The universe we live in is expanding. We know this because we see galaxies and groups of galaxies steadily moving apart in the universe. This expansion has been occuring since the universe was formed 15 billion years ago in a very hot, dense event known as the Big Bang.13.7 billion years
Before 1999, astronomers had estimated that the age of the universe was between 7 and 20 billion years. But with advances in technology and the development of new techniques we now know the age of the universe is 13.7 billion years, with an uncertainty of only 200 million years.The universe, being all there is, is infinitely big and has no edge, so there's no outside to even talk about. Oh, sure, there's an outside to our observable patch of the universe. The cosmos is only so old, and light only travels so fast.
Is the Hubble constant actually constant : Because light from a distant object has traveled for billions of years to reach us, our observations are not only affected by the present-day value of the Hubble constant, but also what it was when the universe was expanding more slowly. In other words, the Hubble constant isn't a constant at all!
What is the universe shaped like
Physicists think the universe is flat. Several lines of evidence point to this flat universe: light left over from the Big Bang, the rate of expansion of the universe at different locations, and the way the universe "looks" from different angles, experts told Live Science.
Is the universe endless : The observable universe is certainly finite, and indeed we know approximately how large it is. It's very large—literally incomprehensibly so to human intuition, in fact—but still finite. Current cosmological evidence suggest the entire universe is isotropic, spatially flat, and infinite.
In an open universe the total volume of space and the number of galaxies contained in it are infinite. flat
The current theoretical belief (because it is predicted by the theory of cosmic inflation) is that the universe is flat, with exactly the amount of mass required to stop the expansion (the corresponding average critical density that would just stop the is called the closure density).
Why is the universe not homogeneous
On the largest cosmic scales, the Universe is both homogeneous and isotropic. Homogeneity means that there is no preferred location in the Universe. That is, no matter where you are in the Universe, if you look at the Universe, it will look the same. Isotropy means that there is no preferred direction in the Universe.Hubble limit as an event horizon
For objects at the Hubble limit, the space between us and the object of interest has an average expansion speed of c. So, in a universe with constant Hubble parameter, light emitted at the present time by objects outside the Hubble limit would never be seen by an observer on Earth.But, theoretical physicist Glenn Starkman and colleagues argue, there's still a chance that the universe does have something in common with a doughnut. That's because earlier research considered only a small subset of the possible topologies the universe could have. As far as cosmologists can tell, space is almost perfectly flat. But what does this mean The theory of general relativity, under which space itself can curve, allows for the universe to take one of three forms: flat like a sheet of paper, closed like a sphere, or open like a saddle.
Does space last forever : Current observations suggest that the expansion of the universe will continue forever. The prevailing theory is that the universe will cool as it expands, eventually becoming too cold to sustain life.
Does space ever end : In either case, you could never get to the end of the universe or space. Scientists now consider it unlikely the universe has an end – a region where the galaxies stop or where there would be a barrier of some kind marking the end of space.
Does space end or not
By all accounts, the universe appears to have no boundary. It has no end. On the other hand, the universe is only as big as the area expanding to fill it all up. And it's been doing that since the big bang. Most cosmological evidence points to the universe's density as being just right — the equivalent of around six protons per 1.3 cubic yards — and that it expands in every direction without curving positively or negatively. In other words, the universe is flat.By definition, the observable universe would be a sphere. In that space marks the edge of the observable universe where the microwave background is from has been moving away from us at pretty much the same same speed in all dimensions. Currently the universe is almost perfectly flat.
Why is the universe so uniform : The main idea was that our part of the world emerged as a result of an exponentially rapid stretching of space called cosmic inflation. As all "wrinkles" and non-uniformities of space stretched out and disappeared, the universe became incredibly smooth.
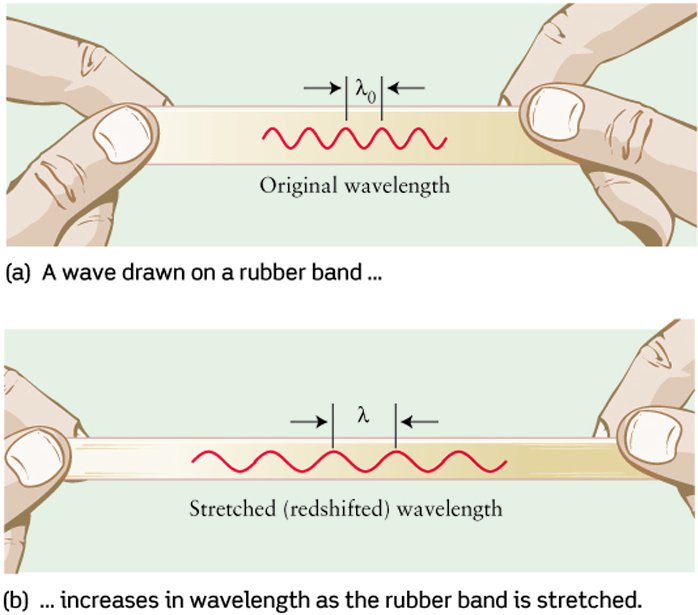
Antwort Is the universe like a rubber band? Weitere Antworten – How do we know that we live in an expanding universe
The universe we live in is expanding. We know this because we see galaxies and groups of galaxies steadily moving apart in the universe. This expansion has been occuring since the universe was formed 15 billion years ago in a very hot, dense event known as the Big Bang.13.7 billion years
Before 1999, astronomers had estimated that the age of the universe was between 7 and 20 billion years. But with advances in technology and the development of new techniques we now know the age of the universe is 13.7 billion years, with an uncertainty of only 200 million years.The universe, being all there is, is infinitely big and has no edge, so there's no outside to even talk about. Oh, sure, there's an outside to our observable patch of the universe. The cosmos is only so old, and light only travels so fast.

