Q. How can I tell if a graph is misleading or distorted
The title is vague.
Neither axis is labeled.
The distance between data points on the Y-axis is not given.
The Y-axis does not show any scale.
What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.Show the data clearly
Check the data points plotted can be detected, and are not covered up or obscured. Don't assume the viewer is a mind-reader … label titles and axes clearly and accurately. Maintain constant measurement scales and avoid distortions.
How do you check if two graphs are the same : But how do you tell if two graphs are isomorphic Well the low brow way is to move the vertices of one onto the vertices of another in such a way that the edges of both overlap the edges of the other. If this is possible, then the two graphs are said to be the same, isomorphic. If you can't then they're not.
How can a graph be wrong
This is one of the most common ways graphs misrepresent. Data by distorting the scale zooming in on a small portion of the y-axis exaggerate a barely detectable. Difference between the things being
How can a chart be misleading : There are numerous ways in which a misleading graph may be constructed.
Excessive usage. The use of graphs where they are not needed can lead to unnecessary confusion/interpretation.
Biased labeling.
Pie chart.
Improper scaling.
Truncated graph.
Axis changes.
No scale.
Improper intervals or units.
Graphs are often made misleading for advertising or other purposes, or even just by accident, by: • Leaving gaps/changing the scale in vertical axes • Uneven shading/colours • Unfair emphasis on some sections • Distorting areas in histograms (bar widths should always be equal – if you have different widths then the bar … One possible method for comparing graphs is to look at specific “features” of the graph, such as the degree distribution, betweenness centrality distribution, diameter, number of triangles, number of k-cliques, etc.
How to tell if a graph is equivalent
And what are the edges. So in number one we can see that vertices a goes to B vertices B after it goes also to C and B goes to D.
1 Choosing the wrong type of display. One of the first decisions you have to make when creating a graphical display is what type of display to use.
2 Using too many elements.
3 Misusing scales and axes.
4 Ignoring design principles.
5 Not checking for errors.
6 Not testing for clarity.
7 Here's what else to consider.
A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data. Misleading statistics can come from:
Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample.
Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors.
Neglecting the baseline: ignoring an important baseline for comparison.
How to explain graph results : Here are steps you can use to explain a graph effectively:
Introduce the graph. Introduce the graph to your audience by presenting the title and explaining the topic of the graph.
Identify variables. Graphs such as bar and line graphs have a y- and x-axis.
Highlight key information.
Share conclusions.
How do you analyze different graphs : Here are some steps to help you read a graph:
Determine the type of graph.
Read the title or legend.
Examine any other text.
Identify the variables on the axes and what they represent.
Observe the x-axis and y-axis.
Determine what each number on the graph means.
Identify patterns in the data.
How do you know if a graph is regular
A graph is regular if every vertex has the same degree. We may call the graph k-‐regular if every vertex has degree k. A path is a route that you travel along edges and through vertices in a graph. All of the vertices and edges in a path are connected to one another. If two graphs have the same edge structure then we will declare them to be equivalent even though the vertices might be distinct or differ by a rearrangement.Some common features of graphs that may lead to incorrect interpretations are:
Omitting the baseline.
Showing an inappropriate or irregular scale.
Scale or labels not clearly given.
Leaving data out.
Using pictures or three-dimensional graphics that distort differences.
Using the wrong graph for a given data type.
How can you identify misleading statistics : Seven signs of potentially misleading statistics.
Everything is up statistic. Prefers numbers over rates.
Best foot statistic. Using mean vs.
Half-truth statistic. Special subgroup highlighted.
Antwort How do you know if a graph is wrong? Weitere Antworten – How can you tell if a graph is misleading
Q. How can I tell if a graph is misleading or distorted
What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.Show the data clearly
Check the data points plotted can be detected, and are not covered up or obscured. Don't assume the viewer is a mind-reader … label titles and axes clearly and accurately. Maintain constant measurement scales and avoid distortions.

How do you check if two graphs are the same : But how do you tell if two graphs are isomorphic Well the low brow way is to move the vertices of one onto the vertices of another in such a way that the edges of both overlap the edges of the other. If this is possible, then the two graphs are said to be the same, isomorphic. If you can't then they're not.
How can a graph be wrong
This is one of the most common ways graphs misrepresent. Data by distorting the scale zooming in on a small portion of the y-axis exaggerate a barely detectable. Difference between the things being
How can a chart be misleading : There are numerous ways in which a misleading graph may be constructed.
