What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.INVESTIGATION: Misleading graphs
Omitting the baseline.
Showing an inappropriate or irregular scale.
Scale or labels not clearly given.
Leaving data out.
Using pictures or three-dimensional graphics that distort differences.
Using the wrong graph for a given data type.
The “classic” types of misleading graphs include cases where: The Vertical scale is too big or too small, or skips numbers, or doesn't start at zero. The graph isn't labeled properly. Data is left out.
What makes a chart bad : Graphs are often made misleading for advertising or other purposes, or even just by accident, by: • Leaving gaps/changing the scale in vertical axes • Uneven shading/colours • Unfair emphasis on some sections • Distorting areas in histograms (bar widths should always be equal – if you have different widths then the bar …
How can statistics be misleading
Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors. Neglecting the baseline: ignoring an important baseline for comparison.
How can visuals be misleading : A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data.
2 Disadvantages of graphs and charts
One of the main disadvantages is that they can be misleading, confusing, or inaccurate if they are not designed, labeled, or interpreted correctly. They can also create bias or distortion, as you can manipulate the data or the visual elements to emphasize or hide certain aspects. A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data.
How can data be misrepresented
Other ways of misrepresenting data include drawing unwarranted inference from data, creating deceptive graphs of figures, and using suggestive language for rhetorical effect.Extending labels on the y-axis is an example of misleading data visualization It can hide the trends we're trying to show, which can alter the magnitude of a change. In the graph below, we can see the average yearly global temperature from 1880 to 2015.Graphs may be misleading by being excessively complex or poorly constructed. Even when constructed to display the characteristics of their data accurately, graphs can be subject to different interpretations, or unintended kinds of data can seemingly and ultimately erroneously be derived.
1 Choosing the wrong type of display. One of the first decisions you have to make when creating a graphical display is what type of display to use.
2 Using too many elements.
3 Misusing scales and axes.
4 Ignoring design principles.
5 Not checking for errors.
6 Not testing for clarity.
7 Here's what else to consider.
What are the 4 ways that statistics can be misleading : Statistics can be misleading in a number of ways. In this lesson, we'll discuss four different ways: inventing false statistical information, misinformation, neglecting the baseline, and making fallacious comparisons.
What is a misleading data visualization : However, these valuable insights can be compromised by perpetuating misinformation. Misleading visualizations are primarily defined as those that interfere with the viewers' abilities to read off and compare the values from the visuals.
Why can data be misleading
Errors in how data is collected, analyzed, and presented can all result in many examples of misleading statistics in the media. Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors. Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors. Neglecting the baseline: ignoring an important baseline for comparison.By understanding and being aware of this, you'll be able to spot instances when the data display is intentionally misleading.
Overloading viewers with too many variables.
Truncating y-axis in graphs.
Extending labels on the y-axis.
Exaggerated or improper scaling.
Improper extraction – Cherry Picking.
What are 5 ways in which data and graphs can be changed to be misleading : 10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization
Pie charts that don't sum to 100% Pie charts should, by definition, sum to 100%.
Antwort How are charts misleading? Weitere Antworten – How can a graph be misleading
What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.INVESTIGATION: Misleading graphs
The “classic” types of misleading graphs include cases where: The Vertical scale is too big or too small, or skips numbers, or doesn't start at zero. The graph isn't labeled properly. Data is left out.
