To really understand Earth, you need to travel 6,400 kilometers (3,977 miles) beneath our feet. Starting at the center, Earth is composed of four distinct layers. They are, from deepest to shallowest, the inner core, the outer core, the mantle and the crust.The Earth is composed of four different layers. Many geologists believe that as the Earth cooled the heavier, denser materials sank to the center and the lighter materials rose to the top.
What layer is 5000 km deep : Outer core (2900 km – 5000 km below the Earth's surface). 30 % of the Earth's total mass.
Which layer is 500 km above Earth
the exosphere The atmosphere is comprised of layers based on temperature. These layers are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. A further region at about 500 km above the Earth's surface is called the exosphere.
What is the D layer : The D” layer, the lowermost portion of the mantle, sits just above the molten iron-rich outer core. Seismic observations have revealed a region with an intriguingly complex signature. This relatively thin layer, varying around 250 km in thickness, may hold the key to understanding how the core and mantle interact.
The thermosphere The thermosphere is the hottest layer of the atmosphere. the crust Therefore, the earth's thinnest layer is the crust.
What layer is 5000 km into Earth
Outer Core
This liquid layer of iron and nickel is 5,150km deep. The outer core flows around the centre of the Earth, and the movement of the metals creates our planet's magnetic field.The E prime layer is a distinct layer formed at the outermost part of Earth's core. This layer is formed by surface water penetrating deep into the planet over billions of years. Composition: It is a hydrogen-rich and silica-depleted layer.The electron density of the E-region peaks around noon hours and at the geographic equator. It diminishes during night, however, due to the slower recombination in comparison with the D-region, it does not disappear. Electrons recombine with atomic ions (such as Na+ or O+) very inefficiently. The different layers of the atmosphere
The Troposphere. This is the lowest part of the atmosphere – the part we live in.
The Stratosphere. This extends upwards from the tropopause to about 50 km.
The Mesosphere.
The Thermosphere and Ionosphere.
The Exosphere.
The Magnetosphere.
What layer is the hottest : thermosphere The coldest layer of atmosphere is the mesosphere while the hottest layer of the atmosphere is thermosphere.
Which layer is the hardest layer : The crust The crust is the thinnest, yet hardest layer.
What is the fifth layer of the earth
main mechanical layers. These five layers are the: Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer Core, and Inner Core. E Prime (it means English Prime) defines a way of speaking English without using the verb "to be" in any way ("be, is, am, are, was, were, been, and being").An E-Prime is a number in E that can not be factored. 2 for example is an E-Prime since there is no factorization of 2 except 2 = 2.
Which layer is the last : Exosphere Exosphere. This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. It extends from about 375 miles (600 km) to 6,200 miles (10,000 km ) above the earth.
Antwort Is there a 5th layer of Earth? Weitere Antworten – What layer is 2000 km down
To really understand Earth, you need to travel 6,400 kilometers (3,977 miles) beneath our feet. Starting at the center, Earth is composed of four distinct layers. They are, from deepest to shallowest, the inner core, the outer core, the mantle and the crust.The Earth is composed of four different layers. Many geologists believe that as the Earth cooled the heavier, denser materials sank to the center and the lighter materials rose to the top.

What layer is 5000 km deep : Outer core (2900 km – 5000 km below the Earth's surface). 30 % of the Earth's total mass.
Which layer is 500 km above Earth
the exosphere
The atmosphere is comprised of layers based on temperature. These layers are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. A further region at about 500 km above the Earth's surface is called the exosphere.
What is the D layer : The D” layer, the lowermost portion of the mantle, sits just above the molten iron-rich outer core. Seismic observations have revealed a region with an intriguingly complex signature. This relatively thin layer, varying around 250 km in thickness, may hold the key to understanding how the core and mantle interact.
The thermosphere

