The value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average is calculated by determining the average value of the stock prices of the 30 listed companies. However, calculating that average value is not as simple as totaling the 30 stock prices and dividing by 30.The Dow is price-weighted. This means that price changes in the highest-priced stocks have greater impact on the index level than price changes in the lower-priced stocks.The index gives equal exposure to all Dow 30 constituents. The same weight is given to each stock in the index, allowing for the performance of lower priced companies to contribute as much as the higher priced companies within the index.
How is the S&P 500 index weighted : The S&P 500 index is weighted by market capitalization (share price times number of shares outstanding). This means that a company's valuation determines how much influence it has over the index's performance. Each listed company doesn't simply represent 1/500th of the index.
How is the S&P 500 value calculated
The S&P 500's value is calculated based on the market cap of each company, which is equal to the share price of the company multiplied by the total number of shares outstanding. The share count is adjusted to consider only the shares available to be traded in the open markets.
How does the Dow Jones index work : To calculate the DJIA, the current prices of the 30 stocks that make up the index are added and then divided by the Dow divisor, which is constantly modified.
As the Nasdaq-100® is a modified market capitalization-weighted index, companies are assigned different weights based on their market value or size. Bigger companies carry more weight and thus have a bigger impact on the overall performance of the index. The NYSE Composite Index uses market capitalization to calculate the weights of the index constituents. Market capitalization works by multiplying the outstanding number of shares that a company owns by the market price per share.
Is Nasdaq 100 market weighted
As the Nasdaq-100® is a modified market capitalization-weighted index, companies are assigned different weights based on their market value or size. Bigger companies carry more weight and thus have a bigger impact on the overall performance of the index.While both the DJIA and S&P 500 are used by investors to determine the general trend of the U.S. stock market, the S&P 500 is more encompassing, as it is based on a larger sample of total U.S. stocks.Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general. To determine the weight of each stock in a value-weighted index, the price of the stock is multiplied by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if Stock A has five million outstanding shares and is trading at $15, then its weight in the index is $75 million.
What is the difference between the Dow Jones and the S&P 500 : Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general.
What does it mean when the Dow drops 1,000 points : When the Dow gains or loses a point, it reflects changes in the prices of its component stocks. The index is price-weighted, meaning it moves in line with the price changes of its components on a point basis, adjusted by a divisor.
How is Dow Jones different from S&P
The Dow tracks 30 large U.S. companies but has limited representation. The Nasdaq indexes, associated with the Nasdaq exchange, focus more heavily on tech and other stocks. The S&P 500, with 500 large U.S. companies, offers a more comprehensive market view, weighted by market capitalization. The 30 stocks which make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average are: 3M, American Express, Amgen, Apple, Boeing, Caterpillar, Chevron, Cisco Systems, Coca-Cola, Disney, Dow, Goldman Sachs, Home Depot, Honeywell, IBM, Intel, Johnson & Johnson, JP Morgan Chase, McDonald's, Merck, Microsoft, Nike, Procter & Gamble, …The Nasdaq 100 Index is constructed with a modified capitalization method, which uses the individual weights of included items according to their market capitalization. 2 Weighting limits the influence of the largest companies and balances the index among all members.
How does Nasdaq weighting work : The stocks' weights in the index are based on their market capitalizations, with certain rules capping the influence of the largest components. It is limited to companies from a single exchange, and it does not have any financial companies.
Antwort How is Dow Jones weighted? Weitere Antworten – How is the Dow Jones calculated
The value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average is calculated by determining the average value of the stock prices of the 30 listed companies. However, calculating that average value is not as simple as totaling the 30 stock prices and dividing by 30.The Dow is price-weighted. This means that price changes in the highest-priced stocks have greater impact on the index level than price changes in the lower-priced stocks.The index gives equal exposure to all Dow 30 constituents. The same weight is given to each stock in the index, allowing for the performance of lower priced companies to contribute as much as the higher priced companies within the index.
How is the S&P 500 index weighted : The S&P 500 index is weighted by market capitalization (share price times number of shares outstanding). This means that a company's valuation determines how much influence it has over the index's performance. Each listed company doesn't simply represent 1/500th of the index.
How is the S&P 500 value calculated
The S&P 500's value is calculated based on the market cap of each company, which is equal to the share price of the company multiplied by the total number of shares outstanding. The share count is adjusted to consider only the shares available to be traded in the open markets.
How does the Dow Jones index work : To calculate the DJIA, the current prices of the 30 stocks that make up the index are added and then divided by the Dow divisor, which is constantly modified.
As the Nasdaq-100® is a modified market capitalization-weighted index, companies are assigned different weights based on their market value or size. Bigger companies carry more weight and thus have a bigger impact on the overall performance of the index.

The NYSE Composite Index uses market capitalization to calculate the weights of the index constituents. Market capitalization works by multiplying the outstanding number of shares that a company owns by the market price per share.
Is Nasdaq 100 market weighted
As the Nasdaq-100® is a modified market capitalization-weighted index, companies are assigned different weights based on their market value or size. Bigger companies carry more weight and thus have a bigger impact on the overall performance of the index.While both the DJIA and S&P 500 are used by investors to determine the general trend of the U.S. stock market, the S&P 500 is more encompassing, as it is based on a larger sample of total U.S. stocks.Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general.