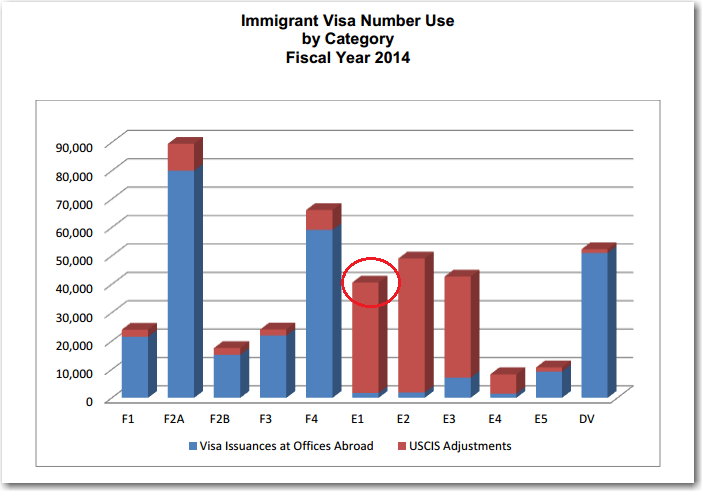
What makes a chart bad : Graphs are often made misleading for advertising or other purposes, or even just by accident, by: • Leaving gaps/changing the scale in vertical axes • Uneven shading/colours • Unfair emphasis on some sections • Distorting areas in histograms (bar widths should always be equal – if you have different widths then the bar …
How can statistics be misleading
Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors. Neglecting the baseline: ignoring an important baseline for comparison.
How can visuals be misleading : A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data.
2 Disadvantages of graphs and charts
One of the main disadvantages is that they can be misleading, confusing, or inaccurate if they are not designed, labeled, or interpreted correctly. They can also create bias or distortion, as you can manipulate the data or the visual elements to emphasize or hide certain aspects.
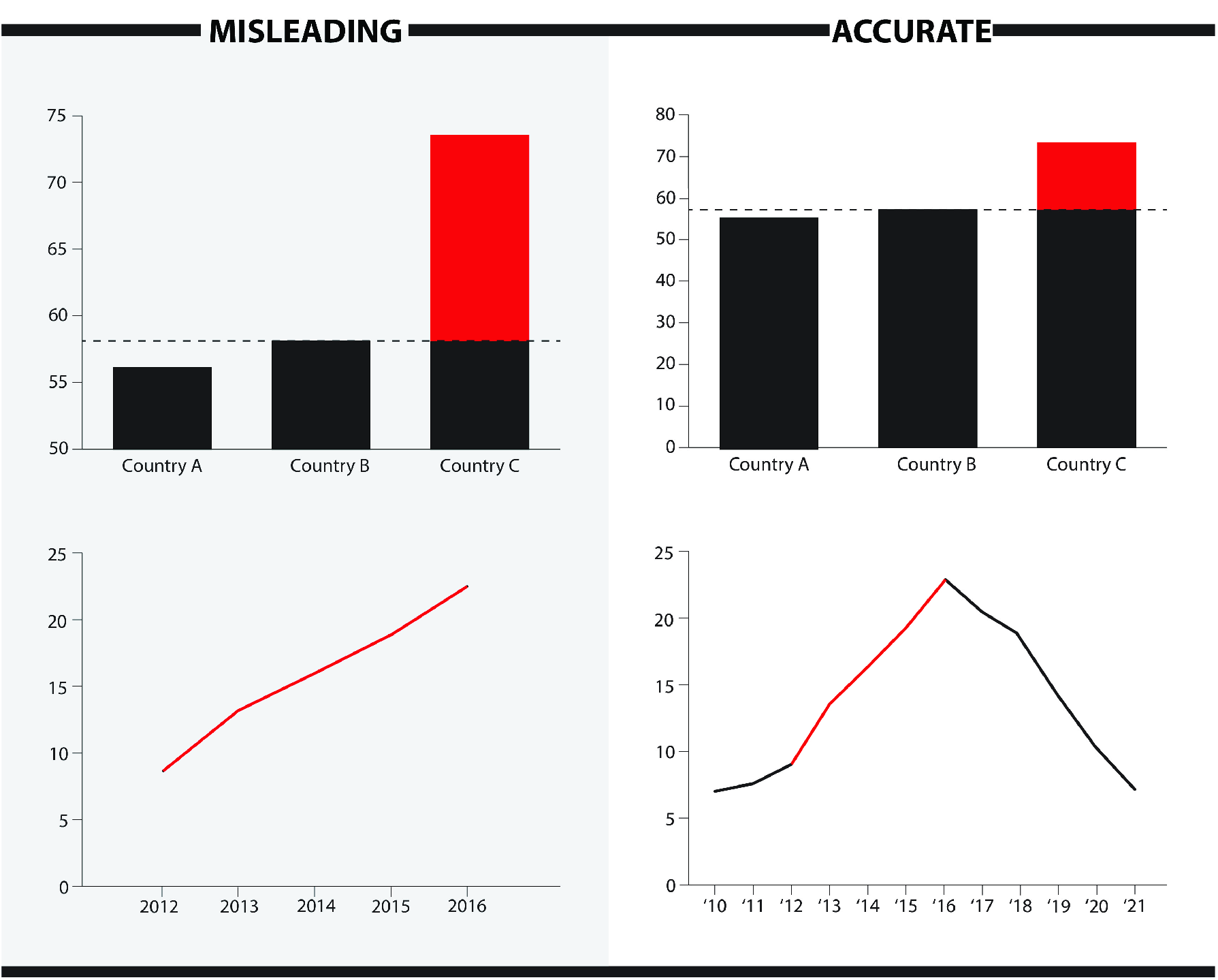
A very common misleading data visualization example is changing the value of the y-axis's starting point from zero to any other number. This blows up the differences when comparing data.
