The EV and EVSE communicate with each other over Power Line Communication (PLC). During the communication, EV and EVSE exchange various messages over IPV6 UDP/TCP Protocols. These messages have been described in ISO 15118 Part 2.Luckily, your EV should be supplied with a cable that has the plug it requires, and at the infrastructure (charger) end, the cables are all compatible. Rapid chargers use what are known as tethered cables – i.e. they are permanently connected to, and cannot be removed from, the charging unit.Standardised Communication Protocols for EV charging
ISO/IEC 15118 facilitates communication between the EV and the EVSE.
CHAdeMO is a protocol originally developed in Japan that accompanies its specific CHAdeMO plug, allowing physical bidirectional DC charging.
How do EV charging networks work : How Does EV Charging Work At its most basic, an EV charger pulls an electrical current from either a 240v outlet or the grid it's hardwired to and delivers that electricity to the vehicle, just like any other appliance or device you charge by plugging into the wall.
What is communication in EV
The IEC 61851-24[2] is the standard for the digital communication between a DC EV Charging station and the EV, for the control of DC charging. Based on the physical layer, EVSE communicates using CAN bus or through Power Line Communication (PLC).
Does EV charger need network connection : WiFi EV chargers require a stable internet connection at its installation location whereas a mobile data charger can be installed pretty much anywhere there's mobile data.
EV Charging Connector Types: What You Need to Know
Four types of plugs exist, two for alternating current (AC) which allow charging up to 43 kW and two for direct current (DC) which allow fast charging up to 350 kW. The answer in its shortest form is yes – due to smart charging regulations, home EV chargers do need Wi-Fi or at least some form of connectivity (4G) between your EV charger, your EV and the electricity grid in order to access smart features.
Do EV charging stations need internet
WiFi EV chargers require a stable internet connection at its installation location whereas a mobile data charger can be installed pretty much anywhere there's mobile data. You might need to pay a small monthly fee in future with mobile data EV chargers however.Most EVs rely on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol for communication between vehicle components and external systems. The Modbus and Local Interconnect Network (LIN) protocols are used by some auxiliary vehicle components that do not require real-time data communication.There are two main types of signals used in electronics: analog and digital signals. Many chargers provide software that allows for the collection and reporting of charging session data. If unavailable, data may be recorded by the charging vehicle's onboard systems.
Why do EV chargers need to be smart : This can reduce the need for expensive grid updates and improve the overall efficiency of the electricity system. Optimised range performance – smart chargers can help to optimise the range and performance of your EV by keeping the battery charged to the manufacturer's recommended level.
Why do EV chargers have 2 cables : And also Drive redundancy. So if one cable goes down the second cable is there to be used.
Are public EV chargers tethered
Your charging cable will enable you to charge from untethered home chargers, workplace chargers and public charging points, the majority of which require you to bring your own cable*. Rapid chargers (and a few public AC chargers) have “tethered” cables meaning you do not need to use an additional cable. EVEC EV Charger | 7.4kW 32 Amp | Socketed | Complies Smart Charge Regs.What are the different methods of communication
Verbal communication.
Non-verbal communication.
Written communication.
Listening.
Visual communication.
What is the EV pilot communication : The Communication Pilot is a wire connection between EV and EV Charger. It is primarily a saftey measure for the charging process. Without the Communciation Pilot no EV will start charging. The Communication Pilot is a 1 kHz signal with a ± 12 Volt DC square wave generated by the EV Charger.
Antwort How does an EV communicate with a charger? Weitere Antworten – How does EV communicate with charging station
The EV and EVSE communicate with each other over Power Line Communication (PLC). During the communication, EV and EVSE exchange various messages over IPV6 UDP/TCP Protocols. These messages have been described in ISO 15118 Part 2.Luckily, your EV should be supplied with a cable that has the plug it requires, and at the infrastructure (charger) end, the cables are all compatible. Rapid chargers use what are known as tethered cables – i.e. they are permanently connected to, and cannot be removed from, the charging unit.Standardised Communication Protocols for EV charging
How do EV charging networks work : How Does EV Charging Work At its most basic, an EV charger pulls an electrical current from either a 240v outlet or the grid it's hardwired to and delivers that electricity to the vehicle, just like any other appliance or device you charge by plugging into the wall.
What is communication in EV
The IEC 61851-24[2] is the standard for the digital communication between a DC EV Charging station and the EV, for the control of DC charging. Based on the physical layer, EVSE communicates using CAN bus or through Power Line Communication (PLC).
Does EV charger need network connection : WiFi EV chargers require a stable internet connection at its installation location whereas a mobile data charger can be installed pretty much anywhere there's mobile data.
