DCD/Dyspraxia is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting motor function and organisation; continues into adulthood and associated with Joint Hypermobility Syndrome (JHS).Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (previously known as joint hypermobility syndrome) Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Marfan syndrome. Osteogenesis Imperfecta.The connective tissues of hypermobile people are weaker compared with non-hypermobile individuals and therefore their muscle needs to be twice as strong to stabilise their joints and to be able to function normally, otherwise they would use twice as much energy on simple tasks, which will lead to fatigue and pain.
Is hypermobility linked to autism : Many studies have shown a strong link between hypermobility and Autism, with up to 80% of Autistic individuals experiencing hypermobility. This connection is not fully understood, but researchers believe that there may be a genetic component involved.
How rare is hypermobility
The hypermobile and classical forms are most common; the hypermobile type may affect as many as 1 in 5,000 to 20,000 people, while the classical type probably occurs in 1 in 20,000 to 40,000 people.
Are people with hypermobility stronger : Independent sample t-tests showed that hypermobile males were significantly weaker compared to non-hypermobile males with respect to elbow extensor strength for both right (p = 0.02) and left (p = 0.03) extremities (Table 2, unadjusted mean strength).
Individuals who suffer from Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome are young-looking, with velvety skin, a small face, and a thin nose, making them look younger as if they have never aged. This is especially seen in the case of the vascular type/ vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. In neurodivergent adults, there is a strong link between the expression of joint hypermobility, dysautonomia, and pain, more so than in the comparison group. Moreover, joint hypermobility mediates the link between neurodivergence and symptoms of dysautonomia and pain.
Is being hypermobile good or bad
In most people, hypermobility doesn't cause any pain or medical issues. However, for some people, hypermobility causes joint pain, joint and ligament injuries, tiredness (fatigue), bowel issues and other symptoms. Joint hypermobility syndrome is most common in children and young people.Hypermobility can be associated with recurrent pains at the end of the day or at night in the knees, feet and/or ankles. It might affect the fingers and hands. Rarely mild joint swelling may come and go but does not tend to persist. Hypermobility often improves with age.This has led to the suggestion that routine screening for neuropsychiatric symptoms may be necessary for children with EDS or hEDS. However, it is important to remember that not all hypermobility is a sign of autism risk or a connective tissue disorder. Managing hypermobility and ADHD can take time and experimentation, but some strategies can help. For hypermobility, gentle exercise and physical therapy can help strengthen muscles and reduce pain. For ADHD, medication, treatment, and organizational strategies can all help manage symptoms.
Do hypermobile people look younger : Due to the collagen in the skin being extra stretchy, many EDS patients experience a lack of wrinkles as they age. This collagen may help EDS patients look younger and can also cause skin to feel extremely soft.
Are hypermobile people weaker : The connective tissues of hypermobile people are weaker compared with non-hypermobile individuals and therefore their muscle needs to be twice as strong to stabilise their joints and to be able to function normally, otherwise they would use twice as much energy on simple tasks, which will lead to fatigue and pain.
Does hypermobility ever go away
There's no cure for joint hypermobility syndrome. The main treatment is improving muscle strength and fitness so your joints are better protected. A GP may refer you to a physiotherapist, occupational therapist or podiatrist for specialist advice. You can also pay for these services privately. Patients with classical and hypermobility types of EDS may have a longer lifespan. Patients with these forms of EDS live healthy but somewhat restricted lives.What Is the Life Expectancy of Someone With Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Ehlers-Danlos syndrome typically progress slowly, and the prognosis depends upon the type of EDS and the severity of the condition. Patients with the classical and hypermobility forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have a normal life expectancy.
Can hypermobility be a good thing : For some people the extra flexibility may be a benefit. For example ballet dancers or gymnasts. But, some people with joint hypermobility can have symptoms like: pain and stiffness in the joints and muscles.
