Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.As First Consul, Napoleon instituted a number of lasting reforms: centralised administration of government, a higher education system, a central bank, law codes and a road and sewer system, many of which are still in place today.How did Europe change after Napoleon Europe changed politically; the French Empire crumbled. Conservative monarchies returned to power at the cost of radical republics created by Napoleon.
What was the role of Napoleon in the modernization of Europe : He saw himself as a moderniser of Europe. Napoleon introduced and inculcated many laws such as the protection of private property and a uniform system of weights and measures provided by the decimal system. A lot of his measures carried the revolutionary ideas of liberty and modern laws to the other parts of Europe.
What was Napoleon’s greatest contribution to European society
Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.
How did the Napoleonic Code impact Europe : The 1804 Napoleonic Code, which influenced civil law codes across the world, replaced the fragmented laws of pre-revolutionary France, recognizing the principles of civil liberty, equality before the law (although not for women in the same sense as for men), and the secular character of the state.
He established civil code in 1804 also known as the Napoleonic Code. It did away with all privileges based on birth. It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. For many in Europe, Napoleon was a hero—even a liberator. Many Poles celebrated him for expelling their Russian rulers and helping them to create their own country. Similarly, many in Italy believed he had freed them from Austrian rule.
What changes did Napoleon introduce in Europe
It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. In towns too, guild systems were removed. Transport and communication systems were improved.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.Napoleon Bonaparte was a towering figure in history. He seized power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, remade the country and conquered much of Europe. A single exile was not enough to keep him from threatening a long-standing power structure on the continent. Napoleon played a key role in the French Revolution (1789–99), served as first consul of France (1799–1804), and was the first emperor of France (1804–14/15). Today Napoleon is widely considered one of the greatest military generals in history.
How did Napoleonic Wars affect the world : The most striking global consequence of the Napoleonic Wars was the independence of South America. Most of the continent had been part of the Spanish empire, with Brazil ruled by the Portuguese. The European war triggered, but did not cause, the Latin American wars of independence.
What were the changes made by Napoleon : Napoleon introduced the Civil Code of 1804, also known as the Napoleonic Code. This Code removed all privileges based on birth. The Right to Property was secured and the Feudal system was finally abolished and simplified administrative divisions were introduced in its place.
What changes did Napoleon make to the economy
Napoleon Bonaparte created the Banque de France to foster economic recovery after the strong recession of the revolutionary period. This new institution was charged with issuing notes payable to bearer on sight, in return for discounting of trade bills. Napoleon Bonaparte was one of the most successful generals of the French revolutionary armies. He was emperor of France from 1804-14, and in 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte (1768-1821) is regarded as one of history's greatest military leaders.Napoleon's character is intended to symbolize Joseph Stalin as part of the story's broader allegory for the Russian Revolution. He epitomizes a selfish, controlling leader who prioritizes himself, his supporters, and his power over the struggles of the citizens that he is controlling.
How did the Napoleonic Code change Europe : The Napoleonic Code abolished a previous patchwork of feudal laws (the French writer Voltaire once complained that a man travelling across France would have to change laws as often as he changed horses) and established a civil code that stressed the rule of law; for instance, the Napoleonic Code provided that laws …
Antwort How did Napoleon impact Europe and the world? Weitere Antworten – What was the impact of Napoleon on Europe
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.As First Consul, Napoleon instituted a number of lasting reforms: centralised administration of government, a higher education system, a central bank, law codes and a road and sewer system, many of which are still in place today.How did Europe change after Napoleon Europe changed politically; the French Empire crumbled. Conservative monarchies returned to power at the cost of radical republics created by Napoleon.
What was the role of Napoleon in the modernization of Europe : He saw himself as a moderniser of Europe. Napoleon introduced and inculcated many laws such as the protection of private property and a uniform system of weights and measures provided by the decimal system. A lot of his measures carried the revolutionary ideas of liberty and modern laws to the other parts of Europe.
What was Napoleon’s greatest contribution to European society
Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.
How did the Napoleonic Code impact Europe : The 1804 Napoleonic Code, which influenced civil law codes across the world, replaced the fragmented laws of pre-revolutionary France, recognizing the principles of civil liberty, equality before the law (although not for women in the same sense as for men), and the secular character of the state.
He established civil code in 1804 also known as the Napoleonic Code. It did away with all privileges based on birth. It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues.
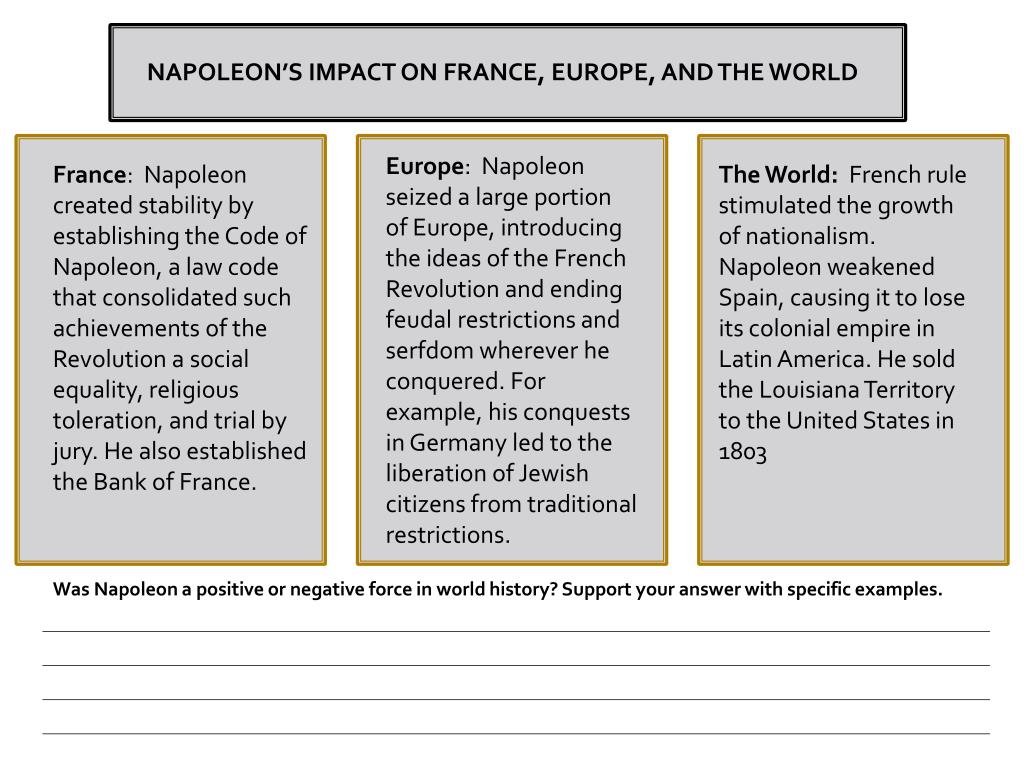
For many in Europe, Napoleon was a hero—even a liberator. Many Poles celebrated him for expelling their Russian rulers and helping them to create their own country. Similarly, many in Italy believed he had freed them from Austrian rule.
What changes did Napoleon introduce in Europe
It established equality before the law and secured the right to property. He simplified administrative divisions, the abolished feudal system, and freed peasants from serfdom and manorial dues. In towns too, guild systems were removed. Transport and communication systems were improved.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.Napoleon Bonaparte was a towering figure in history. He seized power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, remade the country and conquered much of Europe. A single exile was not enough to keep him from threatening a long-standing power structure on the continent.

Napoleon played a key role in the French Revolution (1789–99), served as first consul of France (1799–1804), and was the first emperor of France (1804–14/15). Today Napoleon is widely considered one of the greatest military generals in history.
How did Napoleonic Wars affect the world : The most striking global consequence of the Napoleonic Wars was the independence of South America. Most of the continent had been part of the Spanish empire, with Brazil ruled by the Portuguese. The European war triggered, but did not cause, the Latin American wars of independence.
What were the changes made by Napoleon : Napoleon introduced the Civil Code of 1804, also known as the Napoleonic Code. This Code removed all privileges based on birth. The Right to Property was secured and the Feudal system was finally abolished and simplified administrative divisions were introduced in its place.
What changes did Napoleon make to the economy
Napoleon Bonaparte created the Banque de France to foster economic recovery after the strong recession of the revolutionary period. This new institution was charged with issuing notes payable to bearer on sight, in return for discounting of trade bills.

Napoleon Bonaparte was one of the most successful generals of the French revolutionary armies. He was emperor of France from 1804-14, and in 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte (1768-1821) is regarded as one of history's greatest military leaders.Napoleon's character is intended to symbolize Joseph Stalin as part of the story's broader allegory for the Russian Revolution. He epitomizes a selfish, controlling leader who prioritizes himself, his supporters, and his power over the struggles of the citizens that he is controlling.
How did the Napoleonic Code change Europe : The Napoleonic Code abolished a previous patchwork of feudal laws (the French writer Voltaire once complained that a man travelling across France would have to change laws as often as he changed horses) and established a civil code that stressed the rule of law; for instance, the Napoleonic Code provided that laws …