Britain abolished slavery throughout its empire by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (with the notable exception of India), the French colonies re-abolished it in 1848 and the U.S. abolished slavery in 1865 with the 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.Dec 18, 1865 CE: Slavery is Abolished. On December 18, 1865, the 13th Amendment was adopted as part of the United States Constitution. The amendment officially abolished slavery, and immediately freed more than 100,000 enslaved people, from Kentucky to Delaware.Athenian slave society was finally destroyed by Philip II of Macedonia at the battle of Chaeronea (338 bce), when, on the motion of Lycurgus, many (but not all) slaves were freed.
When did slavery end in Italy : Slavery in Italy officially ended in 1880. The process of abolishing slavery in Italy occurred gradually over several decades. Here is a summary of the timeline: Early Abolition Efforts: During the period of Italian unification in the 19th century, various regions within Italy took steps to abolish slavery.
Why did slavery disappear in Europe
This shift away from slavery in Europe and the Byzantine empire is explained, to the extent that it is explained, as a consequence of political and socio-economic change rather than a matter of ideology. Slavery declined in the Christian kingdoms of northern Spain after the fall of the Umayyad caliphate in 1031.
How long was slavery in Europe : Slavery was common in Europe from the 1500s to the 1800s, but it has received less attention by historiography and is less prominent in public memory than colonial slavery and the Atlantic slave trade. Two main reasons may explain why slavery in Europe in the early modern and modern periods is forgotten.
On July 18–19, 1845, the Mackau Laws were passed, which paved the way towards the abolition of slavery in France. On April 27, 1848, the Proclamation of the Abolition of Slavery in the French Colonies was made. The effective abolition was enacted with the Decree abolishing Slavery of 27 April 1848. April 27, 1848 Victor Schœlcher and the Second Republic permanently abolished slavery in France and the colonies on April 27, 1848.
When did slavery end in England
It was only after many failed attempts that, in 1807, the slave trade in the British Empire was abolished. However, slaves in the colonies (excluding areas ruled by the East India Company) were not freed until 1838 – and only after slave-owners, rather than the slaves themselves, received compensation.April 27, 1848 Victor Schœlcher and the Second Republic permanently abolished slavery in France and the colonies on April 27, 1848.In 1817 Spain signed a treaty with the United Kingdom that abolished the transatlantic slave trade. However, as can be seen in Figure 1, the arrival of new slaves to Spanish America, especially Cuba and Puerto Rico, continued until very late in the nineteenth century. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948. The United Nations adopts The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which abolishes slavery internationally.
Why did the British end slavery : Merchants began to demand an end to the monopolies on the British market held by the Caribbean colonies and pushed instead for free trade. The persistent struggles of enslaved Africans and a growing fear of slave uprisings among plantation owners were another major factor.
Which country had the longest slavery : According to Korean Studies scholar Mark A. Peterson of Brigham Young University, Korea has the longest unbroken chain of indentured servitude or slavery of any society in history (spanning about 1,500 years) in part due to the fact that the social structure was one of the most stable in world history with a single …
Which country had the most slaves
India Nations with the highest number of people living in modern slavery included India, China, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey, Bangladesh, and the United States. France incorporated slavery in all of its early modern overseas colonies, including Canada, and was the first nation-state in the world to issue a general emancipation act (see the separate Oxford Bibliographies articles on French Atlantic World, the Haitian Revolution, Emancipation, and Abolition of Slavery).The Abolition of Slavery in 1848
The Danish ban on the transatlantic slave trade in 1792 marked the beginning of the end of slavery. Fifty years later, in 1847, the state of Denmark ruled that slavery be phased out over a 12 year period, beginning with all new-born babies of enslaved women.
When did Dutch abolish slavery : 1863 This comes 150 years after the actual abolition of slavery in the then Dutch colonies in 1873. In this year, the 10-year period of state supervision, instituted after the formal abolition of slavery in 1863, ended.
Antwort How did slavery end in Europe? Weitere Antworten – When did slavery in Europe end
Britain abolished slavery throughout its empire by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (with the notable exception of India), the French colonies re-abolished it in 1848 and the U.S. abolished slavery in 1865 with the 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.Dec 18, 1865 CE: Slavery is Abolished. On December 18, 1865, the 13th Amendment was adopted as part of the United States Constitution. The amendment officially abolished slavery, and immediately freed more than 100,000 enslaved people, from Kentucky to Delaware.Athenian slave society was finally destroyed by Philip II of Macedonia at the battle of Chaeronea (338 bce), when, on the motion of Lycurgus, many (but not all) slaves were freed.
When did slavery end in Italy : Slavery in Italy officially ended in 1880. The process of abolishing slavery in Italy occurred gradually over several decades. Here is a summary of the timeline: Early Abolition Efforts: During the period of Italian unification in the 19th century, various regions within Italy took steps to abolish slavery.
Why did slavery disappear in Europe
This shift away from slavery in Europe and the Byzantine empire is explained, to the extent that it is explained, as a consequence of political and socio-economic change rather than a matter of ideology. Slavery declined in the Christian kingdoms of northern Spain after the fall of the Umayyad caliphate in 1031.
How long was slavery in Europe : Slavery was common in Europe from the 1500s to the 1800s, but it has received less attention by historiography and is less prominent in public memory than colonial slavery and the Atlantic slave trade. Two main reasons may explain why slavery in Europe in the early modern and modern periods is forgotten.
On July 18–19, 1845, the Mackau Laws were passed, which paved the way towards the abolition of slavery in France. On April 27, 1848, the Proclamation of the Abolition of Slavery in the French Colonies was made. The effective abolition was enacted with the Decree abolishing Slavery of 27 April 1848.

April 27, 1848
Victor Schœlcher and the Second Republic permanently abolished slavery in France and the colonies on April 27, 1848.
When did slavery end in England
It was only after many failed attempts that, in 1807, the slave trade in the British Empire was abolished. However, slaves in the colonies (excluding areas ruled by the East India Company) were not freed until 1838 – and only after slave-owners, rather than the slaves themselves, received compensation.April 27, 1848
Victor Schœlcher and the Second Republic permanently abolished slavery in France and the colonies on April 27, 1848.In 1817 Spain signed a treaty with the United Kingdom that abolished the transatlantic slave trade. However, as can be seen in Figure 1, the arrival of new slaves to Spanish America, especially Cuba and Puerto Rico, continued until very late in the nineteenth century.
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
1948. The United Nations adopts The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which abolishes slavery internationally.
Why did the British end slavery : Merchants began to demand an end to the monopolies on the British market held by the Caribbean colonies and pushed instead for free trade. The persistent struggles of enslaved Africans and a growing fear of slave uprisings among plantation owners were another major factor.
