Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.Selecting the right chart type
Ask yourself how many variables you want to show, how many data points you want to display, and how you want to scale your axis. Line, bar, and column charts represent change over time. Pyramids and pie charts display parts of a whole.Line graphs are used to track changes over short and long periods of time. When smaller changes exist, line graphs are better to use than bar graphs. Line graphs can also be used to compare changes over the same period of time for more than one group.
How to choose chart type : A line chart, area chart, and column chart are the most common chart types used to visualize change over time. In most cases, they can be used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between them. Line charts and area charts are the best tools to visualize data that goes up and down from day to day.
How to choose a visualization
How to Choose the Right Visualizations
Tabular format is best used when exact quantities of numbers must be known.
Line charts are best used when trying to visualize continuous data over time.
Bar charts are best used when showing comparisons between categories.
Pie charts are best used to compare parts to the whole.
How do you determine the best data chart : If you have nominal data, use bar charts or histograms if your data is discrete, or line/ area charts if it is continuous. If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts.
Different data types require different charts. Some types of data are incompatible with certain types of charts. If you have continuous data, you need a line chart, area chart, or scatter plot. If you have categorical data, you need a bar graph or pie chart. You would use:
Bar graphs to show numbers that are independent of each other.
Pie charts to show you how a whole is divided into different parts.
Line graphs show you how numbers have changed over time.
Cartesian graphs have numbers on both axes, which therefore allow you to show how changes in one thing affect another.
What are the five major rules of graphing
Show the data clearly
Check the data points plotted can be detected, and are not covered up or obscured.
Don't assume the viewer is a mind-reader … label titles and axes clearly and accurately.
Maintain constant measurement scales and avoid distortions.
For example, if you want to show a trend over time, a line chart or an area chart might be more appropriate. If you want to compare data points, a bar chart or a column chart might be a better choice. If you want to show a distribution, a histogram or a box plot might be more useful.If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts. If you want to compare values, use a pie chart — for relative comparison — or bar charts — for precise comparison. If you want to compare volumes, use an area chart or a bubble chart. When choosing a chart you should choose the one that fits the size of your data best and represents it clearly without cluttering.
What is the easiest graph to use : Bar Graphs
The simplest and most straightforward way to compare various categories is the classic bar graph. The universally-recognized graph features a series of bars of varying lengths. One axis of a bar graph features the categories being compared, while the other axis represents the value of each.
How to understand graphs : How to read a graph
Determine the type of graph.
Read the title or legend.
Examine any other text.
Identify the variables on the axes and what they represent.
Observe the x-axis and y-axis.
Determine what each number on the graph means.
Identify patterns in the data.
Find where your data falls on the graph.
How do you classify a graph
The model learns to classify graphs using three main steps:
Embed nodes using several rounds of message passing.
Aggregate these node embeddings into a single graph embedding (called readout layer).
Train a classifier based on graph embeddings.
If a vertical line drawn anywhere on the graph of a relation only intersects the graph at one point, then that graph represents a function.The ordinate/height of the graph must be 75% of the abscissa/base. This is called 75% rule.
How to choose graph scale : Choosing the right scale for a graph depends on the nature of the data and the story you want the graph to tell. 1st, we need to ensure the scale covers the entire range of your data. If the scale is too small, important details might be lost; if it's too large, subtle variations may become indistinguishable.
Antwort How do I know which graph to use? Weitere Antworten – How do I know what graph to use for my data
Bar charts are good for comparisons, while line charts work better for trends. Scatter plot charts are good for relationships and distributions, but pie charts should be used only for simple compositions — never for comparisons or distributions.Selecting the right chart type
Ask yourself how many variables you want to show, how many data points you want to display, and how you want to scale your axis. Line, bar, and column charts represent change over time. Pyramids and pie charts display parts of a whole.Line graphs are used to track changes over short and long periods of time. When smaller changes exist, line graphs are better to use than bar graphs. Line graphs can also be used to compare changes over the same period of time for more than one group.

How to choose chart type : A line chart, area chart, and column chart are the most common chart types used to visualize change over time. In most cases, they can be used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between them. Line charts and area charts are the best tools to visualize data that goes up and down from day to day.
