Many people are allergic to English ivy. Touching its sap alone can cause contact or allergic contact dermatitis, which is a very itchy—and uncomfortable—rash. Contact with English ivy can also cause swelling and shortness of breath.As with many common garden, house and wild plants, ivy isn't food and is mildly poisonous if eaten. If you were to eat some, you might get an upset stomach. It is toxic to cats, dogs and horses, but not birds or livestock. Children under five are most at risk from plant poisoning.Poison Ivy
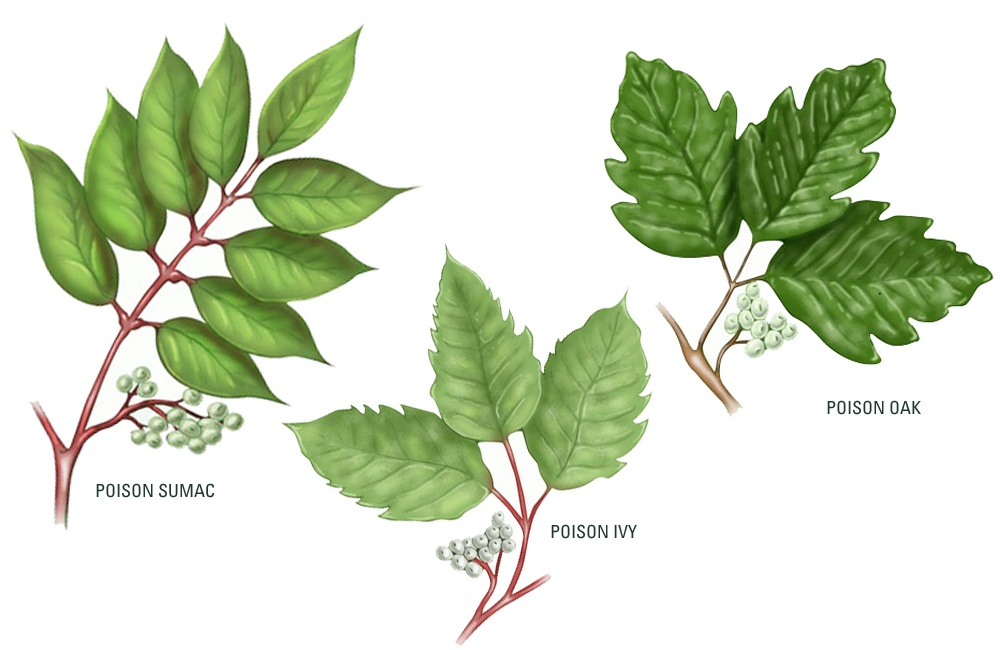
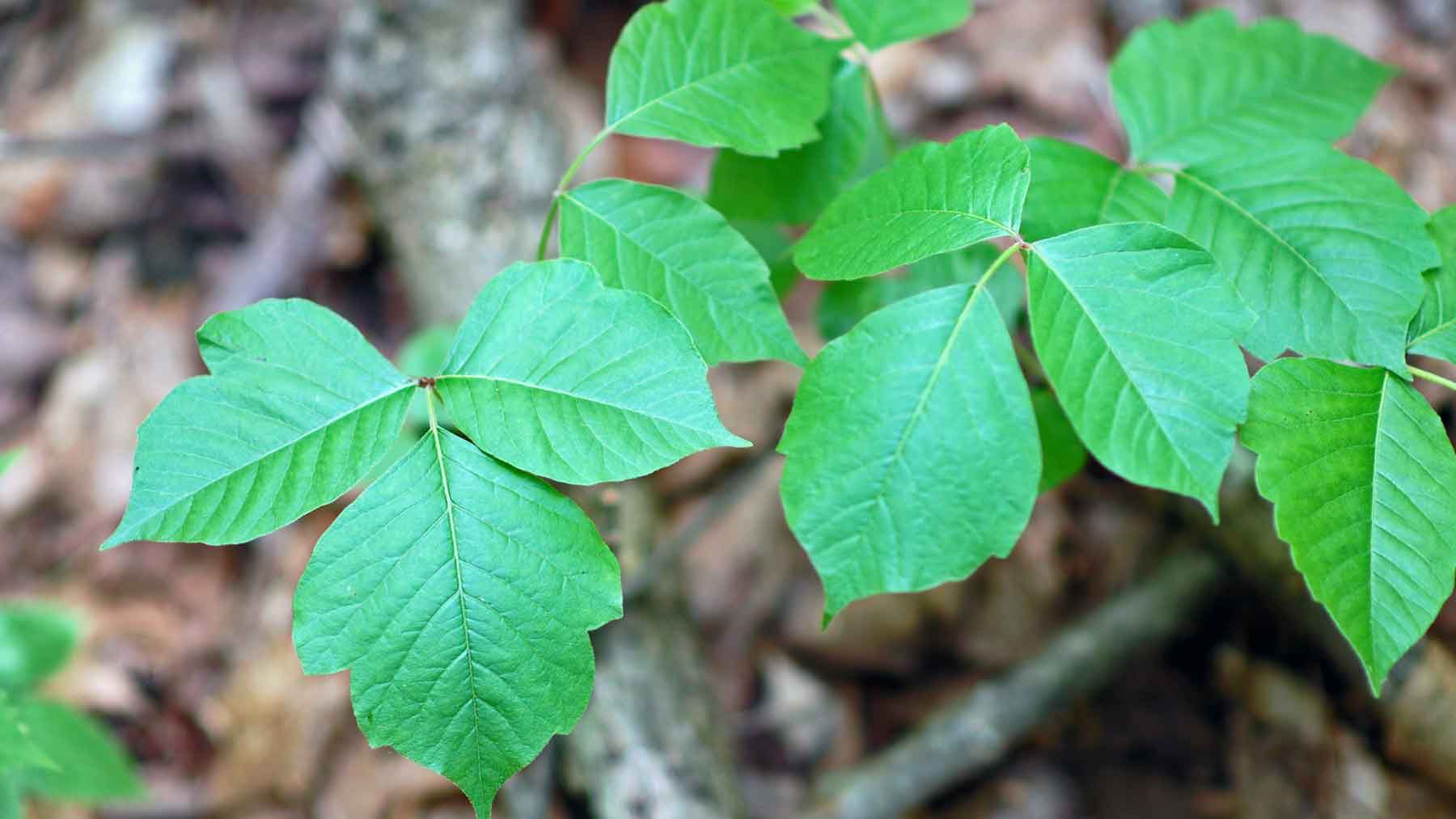
Eastern poison ivy is typically a hairy, ropelike vine with three shiny green leaves budding from one small stem.
Western poison ivy is typically a low shrub with three leaves that does not form a climbing vine.
It may have yellow or green flowers and white to green-yellow or amber berries.
Is ivy edible : The leaves and fruit of English ivy are toxic to humans and livestock and the sap can irritate skin. Despite the economic and environmental cost, nurseries continue to sell English ivy, and consumers continue to buy and plant it in their gardens.
Can touching ivy make you ill
You can get a poison ivy reaction from: Touching the plant. If you touch the leaves, stem, roots or berries of the plant, you may have a reaction. Touching contaminated objects.
What happens if you touch ivy : These plants produce an oily sap that contains urushiol (pronounced yer-OO-shee-all), which causes an irritating, itchy allergic reaction. When you touch the poisonous plant or an object that's been in contact with the plant's oil, you develop an itchy rash on that area of your skin.