Is the Hubble constant actually constant : Because light from a distant object has traveled for billions of years to reach us, our observations are not only affected by the present-day value of the Hubble constant, but also what it was when the universe was expanding more slowly. In other words, the Hubble constant isn't a constant at all!
What is the universe shaped like
Physicists think the universe is flat. Several lines of evidence point to this flat universe: light left over from the Big Bang, the rate of expansion of the universe at different locations, and the way the universe "looks" from different angles, experts told Live Science.
Is the universe endless : The observable universe is certainly finite, and indeed we know approximately how large it is. It's very large—literally incomprehensibly so to human intuition, in fact—but still finite. Current cosmological evidence suggest the entire universe is isotropic, spatially flat, and infinite.
In an open universe the total volume of space and the number of galaxies contained in it are infinite.
flat
The current theoretical belief (because it is predicted by the theory of cosmic inflation) is that the universe is flat, with exactly the amount of mass required to stop the expansion (the corresponding average critical density that would just stop the is called the closure density).
Why is the universe not homogeneous
On the largest cosmic scales, the Universe is both homogeneous and isotropic. Homogeneity means that there is no preferred location in the Universe. That is, no matter where you are in the Universe, if you look at the Universe, it will look the same. Isotropy means that there is no preferred direction in the Universe.Hubble limit as an event horizon
For objects at the Hubble limit, the space between us and the object of interest has an average expansion speed of c. So, in a universe with constant Hubble parameter, light emitted at the present time by objects outside the Hubble limit would never be seen by an observer on Earth.But, theoretical physicist Glenn Starkman and colleagues argue, there's still a chance that the universe does have something in common with a doughnut. That's because earlier research considered only a small subset of the possible topologies the universe could have.

As far as cosmologists can tell, space is almost perfectly flat. But what does this mean The theory of general relativity, under which space itself can curve, allows for the universe to take one of three forms: flat like a sheet of paper, closed like a sphere, or open like a saddle.
Does space last forever : Current observations suggest that the expansion of the universe will continue forever. The prevailing theory is that the universe will cool as it expands, eventually becoming too cold to sustain life.
Does space ever end : In either case, you could never get to the end of the universe or space. Scientists now consider it unlikely the universe has an end – a region where the galaxies stop or where there would be a barrier of some kind marking the end of space.
Does space end or not
By all accounts, the universe appears to have no boundary. It has no end. On the other hand, the universe is only as big as the area expanding to fill it all up. And it's been doing that since the big bang.

Most cosmological evidence points to the universe's density as being just right — the equivalent of around six protons per 1.3 cubic yards — and that it expands in every direction without curving positively or negatively. In other words, the universe is flat.By definition, the observable universe would be a sphere. In that space marks the edge of the observable universe where the microwave background is from has been moving away from us at pretty much the same same speed in all dimensions. Currently the universe is almost perfectly flat.
Why is the universe so uniform : The main idea was that our part of the world emerged as a result of an exponentially rapid stretching of space called cosmic inflation. As all "wrinkles" and non-uniformities of space stretched out and disappeared, the universe became incredibly smooth.