The thermosphere is the hottest layer of the atmosphere.
the crust
Therefore, the earth's thinnest layer is the crust.
What layer is 5000 km into Earth
Outer Core
This liquid layer of iron and nickel is 5,150km deep. The outer core flows around the centre of the Earth, and the movement of the metals creates our planet's magnetic field.The E prime layer is a distinct layer formed at the outermost part of Earth's core. This layer is formed by surface water penetrating deep into the planet over billions of years. Composition: It is a hydrogen-rich and silica-depleted layer.The electron density of the E-region peaks around noon hours and at the geographic equator. It diminishes during night, however, due to the slower recombination in comparison with the D-region, it does not disappear. Electrons recombine with atomic ions (such as Na+ or O+) very inefficiently.
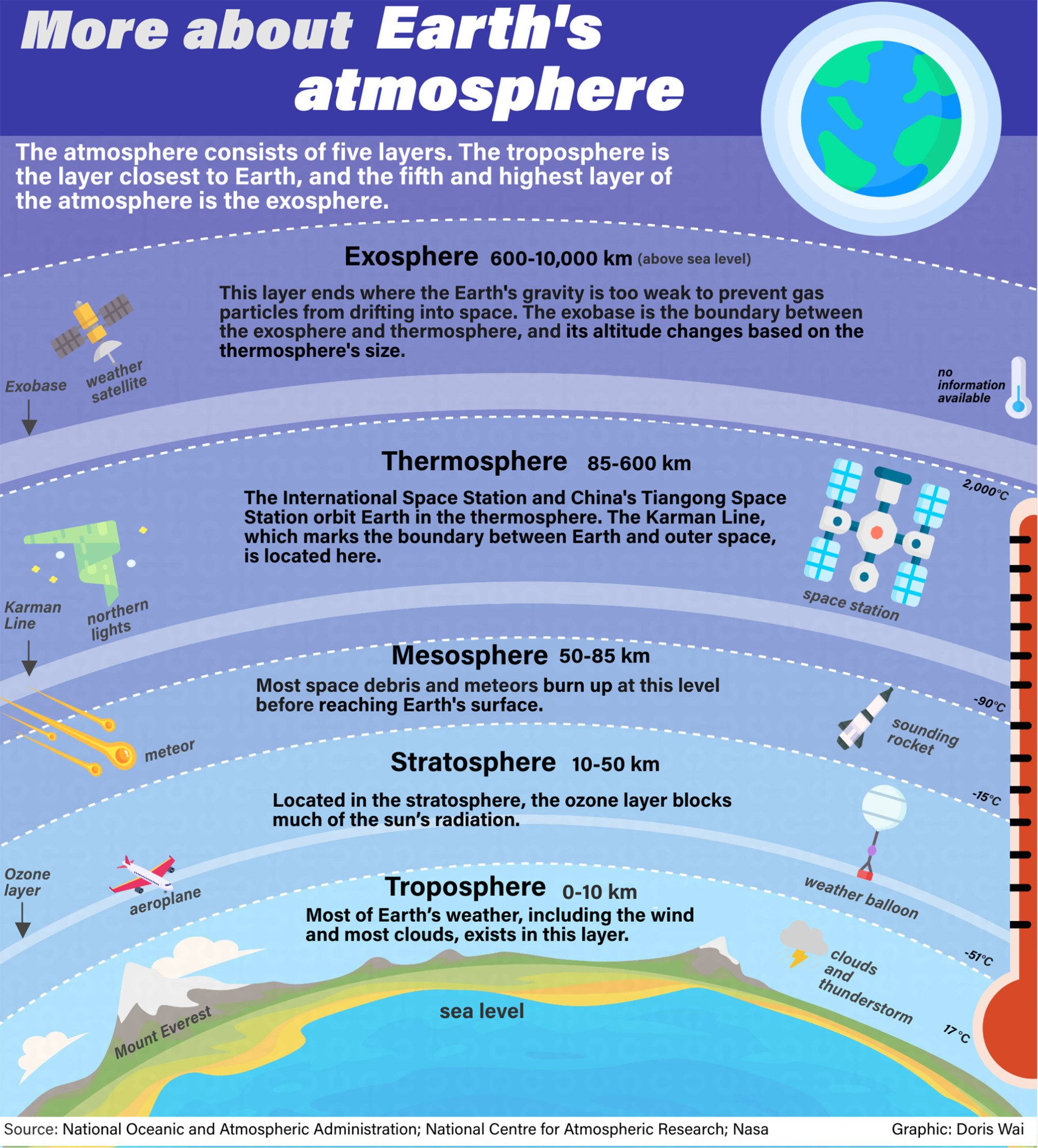
The different layers of the atmosphere
What layer is the hottest : thermosphere
The coldest layer of atmosphere is the mesosphere while the hottest layer of the atmosphere is thermosphere.
Which layer is the hardest layer : The crust
The crust is the thinnest, yet hardest layer.
What is the fifth layer of the earth
main mechanical layers. These five layers are the: Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer Core, and Inner Core.

E Prime (it means English Prime) defines a way of speaking English without using the verb "to be" in any way ("be, is, am, are, was, were, been, and being").An E-Prime is a number in E that can not be factored. 2 for example is an E-Prime since there is no factorization of 2 except 2 = 2.
Which layer is the last : Exosphere
Exosphere. This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. It extends from about 375 miles (600 km) to 6,200 miles (10,000 km ) above the earth.