However, ivy may not be the best houseplant choice if you have pets or children, as contact with the plant can cause a skin rash ( 14 , 15 ). First comes the itching, then a red rash, and then blisters. These symptoms of poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac can emerge any time from a few hours to several days after exposure to the plant oil found in the sap of these poisonous plants. The culprit: the urushiol oil.
Can eating poison ivy hurt you
Toxicity: (1-3)
Exposure to juice or sap from these plants or a puncture wound from the thorns may produce a skin rash or irritation. Ingestion may cause minor symptoms such as rash, vomiting or diarrhea. Ingestion in large amounts can cause serious effects.Wash your skin or your pet's fur.
Within 30 minutes after exposure to urushiol, use soap and water to gently wash off the harmful resin from your skin. Scrub under your fingernails too. Even washing after an hour or so can help reduce the severity of the rash.It is invasive, aggressive, and hazardous to neighboring plants. Invasive ivy doesn't offer benefits to the ecosystem but instead poses a threat. The evergreen plant grows year-round, choking out neighboring vegetation and providing nesting spots for pests. Is everyone allergic to poison ivy It's important to note that not everyone is allergic to poison ivy. While most people will experience an allergic reaction to urushiol, around 85 percent of all people, the remaining 15% will not.
Is everyone allergic to poison ivy : Up to 85% of Americans are allergic to poison ivy, leaving at least 15% resistant to any reaction. If you are allergic to poison ivy, you're more likely to be allergic to poison oak and poison sumac, because all three plants contain the same rash-triggering plant oil called urushiol (pronounced yoo-ROO-shee-all).
Is it OK to touch poison ivy : You can get a poison ivy reaction from: Touching the plant. If you touch the leaves, stem, roots or berries of the plant, you may have a reaction. Touching contaminated objects.
Why is ivy a problem
It is both a vigorous climber and also creates a dense groundcover, which if left unchecked can become dominant. With its vigorous growth, English Ivy competes with the native plants and can have a devastating impact upon the habitat of native fauna, as it reduces the variety of food sources that are available. Its dense cover can hide defects in the fabric of the building and hinder maintenance work. Ivy may also provide access for intruders and harbour pests such as mice. Where brickwork is sound, the main problem is to keep growth away from gutters and paint work.Not everyone is. Up to 85% of Americans are allergic to poison ivy, leaving at least 15% resistant to any reaction.
How common is it to get poison ivy : This is the most common allergic reaction in the U.S., and affects as many as 50 million Americans each year. Poison Ivy, sumac and oak grow everywhere in the United States except Hawaii, Alaska and some deserts in Nevada.
Antwort How poisonous is ivy? Weitere Antworten – Is ivy poisonous to touch
Many people are allergic to English ivy. Touching its sap alone can cause contact or allergic contact dermatitis, which is a very itchy—and uncomfortable—rash. Contact with English ivy can also cause swelling and shortness of breath.As with many common garden, house and wild plants, ivy isn't food and is mildly poisonous if eaten. If you were to eat some, you might get an upset stomach. It is toxic to cats, dogs and horses, but not birds or livestock. Children under five are most at risk from plant poisoning.Poison Ivy
Is ivy edible : The leaves and fruit of English ivy are toxic to humans and livestock and the sap can irritate skin. Despite the economic and environmental cost, nurseries continue to sell English ivy, and consumers continue to buy and plant it in their gardens.
Can touching ivy make you ill
You can get a poison ivy reaction from: Touching the plant. If you touch the leaves, stem, roots or berries of the plant, you may have a reaction. Touching contaminated objects.
What happens if you touch ivy : These plants produce an oily sap that contains urushiol (pronounced yer-OO-shee-all), which causes an irritating, itchy allergic reaction. When you touch the poisonous plant or an object that's been in contact with the plant's oil, you develop an itchy rash on that area of your skin.
However, ivy may not be the best houseplant choice if you have pets or children, as contact with the plant can cause a skin rash ( 14 , 15 ).

First comes the itching, then a red rash, and then blisters. These symptoms of poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac can emerge any time from a few hours to several days after exposure to the plant oil found in the sap of these poisonous plants. The culprit: the urushiol oil.
Can eating poison ivy hurt you
Toxicity: (1-3)
Exposure to juice or sap from these plants or a puncture wound from the thorns may produce a skin rash or irritation. Ingestion may cause minor symptoms such as rash, vomiting or diarrhea. Ingestion in large amounts can cause serious effects.Wash your skin or your pet's fur.
Within 30 minutes after exposure to urushiol, use soap and water to gently wash off the harmful resin from your skin. Scrub under your fingernails too. Even washing after an hour or so can help reduce the severity of the rash.It is invasive, aggressive, and hazardous to neighboring plants. Invasive ivy doesn't offer benefits to the ecosystem but instead poses a threat. The evergreen plant grows year-round, choking out neighboring vegetation and providing nesting spots for pests.
Is everyone allergic to poison ivy It's important to note that not everyone is allergic to poison ivy. While most people will experience an allergic reaction to urushiol, around 85 percent of all people, the remaining 15% will not.
Is everyone allergic to poison ivy : Up to 85% of Americans are allergic to poison ivy, leaving at least 15% resistant to any reaction. If you are allergic to poison ivy, you're more likely to be allergic to poison oak and poison sumac, because all three plants contain the same rash-triggering plant oil called urushiol (pronounced yoo-ROO-shee-all).
Is it OK to touch poison ivy : You can get a poison ivy reaction from: Touching the plant. If you touch the leaves, stem, roots or berries of the plant, you may have a reaction. Touching contaminated objects.
Why is ivy a problem
It is both a vigorous climber and also creates a dense groundcover, which if left unchecked can become dominant. With its vigorous growth, English Ivy competes with the native plants and can have a devastating impact upon the habitat of native fauna, as it reduces the variety of food sources that are available.

Its dense cover can hide defects in the fabric of the building and hinder maintenance work. Ivy may also provide access for intruders and harbour pests such as mice. Where brickwork is sound, the main problem is to keep growth away from gutters and paint work.Not everyone is. Up to 85% of Americans are allergic to poison ivy, leaving at least 15% resistant to any reaction.
How common is it to get poison ivy : This is the most common allergic reaction in the U.S., and affects as many as 50 million Americans each year. Poison Ivy, sumac and oak grow everywhere in the United States except Hawaii, Alaska and some deserts in Nevada.