Antwort Is hypermobility linked to ADHD? Weitere Antworten – Is hypermobility linked to dyspraxia
DCD/Dyspraxia is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting motor function and organisation; continues into adulthood and associated with Joint Hypermobility Syndrome (JHS).Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (previously known as joint hypermobility syndrome) Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Marfan syndrome. Osteogenesis Imperfecta.The connective tissues of hypermobile people are weaker compared with non-hypermobile individuals and therefore their muscle needs to be twice as strong to stabilise their joints and to be able to function normally, otherwise they would use twice as much energy on simple tasks, which will lead to fatigue and pain.
Is hypermobility linked to autism : Many studies have shown a strong link between hypermobility and Autism, with up to 80% of Autistic individuals experiencing hypermobility. This connection is not fully understood, but researchers believe that there may be a genetic component involved.
How rare is hypermobility
The hypermobile and classical forms are most common; the hypermobile type may affect as many as 1 in 5,000 to 20,000 people, while the classical type probably occurs in 1 in 20,000 to 40,000 people.
Are people with hypermobility stronger : Independent sample t-tests showed that hypermobile males were significantly weaker compared to non-hypermobile males with respect to elbow extensor strength for both right (p = 0.02) and left (p = 0.03) extremities (Table 2, unadjusted mean strength).
Individuals who suffer from Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome are young-looking, with velvety skin, a small face, and a thin nose, making them look younger as if they have never aged. This is especially seen in the case of the vascular type/ vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.

In neurodivergent adults, there is a strong link between the expression of joint hypermobility, dysautonomia, and pain, more so than in the comparison group. Moreover, joint hypermobility mediates the link between neurodivergence and symptoms of dysautonomia and pain.
Is being hypermobile good or bad
In most people, hypermobility doesn't cause any pain or medical issues. However, for some people, hypermobility causes joint pain, joint and ligament injuries, tiredness (fatigue), bowel issues and other symptoms. Joint hypermobility syndrome is most common in children and young people.Hypermobility can be associated with recurrent pains at the end of the day or at night in the knees, feet and/or ankles. It might affect the fingers and hands. Rarely mild joint swelling may come and go but does not tend to persist. Hypermobility often improves with age.This has led to the suggestion that routine screening for neuropsychiatric symptoms may be necessary for children with EDS or hEDS. However, it is important to remember that not all hypermobility is a sign of autism risk or a connective tissue disorder.

Managing hypermobility and ADHD can take time and experimentation, but some strategies can help. For hypermobility, gentle exercise and physical therapy can help strengthen muscles and reduce pain. For ADHD, medication, treatment, and organizational strategies can all help manage symptoms.
Do hypermobile people look younger : Due to the collagen in the skin being extra stretchy, many EDS patients experience a lack of wrinkles as they age. This collagen may help EDS patients look younger and can also cause skin to feel extremely soft.
Are hypermobile people weaker : The connective tissues of hypermobile people are weaker compared with non-hypermobile individuals and therefore their muscle needs to be twice as strong to stabilise their joints and to be able to function normally, otherwise they would use twice as much energy on simple tasks, which will lead to fatigue and pain.
Does hypermobility ever go away
There's no cure for joint hypermobility syndrome. The main treatment is improving muscle strength and fitness so your joints are better protected. A GP may refer you to a physiotherapist, occupational therapist or podiatrist for specialist advice. You can also pay for these services privately.
