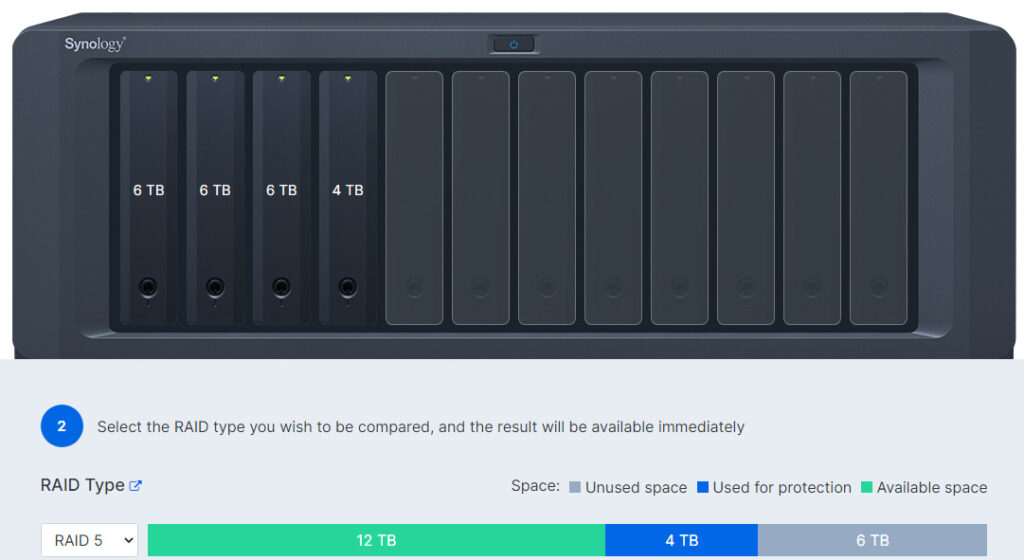
RAID 5 evenly balances reads and writes, and is currently one of the most commonly used RAID methods. It has more usable storage than RAID 1 and RAID 10 configurations and provides performance equivalent to RAID 0. RAID 5 groups have a minimum of three HDDs and no maximum.three to five years
On average, a NAS drive can last anywhere from three to five years. However, with proper care and regular maintenance, it is possible to prolong the lifespan of a NAS drive. Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of a NAS drive.Q: Does a NAS consume a lot of power The power consumption of a NAS varies by model and usage. However, generally speaking, the power consumption of a NAS is not too high and is much lower than that of a traditional desktop computer or server. RAID 1 offers higher fault tolerance compared to RAID 5. In RAID 1, a single disk failure does not result in data loss or downtime, as the mirrored disk contains an exact copy. RAID 5 can tolerate the failure of a single disk but is vulnerable to data loss if multiple disks fail simultaneously.
Is RAID 1 faster than RAID 5 : In RAID 1, the read/write speed will be the same as that of a single disk (maybe a little higher), because the read/write information is performed on both disks simultaneously. The write speed for a RAID 5 array is slightly lower, as time is spent on calculating and recording a checksum on a separate disk.
Do I really need RAID 1 : RAID 0 – Good if data is unimportant and can be lost, but performance is critical (such as with cache). RAID 1 – Good if you are looking to inexpensively gain additional data redundancy and/or read speeds. (This is a good base level for those looking to achieve high uptime and increase the performance of backups.)
Do I need RAID for SSD NAS
SSD RAID may not be necessary, but the system's performance and speed, data security, and reliability and endurance make it a popular method of ensuring data availability and redundancy. typically, a RAID 5 rebuild on large disks (2TB+) can be measured in days. During this time your data is at risk as the server is calculating the missing data and as such, it's painfully slow. In some cases it may not even be usable. URE – Uncorrectable read error.Data transfer with a NAS is much slower than with a SAN. It's also slower than direct attached storage (DAS). Note: you can also use a NAS device as DAS by simply plugging it directly into your computer.
Why would it be bad for NAS to be used : Congestion and delays or interference with other traffic on the LAN can occur. NAS generally does not perform as well as SAN on a large scale, and higher traffic can cause latency.
Antwort Should a NAS use RAID? Weitere Antworten – Should you RAID a NAS
While different RAID levels offer different levels of data redundancy, they are not enough to provide complete data protection for NAS devices. RAID provides protection against physical disk failures by storing multiple copies of NAS data on different disks to achieve fault tolerance objectives.RAID 5's distributed parity provides the most reliable and cost-effective data protection, with an additional disk holding the parity bits for automatically recreating the data in the event of a drive failure. As a result, a minimum of three drives with a capacity utilization of 75% are required.From a software perspective, RAID is a low-level function that operates at the disk level, while NAS is a high-level function that operates at the file level. From a network perspective, RAID is usually internal to a computer or a server, while NAS is external and accessible by multiple clients.