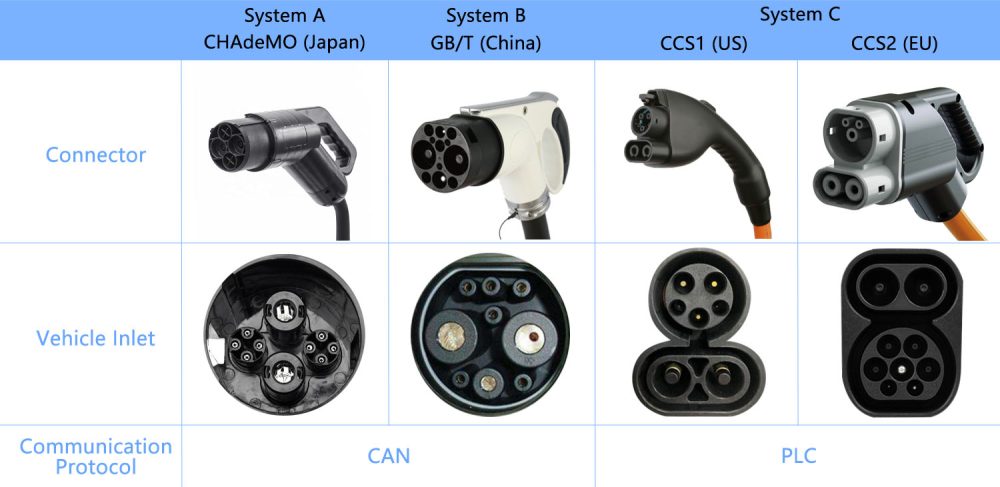
EV Charging Connector Types: What You Need to Know
Four types of plugs exist, two for alternating current (AC) which allow charging up to 43 kW and two for direct current (DC) which allow fast charging up to 350 kW.
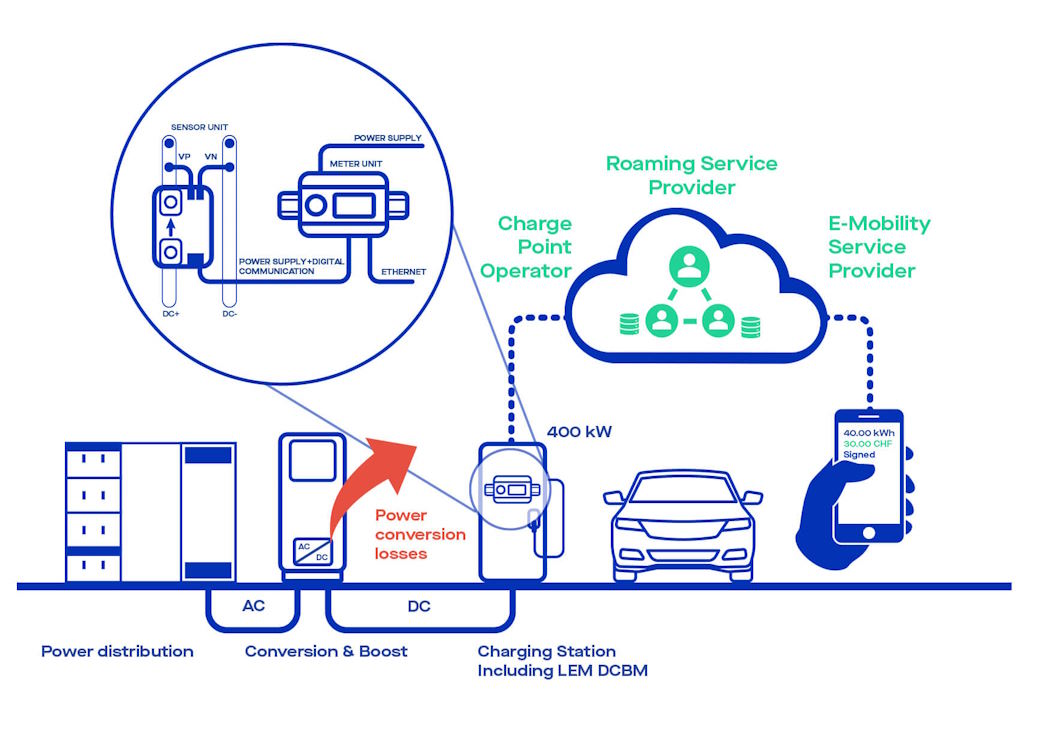
The answer in its shortest form is yes – due to smart charging regulations, home EV chargers do need Wi-Fi or at least some form of connectivity (4G) between your EV charger, your EV and the electricity grid in order to access smart features.
Do EV charging stations need internet
WiFi EV chargers require a stable internet connection at its installation location whereas a mobile data charger can be installed pretty much anywhere there's mobile data. You might need to pay a small monthly fee in future with mobile data EV chargers however.Most EVs rely on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol for communication between vehicle components and external systems. The Modbus and Local Interconnect Network (LIN) protocols are used by some auxiliary vehicle components that do not require real-time data communication.There are two main types of signals used in electronics: analog and digital signals.

Many chargers provide software that allows for the collection and reporting of charging session data. If unavailable, data may be recorded by the charging vehicle's onboard systems.
Why do EV chargers need to be smart : This can reduce the need for expensive grid updates and improve the overall efficiency of the electricity system. Optimised range performance – smart chargers can help to optimise the range and performance of your EV by keeping the battery charged to the manufacturer's recommended level.
Why do EV chargers have 2 cables : And also Drive redundancy. So if one cable goes down the second cable is there to be used.
Are public EV chargers tethered
Your charging cable will enable you to charge from untethered home chargers, workplace chargers and public charging points, the majority of which require you to bring your own cable*. Rapid chargers (and a few public AC chargers) have “tethered” cables meaning you do not need to use an additional cable.

EVEC EV Charger | 7.4kW 32 Amp | Socketed | Complies Smart Charge Regs.What are the different methods of communication
What is the EV pilot communication : The Communication Pilot is a wire connection between EV and EV Charger. It is primarily a saftey measure for the charging process. Without the Communciation Pilot no EV will start charging. The Communication Pilot is a 1 kHz signal with a ± 12 Volt DC square wave generated by the EV Charger.