Which country had the longest slavery : According to Korean Studies scholar Mark A. Peterson of Brigham Young University, Korea has the longest unbroken chain of indentured servitude or slavery of any society in history (spanning about 1,500 years) in part due to the fact that the social structure was one of the most stable in world history with a single …
Which country had the most slaves
India
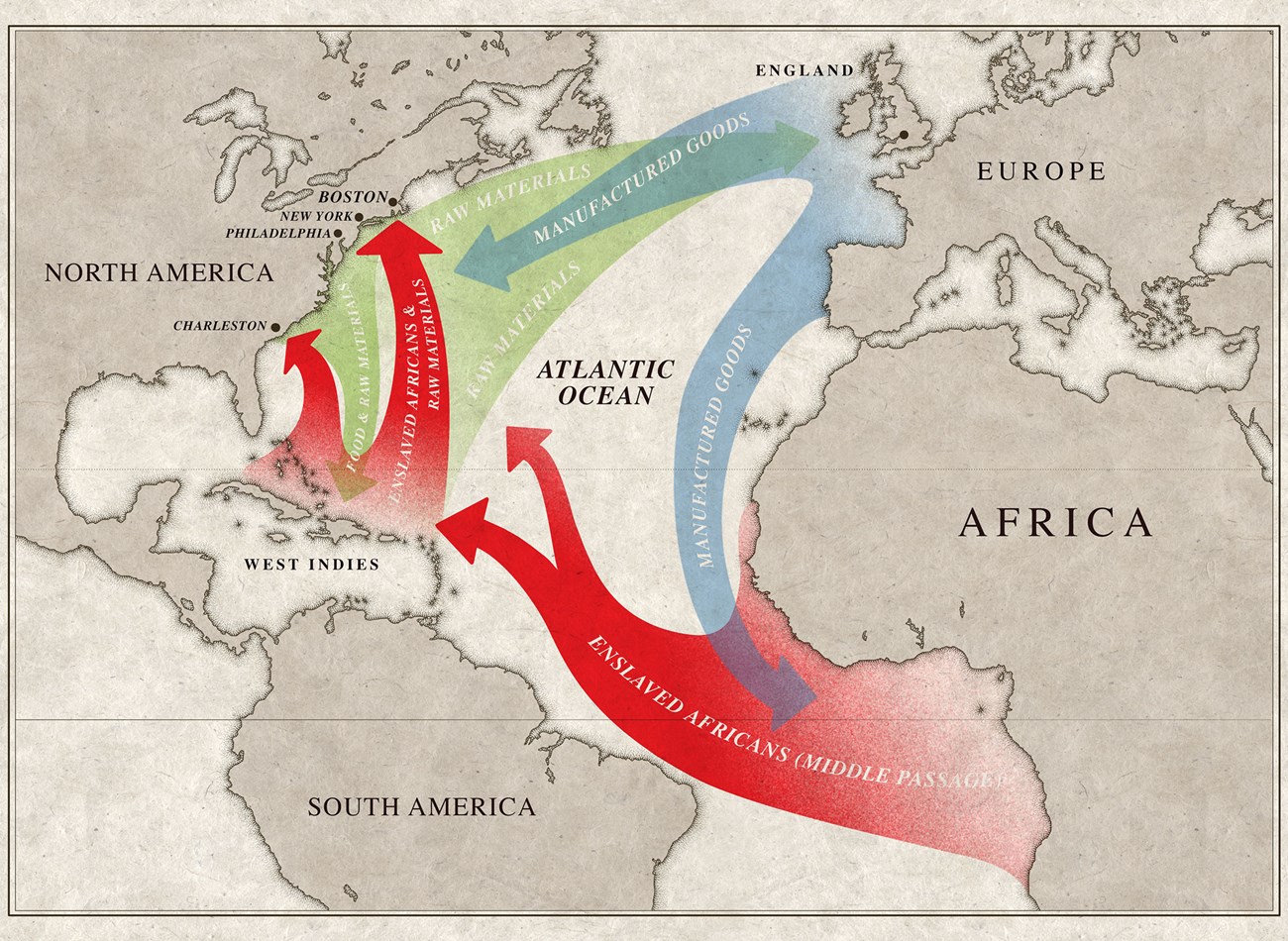
Nations with the highest number of people living in modern slavery included India, China, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey, Bangladesh, and the United States.
France incorporated slavery in all of its early modern overseas colonies, including Canada, and was the first nation-state in the world to issue a general emancipation act (see the separate Oxford Bibliographies articles on French Atlantic World, the Haitian Revolution, Emancipation, and Abolition of Slavery).The Abolition of Slavery in 1848
The Danish ban on the transatlantic slave trade in 1792 marked the beginning of the end of slavery. Fifty years later, in 1847, the state of Denmark ruled that slavery be phased out over a 12 year period, beginning with all new-born babies of enslaved women.
When did Dutch abolish slavery : 1863
This comes 150 years after the actual abolition of slavery in the then Dutch colonies in 1873. In this year, the 10-year period of state supervision, instituted after the formal abolition of slavery in 1863, ended.