quarterly
Index rebalancing is when the index adjusts the share weights and constituent companies included in the S&P 500. The index is rebalanced quarterly, in March, June, September, and December, so that it more accurately reflects the large-cap U.S. equities market.quarterly
Some indexes, like the S&P 500, are rebalanced quarterly, while others are adjusted semiannually or annually. 4 Specialized or thematic indexes might have unique rebalancing schedules. A rebalancing may also occur between scheduled evaluations because of rapid changes in the market.quarterly
The S&P 500® undergoes quarterly updates—more colloquially known as rebalances—after the close of the third Friday in March, June, September and December. These updates typically affect the S&P 500's composition and have turnover implications for investors tracking the index.
Does the S&P 500 fluctuate : The S&P 500 is continuously float-adjusted. The index recalculates when new shares are issued or when a company takes shares off the market through a buyback initiative.
What is the S&P 500 last 10 years return
Stock Market Average Yearly Return for the Last 10 Years
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 12.58% over the last 10 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 10-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 9.52%.
Does the S&P 500 change every year : Just as the U.S. economy evolves, so too does the S&P 500. Typically, the S&P 500 makes roughly 20 changes in a year.
Rebalancings occur after the market close on the third Friday of the quarter ending month. At each quarterly rebalancing, companies are equally-weighted using closing prices as of the second Friday of the quarter ending month as the reference price.
Automatically maintain your asset mix
You never have to rebalance a balanced fund—it's done for you automatically. Some funds maintain a set asset mix, while others grow more conservative over time.
How many corrections has the S&P 500 had
Since the 1950s, the S&P 500 has experienced around 38 market corrections. A market correction is considered to be a decline of 10% or more from the recent closing high. That means that historically speaking, the S&P 500 has experienced a correction every 1.84 years.According to his math, since 1949 S&P 500 investments have doubled ten times, or an average of about seven years each time. In some cases, like 1952 to 1955 or 1995 to 1998, the value of the investment doubled in only three years.One important thing for all investors to learn is that timing the market is impossible. And quite frankly, it's unimportant if you're investing in a high-quality S&P 500 index fund for the long term. Even if you buy at a market peak, your long-term returns should likely be excellent.
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 9.88% over the last 20 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 20-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 7.13%.
What is the average return of the S&P 500 in 30 years : Looking at the S&P 500 for the years 1993 to mid-2023, the average stock market return for the last 30 years is 9.90% (7.22% when adjusted for inflation). Some of this success can be attributed to the dot-com boom in the late 1990s (before the bust), which resulted in high return rates for five consecutive years.
How much will the S&P 500 grow in 10 years : Returns in the S&P 500 over the coming decade are more likely to be in the 3%-6% range, as multiples and margins are unlikely to expand, leaving sales growth, buybacks, and dividends as the main drivers of appreciation.
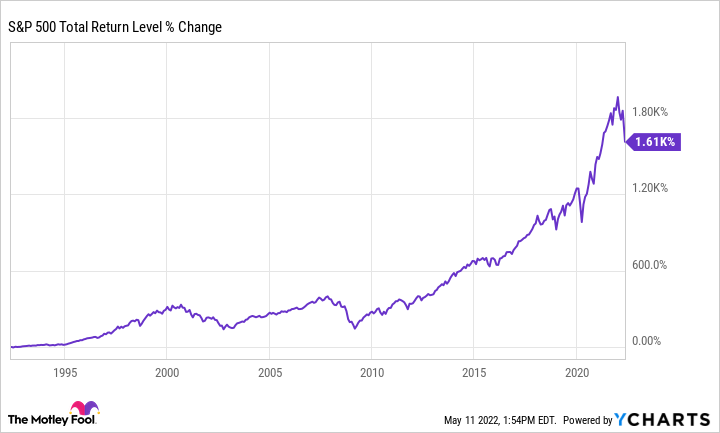
What is the 10 year return on the S&P 500
Basic Info. S&P 500 10 Year Return is at 167.3%, compared to 180.6% last month and 161.0% last year. This is higher than the long term average of 114.6%.
quarterly
As the stock prices move, the weightings in the index will change. A more frequent rebalancing will result in higher index turnover; and less frequent will result in significant deviations from the equal weights. The S&P 500 EWI is rebalanced quarterly to coincide with the quarterly share adjustments of the S&P 500.The two most common strategies for rebalancing are: Periodic rebalancing: You rebalance at fixed intervals, for instance every 6 months, or every year… Threshold-based rebalancing: You rebalance when one of the ETFs in your portfolio goes out of balance by a certain percentage, for instance 5%.