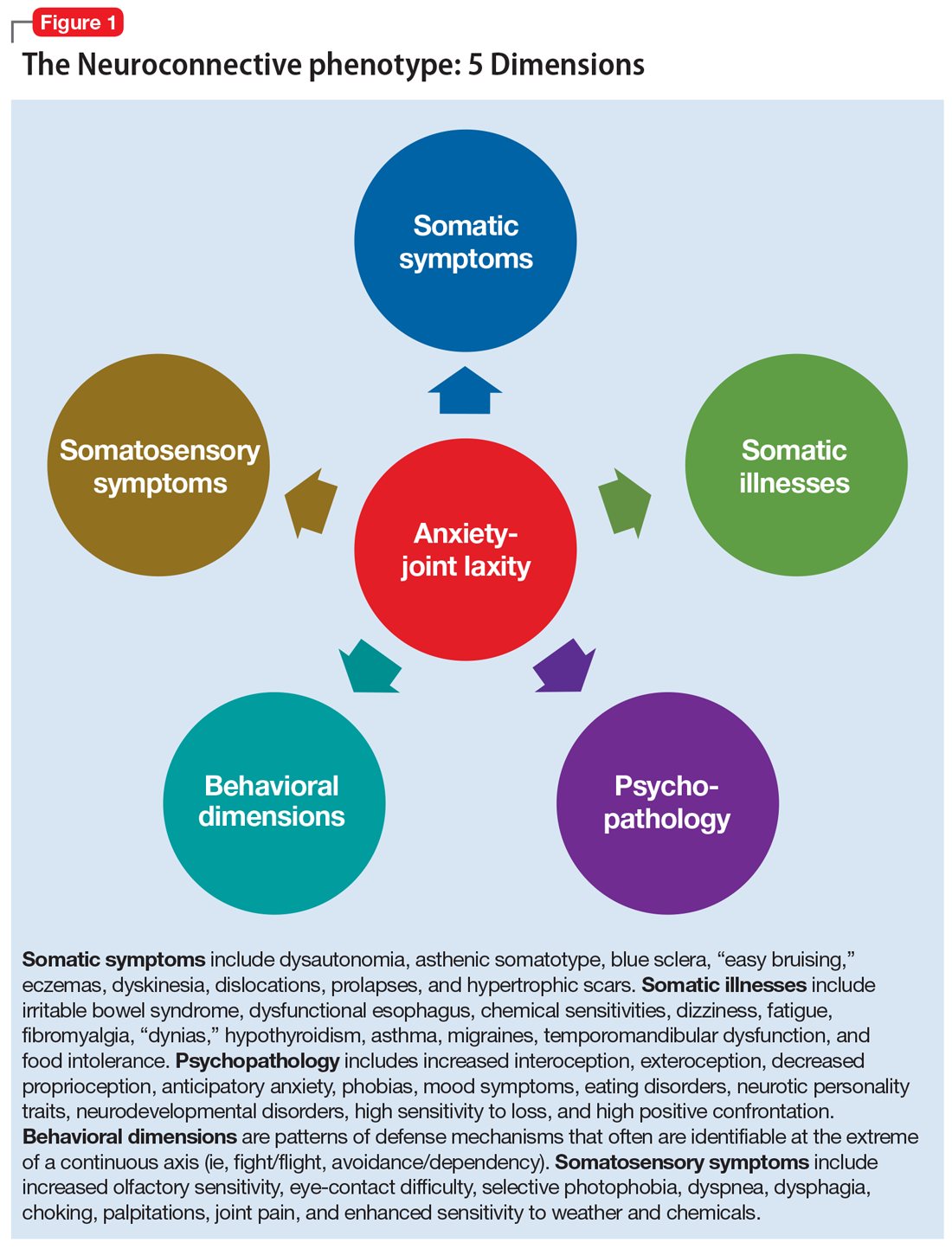
Patients with classical and hypermobility types of EDS may have a longer lifespan. Patients with these forms of EDS live healthy but somewhat restricted lives.What Is the Life Expectancy of Someone With Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Ehlers-Danlos syndrome typically progress slowly, and the prognosis depends upon the type of EDS and the severity of the condition. Patients with the classical and hypermobility forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have a normal life expectancy.
Can hypermobility be a good thing : For some people the extra flexibility may be a benefit. For example ballet dancers or gymnasts. But, some people with joint hypermobility can have symptoms like: pain and stiffness in the joints and muscles.