What is the difference between Synology RAID 5 and RAID 6 : RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failures. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.
Should I shut down my NAS every night
Your files are stored on the NAS server and can be synchronized, or automatically kept up-to-date, on all of your devices. This service needs to always be online so the NAS should always be on. If you are using your NAS for web hosting like I am, you need to keep it online 24/7.
Should I use RAID 1 or 5 for NAS : Efficient Storage Utilization: Compared to RAID 1, RAID 5 provides a more efficient use of disk space. While it still offers data protection through parity checks, it doesn't require a complete copy of all data, thereby using storage capacity more effectively.
RAID 0 is more cost-effective in terms of raw storage space since all the space on the drives is usable. For instance, if you use two 1TB drives in RAID 0, you'll have 2TB of usable space. In contrast, RAID 1 mirrors data, so with two 1TB drives, you'd only have 1TB of usable space due to redundancy.
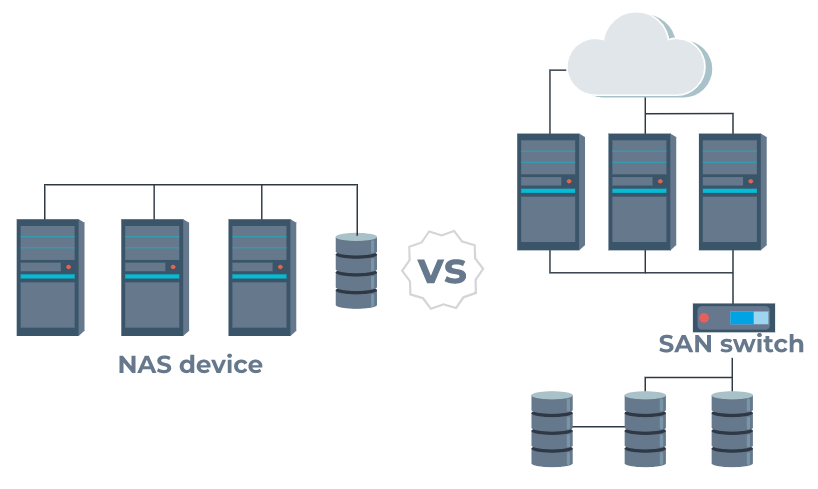
NAS can offer more flexibility and convenience than RAID or SAN, but it also has more overhead and latency in terms of network traffic, bandwidth, and security. SAN can offer more speed and efficiency than RAID or NAS, but it also has more complexity and cost in terms of infrastructure, configuration, and maintenance.
Is RAID 5 still useful
RAID 5 evenly balances reads and writes, and is currently one of the most commonly used RAID methods. It has more usable storage than RAID 1 and RAID 10 configurations and provides performance equivalent to RAID 0. RAID 5 groups have a minimum of three HDDs and no maximum.three to five years
On average, a NAS drive can last anywhere from three to five years. However, with proper care and regular maintenance, it is possible to prolong the lifespan of a NAS drive. Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of a NAS drive.Q: Does a NAS consume a lot of power The power consumption of a NAS varies by model and usage. However, generally speaking, the power consumption of a NAS is not too high and is much lower than that of a traditional desktop computer or server.
RAID 1 offers higher fault tolerance compared to RAID 5. In RAID 1, a single disk failure does not result in data loss or downtime, as the mirrored disk contains an exact copy. RAID 5 can tolerate the failure of a single disk but is vulnerable to data loss if multiple disks fail simultaneously.
Is RAID 1 faster than RAID 5 : In RAID 1, the read/write speed will be the same as that of a single disk (maybe a little higher), because the read/write information is performed on both disks simultaneously. The write speed for a RAID 5 array is slightly lower, as time is spent on calculating and recording a checksum on a separate disk.
Do I really need RAID 1 : RAID 0 – Good if data is unimportant and can be lost, but performance is critical (such as with cache). RAID 1 – Good if you are looking to inexpensively gain additional data redundancy and/or read speeds. (This is a good base level for those looking to achieve high uptime and increase the performance of backups.)
Do I need RAID for SSD NAS
SSD RAID may not be necessary, but the system's performance and speed, data security, and reliability and endurance make it a popular method of ensuring data availability and redundancy.
typically, a RAID 5 rebuild on large disks (2TB+) can be measured in days. During this time your data is at risk as the server is calculating the missing data and as such, it's painfully slow. In some cases it may not even be usable. URE – Uncorrectable read error.Data transfer with a NAS is much slower than with a SAN. It's also slower than direct attached storage (DAS). Note: you can also use a NAS device as DAS by simply plugging it directly into your computer.
Why would it be bad for NAS to be used : Congestion and delays or interference with other traffic on the LAN can occur. NAS generally does not perform as well as SAN on a large scale, and higher traffic can cause latency.