What is the 5% portfolio rule : This is a rule that aims to aid diversification in an investment portfolio. It states that one should not hold more than 5% of the total value of the portfolio in a single security.
Antwort How often does the S&P 500 correct? Weitere Antworten – How often is the S&P 500 reviewed and updated
quarterly
Index rebalancing is when the index adjusts the share weights and constituent companies included in the S&P 500. The index is rebalanced quarterly, in March, June, September, and December, so that it more accurately reflects the large-cap U.S. equities market.quarterly
Some indexes, like the S&P 500, are rebalanced quarterly, while others are adjusted semiannually or annually. 4 Specialized or thematic indexes might have unique rebalancing schedules. A rebalancing may also occur between scheduled evaluations because of rapid changes in the market.quarterly
The S&P 500® undergoes quarterly updates—more colloquially known as rebalances—after the close of the third Friday in March, June, September and December. These updates typically affect the S&P 500's composition and have turnover implications for investors tracking the index.
Does the S&P 500 fluctuate : The S&P 500 is continuously float-adjusted. The index recalculates when new shares are issued or when a company takes shares off the market through a buyback initiative.
What is the S&P 500 last 10 years return
Stock Market Average Yearly Return for the Last 10 Years
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 12.58% over the last 10 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 10-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 9.52%.
Does the S&P 500 change every year : Just as the U.S. economy evolves, so too does the S&P 500. Typically, the S&P 500 makes roughly 20 changes in a year.
Rebalancings occur after the market close on the third Friday of the quarter ending month. At each quarterly rebalancing, companies are equally-weighted using closing prices as of the second Friday of the quarter ending month as the reference price.

Automatically maintain your asset mix
You never have to rebalance a balanced fund—it's done for you automatically. Some funds maintain a set asset mix, while others grow more conservative over time.
How many corrections has the S&P 500 had
Since the 1950s, the S&P 500 has experienced around 38 market corrections. A market correction is considered to be a decline of 10% or more from the recent closing high. That means that historically speaking, the S&P 500 has experienced a correction every 1.84 years.According to his math, since 1949 S&P 500 investments have doubled ten times, or an average of about seven years each time. In some cases, like 1952 to 1955 or 1995 to 1998, the value of the investment doubled in only three years.One important thing for all investors to learn is that timing the market is impossible. And quite frankly, it's unimportant if you're investing in a high-quality S&P 500 index fund for the long term. Even if you buy at a market peak, your long-term returns should likely be excellent.
The historical average yearly return of the S&P 500 is 9.88% over the last 20 years, as of the end of April 2024. This assumes dividends are reinvested. Adjusted for inflation, the 20-year average stock market return (including dividends) is 7.13%.
What is the average return of the S&P 500 in 30 years : Looking at the S&P 500 for the years 1993 to mid-2023, the average stock market return for the last 30 years is 9.90% (7.22% when adjusted for inflation). Some of this success can be attributed to the dot-com boom in the late 1990s (before the bust), which resulted in high return rates for five consecutive years.
How much will the S&P 500 grow in 10 years : Returns in the S&P 500 over the coming decade are more likely to be in the 3%-6% range, as multiples and margins are unlikely to expand, leaving sales growth, buybacks, and dividends as the main drivers of appreciation.
What is the 10 year return on the S&P 500
Basic Info. S&P 500 10 Year Return is at 167.3%, compared to 180.6% last month and 161.0% last year. This is higher than the long term average of 114.6%.

quarterly
As the stock prices move, the weightings in the index will change. A more frequent rebalancing will result in higher index turnover; and less frequent will result in significant deviations from the equal weights. The S&P 500 EWI is rebalanced quarterly to coincide with the quarterly share adjustments of the S&P 500.The two most common strategies for rebalancing are: Periodic rebalancing: You rebalance at fixed intervals, for instance every 6 months, or every year… Threshold-based rebalancing: You rebalance when one of the ETFs in your portfolio goes out of balance by a certain percentage, for instance 5%.
What is the 5% portfolio rule : This is a rule that aims to aid diversification in an investment portfolio. It states that one should not hold more than 5% of the total value of the portfolio in a single security.