European leaders met in the Congress of Vienna in 1814 and 1815 to redraw Europe's boundaries after Napoleon's fall and ensure stability in Europe. They returned the old royal family of France to power and acknowledged Finland, which was taken over by Russia during the wars, as Russian territory.Across France and the rest of Europe the consequences of the Revolution were huge. There were many new developments including the fall of the monarchy, changes in society with the rise of the middle class, and the growth of nationalism.Following the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, European governments were driven by a spirit of conservatism. Conservatives believed that established, traditional institutions of state and society – like the monarchy, the Church, social hierarchies, property and the family – should be preserved.
Was the concert of Europe successful : The Concert of Europe proved to be successful in preventing large-scale wars in Europe. Except for the international Crimean War in the mid-nineteenth century, there were no large-scale conflicts on the European continent.
What happened after the end of Napoleon’s empire
A coalition of European powers defeated Napoleon in the War of the Sixth Coalition, ended the First Empire in 1814, and restored the monarchy to the brothers of Louis XVI. The Bourbon Restoration lasted from (about) April 6, 1814, until the popular uprisings of the July Revolution of 1830.
How did Europe change after Napoleon was defeated in Quizlet : How did Europe change after Napoleon was defeated The French Revolution spread to other countries. France was reduced to half its original size. Many monarchies were restored.
9 November 1799: Napoleonic era begins
On 9 November 1799, as frustration with their leadership reaches a fever pitch, Bonaparte stages a coup d'état, abolishing the Directory and appointing himself France's 'first consul'. This marks the end of the French Revolution and the start of the Napoleonic era. Huge Social, Political and Economic changes took place. The revolutionary ideas had been spread across Europe. The Monarchy in all countries were damaged by conquest. Nationalism became a powerful force in all European Countries.
How did Napoleon have an impact on Europe
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.The Concert of Europe. From 1815 to 1914, the Concert of Europe established a set of principles, rules and practices that helped to maintain balance between the major powers after the Napoleonic Wars, and to spare Europe from another broad conflict. The Concert of Europe was somewhat successful in preventing large-scale wars in Europe. Except for the mid-19th-century international Crimean War, European wars at that time were smaller in scale.
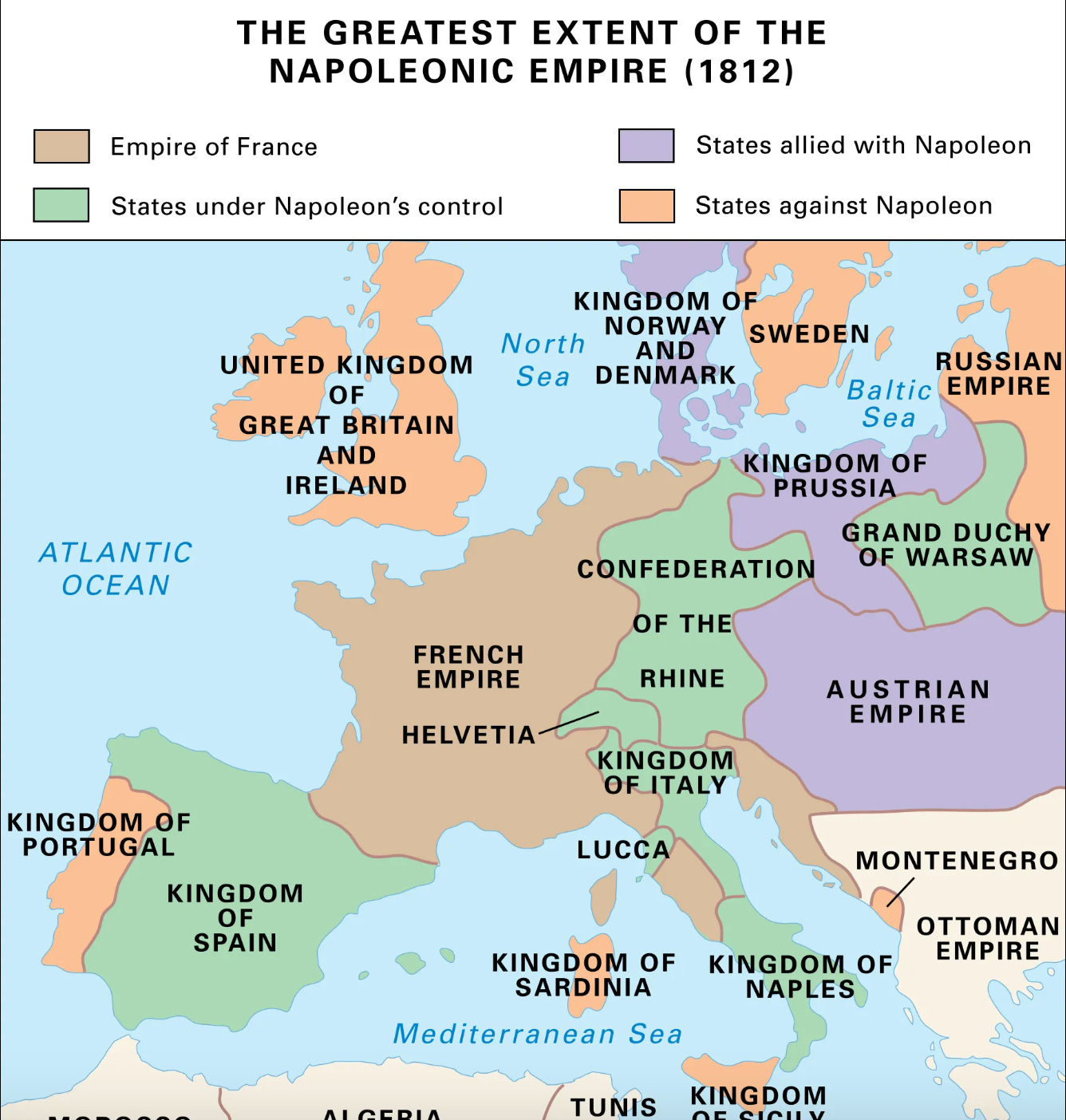
How much of Europe did Napoleon conquer : He now controlled Europe from France to Poland, though the powerful British navy continued to dominate the seas. His empire stretched from Belgium and Holland in the north to Rome in the south, covering nearly half a million square miles and boasting a population of 44 million.