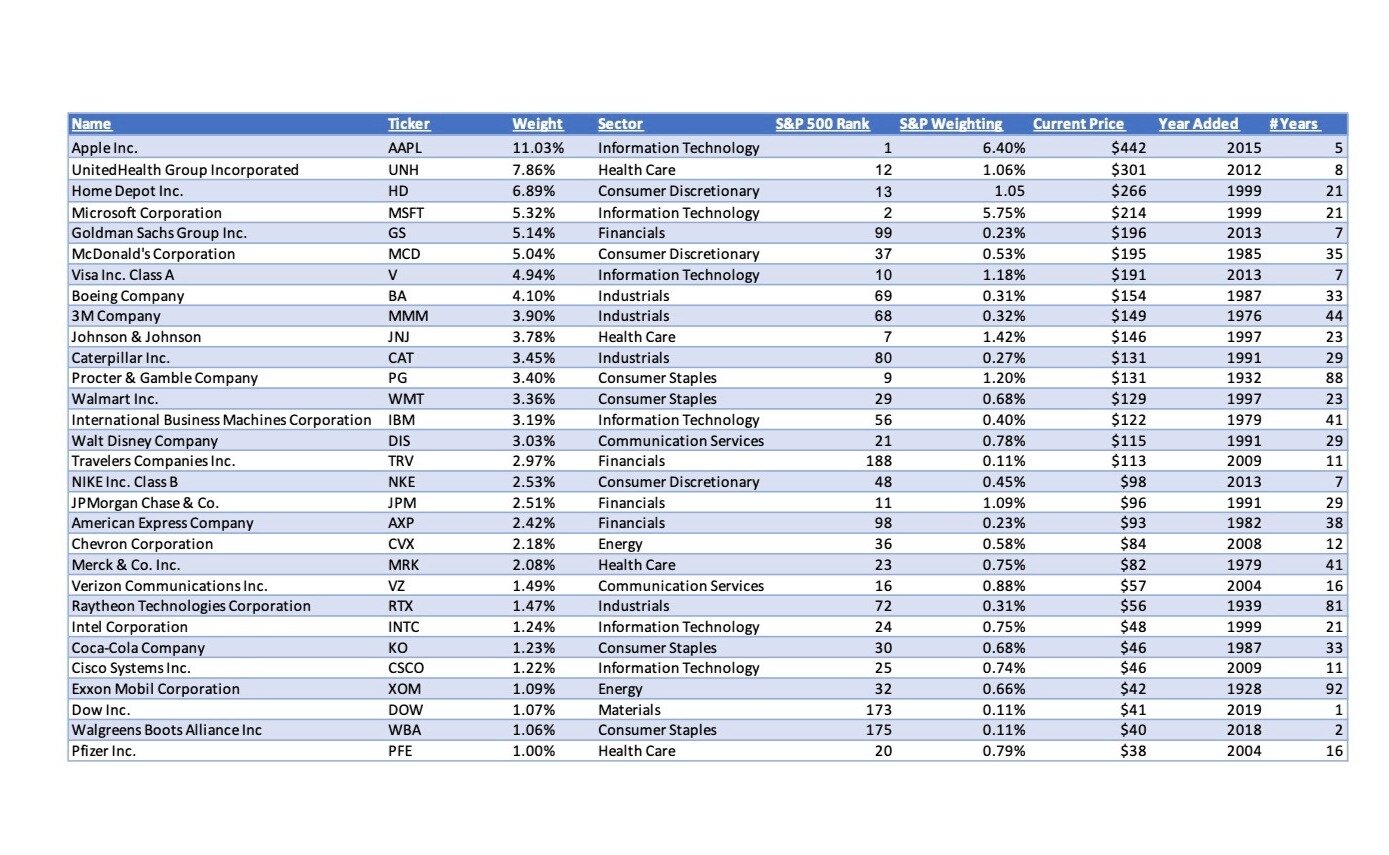
To determine the weight of each stock in a value-weighted index, the price of the stock is multiplied by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if Stock A has five million outstanding shares and is trading at $15, then its weight in the index is $75 million.
What is the difference between the Dow Jones and the S&P 500 : Key Takeaways
The DJIA tracks the stock prices of 30 of the biggest American companies. The S&P 500 tracks 500 large-cap American stocks. Both offer a big-picture view of the state of the stock markets in general.
What does it mean when the Dow drops 1,000 points : When the Dow gains or loses a point, it reflects changes in the prices of its component stocks. The index is price-weighted, meaning it moves in line with the price changes of its components on a point basis, adjusted by a divisor.
How is Dow Jones different from S&P
The Dow tracks 30 large U.S. companies but has limited representation. The Nasdaq indexes, associated with the Nasdaq exchange, focus more heavily on tech and other stocks. The S&P 500, with 500 large U.S. companies, offers a more comprehensive market view, weighted by market capitalization.

The 30 stocks which make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average are: 3M, American Express, Amgen, Apple, Boeing, Caterpillar, Chevron, Cisco Systems, Coca-Cola, Disney, Dow, Goldman Sachs, Home Depot, Honeywell, IBM, Intel, Johnson & Johnson, JP Morgan Chase, McDonald's, Merck, Microsoft, Nike, Procter & Gamble, …The Nasdaq 100 Index is constructed with a modified capitalization method, which uses the individual weights of included items according to their market capitalization. 2 Weighting limits the influence of the largest companies and balances the index among all members.
How does Nasdaq weighting work : The stocks' weights in the index are based on their market capitalizations, with certain rules capping the influence of the largest components. It is limited to companies from a single exchange, and it does not have any financial companies.