Graphs are often made misleading for advertising or other purposes, or even just by accident, by: • Leaving gaps/changing the scale in vertical axes • Uneven shading/colours • Unfair emphasis on some sections • Distorting areas in histograms (bar widths should always be equal – if you have different widths then the bar …
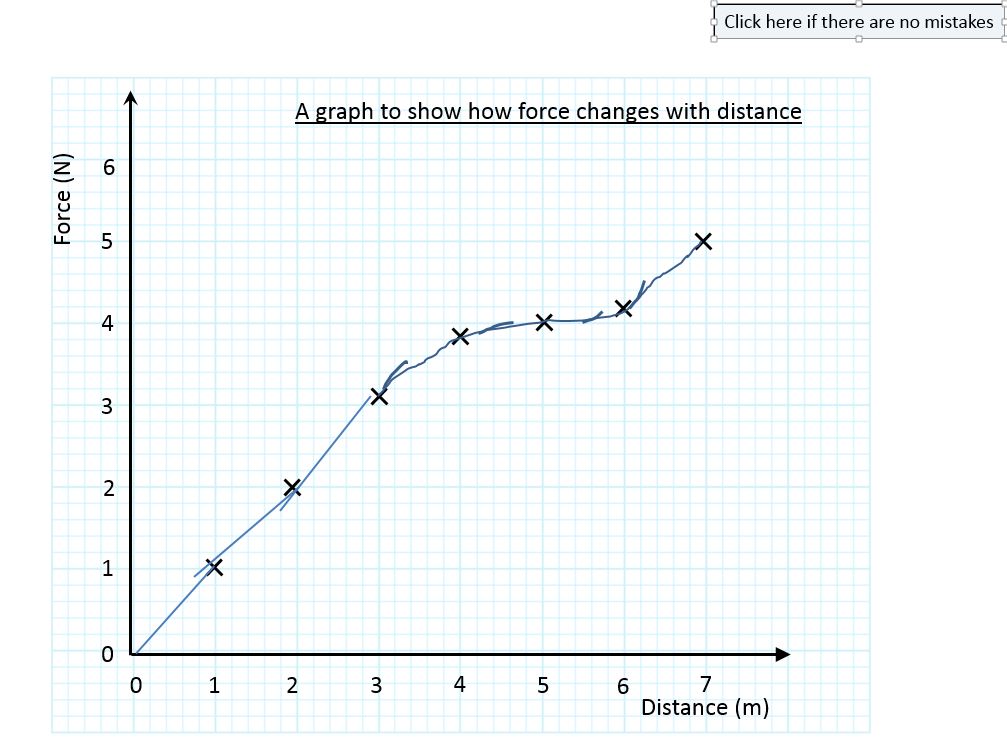
One possible method for comparing graphs is to look at specific “features” of the graph, such as the degree distribution, betweenness centrality distribution, diameter, number of triangles, number of k-cliques, etc.
How to tell if a graph is equivalent
And what are the edges. So in number one we can see that vertices a goes to B vertices B after it goes also to C and B goes to D.
A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data.
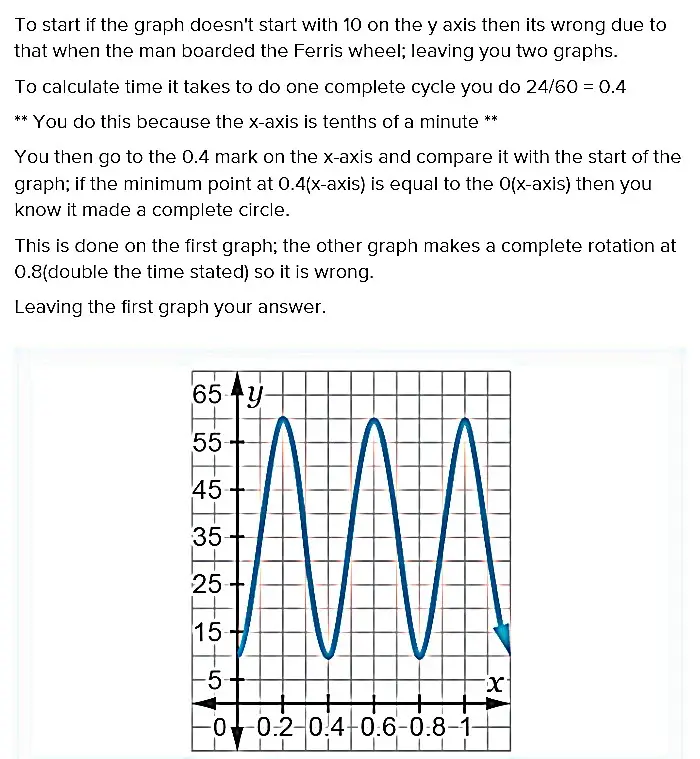
Misleading statistics can come from:
How to explain graph results : Here are steps you can use to explain a graph effectively:
How do you analyze different graphs : Here are some steps to help you read a graph:
How do you know if a graph is regular
A graph is regular if every vertex has the same degree. We may call the graph k-‐regular if every vertex has degree k. A path is a route that you travel along edges and through vertices in a graph. All of the vertices and edges in a path are connected to one another.

If two graphs have the same edge structure then we will declare them to be equivalent even though the vertices might be distinct or differ by a rearrangement.Some common features of graphs that may lead to incorrect interpretations are:
How can you identify misleading statistics : Seven signs of potentially misleading statistics.