How to choose a visualization
How to Choose the Right Visualizations
How do you determine the best data chart : If you have nominal data, use bar charts or histograms if your data is discrete, or line/ area charts if it is continuous. If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts.
Different data types require different charts. Some types of data are incompatible with certain types of charts. If you have continuous data, you need a line chart, area chart, or scatter plot. If you have categorical data, you need a bar graph or pie chart.
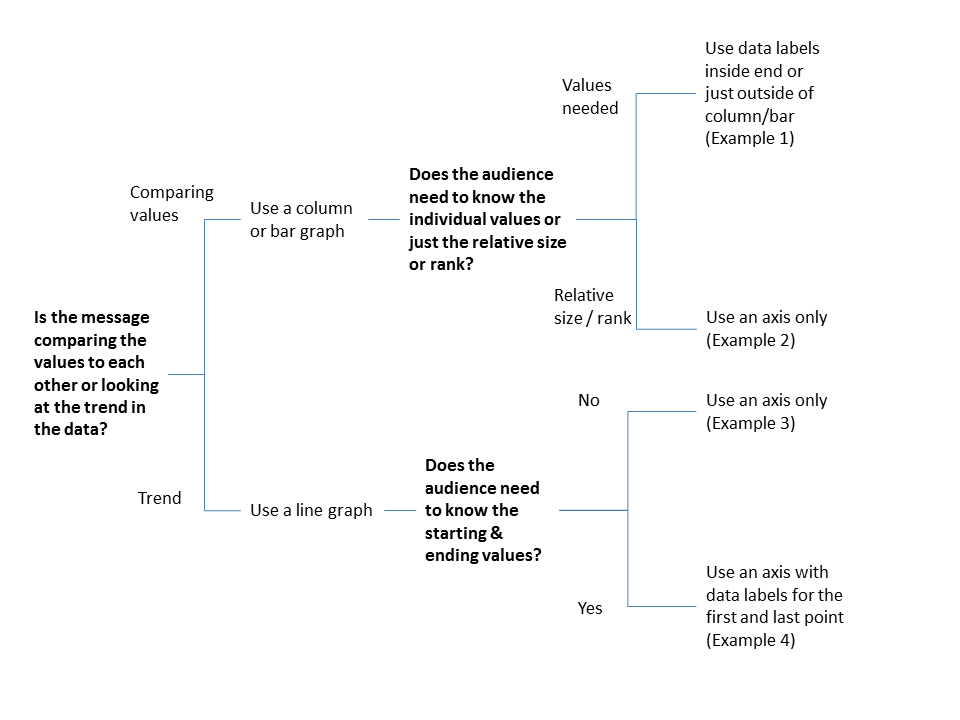
You would use:
What are the five major rules of graphing
Show the data clearly
For example, if you want to show a trend over time, a line chart or an area chart might be more appropriate. If you want to compare data points, a bar chart or a column chart might be a better choice. If you want to show a distribution, a histogram or a box plot might be more useful.If you want to show the relationship between values in your dataset, use a scatter plot, bubble chart, or line charts. If you want to compare values, use a pie chart — for relative comparison — or bar charts — for precise comparison. If you want to compare volumes, use an area chart or a bubble chart.

When choosing a chart you should choose the one that fits the size of your data best and represents it clearly without cluttering.
What is the easiest graph to use : Bar Graphs
The simplest and most straightforward way to compare various categories is the classic bar graph. The universally-recognized graph features a series of bars of varying lengths. One axis of a bar graph features the categories being compared, while the other axis represents the value of each.
How to understand graphs : How to read a graph
How do you classify a graph
The model learns to classify graphs using three main steps:
If a vertical line drawn anywhere on the graph of a relation only intersects the graph at one point, then that graph represents a function.The ordinate/height of the graph must be 75% of the abscissa/base. This is called 75% rule.
How to choose graph scale : Choosing the right scale for a graph depends on the nature of the data and the story you want the graph to tell. 1st, we need to ensure the scale covers the entire range of your data. If the scale is too small, important details might be lost; if it's too large, subtle variations may become indistinguishable.