Why did France go back to a monarchy after the revolution : The Bourbon Restoration (one in 1814 and another in 1815) brought France back under control of the Monarchy under Louis XVIII. Other monarchies of Europe were keen for stability to return to France and were hoping to prevent more revolutionary fervor from disturbing their own thrones.
How did Napoleon change Europe and the world
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today. Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy.Following the defeat of Napoleon in 1814, the Bourbon Monarchy was restored in France. The brothers of the executed Louis XVI, namely Louis XVIII and Charles X, successively mounted the throne and instituted a conservative government aiming to restore the proprieties, if not all the institutions, of the Ancien Régime.
What happened to land after French Revolution : In November 1789, the National Constituent Assembly passed legislation that declared all ecclesiastical property to be at the disposal of the Nation and, beginning in December 1790, local governments began to auction off these properties.
Antwort How did Europe change after Napoleon was defeated? Weitere Antworten – What happened to Europe after Napoleon’s defeat
European leaders met in the Congress of Vienna in 1814 and 1815 to redraw Europe's boundaries after Napoleon's fall and ensure stability in Europe. They returned the old royal family of France to power and acknowledged Finland, which was taken over by Russia during the wars, as Russian territory.Across France and the rest of Europe the consequences of the Revolution were huge. There were many new developments including the fall of the monarchy, changes in society with the rise of the middle class, and the growth of nationalism.Following the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, European governments were driven by a spirit of conservatism. Conservatives believed that established, traditional institutions of state and society – like the monarchy, the Church, social hierarchies, property and the family – should be preserved.
Was the concert of Europe successful : The Concert of Europe proved to be successful in preventing large-scale wars in Europe. Except for the international Crimean War in the mid-nineteenth century, there were no large-scale conflicts on the European continent.
What happened after the end of Napoleon’s empire
A coalition of European powers defeated Napoleon in the War of the Sixth Coalition, ended the First Empire in 1814, and restored the monarchy to the brothers of Louis XVI. The Bourbon Restoration lasted from (about) April 6, 1814, until the popular uprisings of the July Revolution of 1830.
How did Europe change after Napoleon was defeated in Quizlet : How did Europe change after Napoleon was defeated The French Revolution spread to other countries. France was reduced to half its original size. Many monarchies were restored.
9 November 1799: Napoleonic era begins
On 9 November 1799, as frustration with their leadership reaches a fever pitch, Bonaparte stages a coup d'état, abolishing the Directory and appointing himself France's 'first consul'. This marks the end of the French Revolution and the start of the Napoleonic era.

Huge Social, Political and Economic changes took place. The revolutionary ideas had been spread across Europe. The Monarchy in all countries were damaged by conquest. Nationalism became a powerful force in all European Countries.
How did Napoleon have an impact on Europe
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.Undoubtedly, Napoleon's greatest achievement was the spreading of French Revolutionary ideas across Europe and ultimately the world, which would lead to the revolutions of 1830, 1848, and other efforts by the masses to achieve true libertie, egalite, et fraternitie.The Concert of Europe. From 1815 to 1914, the Concert of Europe established a set of principles, rules and practices that helped to maintain balance between the major powers after the Napoleonic Wars, and to spare Europe from another broad conflict.
The Concert of Europe was somewhat successful in preventing large-scale wars in Europe. Except for the mid-19th-century international Crimean War, European wars at that time were smaller in scale.
How much of Europe did Napoleon conquer : He now controlled Europe from France to Poland, though the powerful British navy continued to dominate the seas. His empire stretched from Belgium and Holland in the north to Rome in the south, covering nearly half a million square miles and boasting a population of 44 million.
Why did France go back to a monarchy after the revolution : The Bourbon Restoration (one in 1814 and another in 1815) brought France back under control of the Monarchy under Louis XVIII. Other monarchies of Europe were keen for stability to return to France and were hoping to prevent more revolutionary fervor from disturbing their own thrones.
How did Napoleon change Europe and the world
Napoleon created a new form of government in France, reshaped the boundaries of Europe, and influenced revolutionaries and nationalists the world over. Since his first days in power he aroused controversies that continue today.

Napoleon's conquests cemented the spread of French revolutionary legislation to much of western Europe. The powers of the Roman Catholic church, guilds, and manorial aristocracy came under the gun. The old regime was dead in Belgium, western Germany, and northern Italy.Following the defeat of Napoleon in 1814, the Bourbon Monarchy was restored in France. The brothers of the executed Louis XVI, namely Louis XVIII and Charles X, successively mounted the throne and instituted a conservative government aiming to restore the proprieties, if not all the institutions, of the Ancien Régime.
What happened to land after French Revolution : In November 1789, the National Constituent Assembly passed legislation that declared all ecclesiastical property to be at the disposal of the Nation and, beginning in December 1790, local governments began to auction off these properties.