How can data be misrepresented
Other ways of misrepresenting data include drawing unwarranted inference from data, creating deceptive graphs of figures, and using suggestive language for rhetorical effect.Extending labels on the y-axis is an example of misleading data visualization It can hide the trends we're trying to show, which can alter the magnitude of a change. In the graph below, we can see the average yearly global temperature from 1880 to 2015.Graphs may be misleading by being excessively complex or poorly constructed. Even when constructed to display the characteristics of their data accurately, graphs can be subject to different interpretations, or unintended kinds of data can seemingly and ultimately erroneously be derived.

What are the 4 ways that statistics can be misleading : Statistics can be misleading in a number of ways. In this lesson, we'll discuss four different ways: inventing false statistical information, misinformation, neglecting the baseline, and making fallacious comparisons.
What is a misleading data visualization : However, these valuable insights can be compromised by perpetuating misinformation. Misleading visualizations are primarily defined as those that interfere with the viewers' abilities to read off and compare the values from the visuals.
Why can data be misleading
Errors in how data is collected, analyzed, and presented can all result in many examples of misleading statistics in the media. Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors.
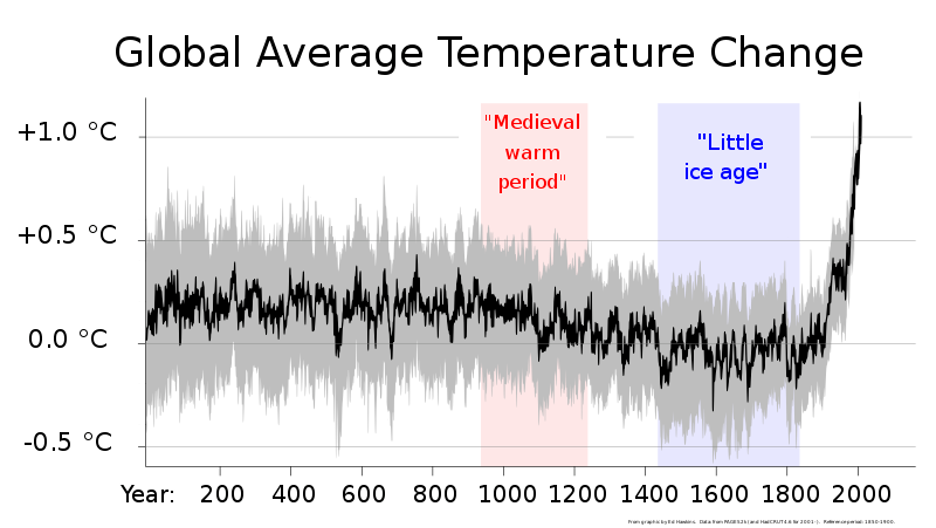
Misleading statistics can come from: Bad sampling: wrong sample size, no representative sample. Misinformation: wholly invented numerical data, fabricated results, not reporting errors. Neglecting the baseline: ignoring an important baseline for comparison.By understanding and being aware of this, you'll be able to spot instances when the data display is intentionally misleading.
What are 5 ways in which data and graphs can be changed to be misleading : 10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization