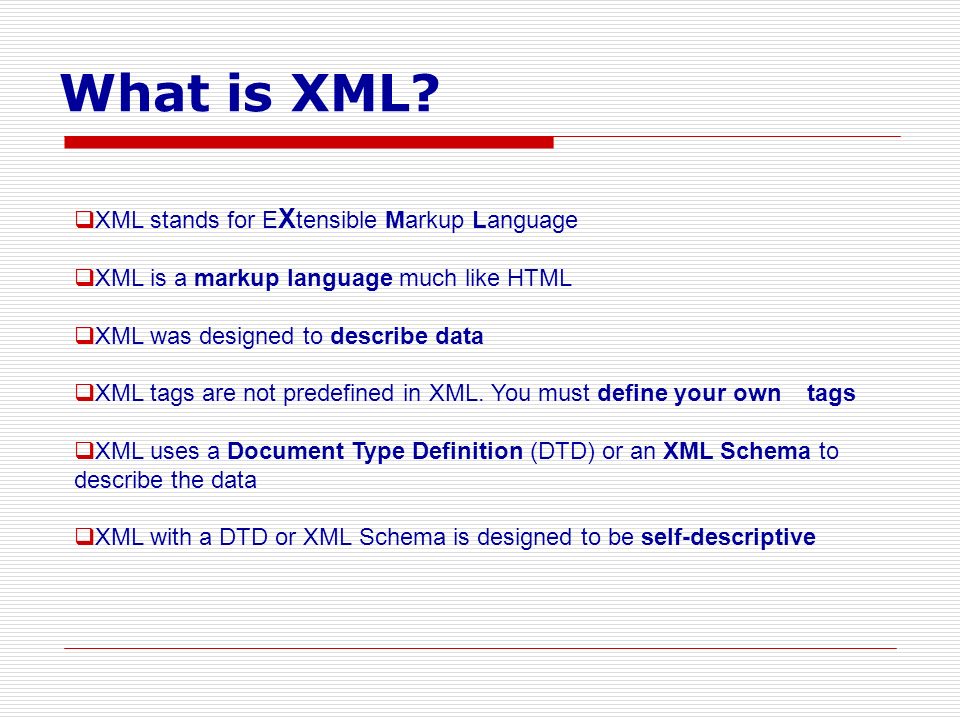
HTML 5 can be written in html and XML. HTML 5 specification is the description of a vocabulary that you can write in two different syntaxes (html and XML) depending on your developer needs, markets and applications.Compatibility: HTML5 is widely supported by web browsers and mobile devices, making it the standard for web development, while XML is used in specific industries and scenarios where structured data exchange is required, such as in software integration or data storage.What is the Difference Between XHTML and HTML5 XHTML is a combination of HTML and XML, while HTML5 is a version of HTML. XHTML has its own parsing requirements, while HTML does not have any specific requirements and uses its own.
Is HTML a subset of XML : Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a cousin to HTML and a nephew to SGML. Although XML is a markup language and therefore part of the family, it has different functions than HTML. XML is a subset of SGML, which gives it rights that an application, such as HTML, does not have. XML can define applications of its own.
Does HTML use XML
XML can be embedded in HTML and parsed with the JavaScript programming language to create webpages that are dynamic.
Can HTML replace XML : 1 Does XML replace HTML No. XML itself does not replace HTML: instead, it provides an alternative which allows you to define your own set of markup elements. HTML is expected to remain in common use for some time to come, and a Document Type Definition for HTML is available in XML syntax as well as in original SGML.
1 Does XML replace HTML No. XML itself does not replace HTML: instead, it provides an alternative which allows you to define your own set of markup elements. HTML is expected to remain in common use for some time to come, and a Document Type Definition for HTML is available in XML syntax as well as in original SGML. HTML5 is the latest version of HTML and supports new markup language functionalities such as multimedia, new tags and elements as well as new APIs. HTML5 also supports audio and video. HTML does not provide native audio and video support. HTML5 provides native audio and video support.
Is XHTML used anymore
Of the two serializations, the W3C suggests that most authors use the HTML syntax, rather than the XHTML syntax. The W3C recommendations of both XHTML 1.0 and XHTML 1.1 were retired on 27 March 2018, along with HTML 4.0, HTML 4.01, and HTML5.XML is short for Extensible Markup Language and is a specification from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It is not a replacement for HTML but is one level up: It is a meta-syntax, used to define new markup languages.HTML is commonly known as the language of the web. HTML's primary purpose is to display content, given in a text-based document, in a graphical form in the browser. In contrast, XML allows different applications to exchange and store data and its structure in a way that is universally understood. Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used.
Is XML used anymore : Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used.
Why XML is obsolete : JSON has been readily praised due to its simplicity and terse semantics, and XML labeled as an antiquated standard of the past due to its verbosity and seemingly excessive complexity.
Does anyone use XML anymore
Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used. The W3C retired HTML5 on 27 March 2018. Additionally, the retirement included HTML 4.0, HTML 4.01, XHTML 1.0, and XHTML 1.1. HTML 5.1, HTML 5.2 and HTML 5.3 were all retired on 28 January 2021, in favour of the HTML living standard.HTML5 is the final version that was released of HTML, which is the hypertext markup language used in the building and structuring of content to be displayed on web pages. Those who use it can also utilise coding such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as Javascript alongside it.
Why did XHTML fail : Others countered that the problems ascribed to the use of XHTML could mostly be attributed to two main sources: the production of invalid XHTML documents by some Web authors and the lack of support for XHTML built into Internet Explorer 6.
Antwort Does HTML5 use XML? Weitere Antworten – Is HTML5 based on XML
HTML 5 can be written in html and XML. HTML 5 specification is the description of a vocabulary that you can write in two different syntaxes (html and XML) depending on your developer needs, markets and applications.Compatibility: HTML5 is widely supported by web browsers and mobile devices, making it the standard for web development, while XML is used in specific industries and scenarios where structured data exchange is required, such as in software integration or data storage.What is the Difference Between XHTML and HTML5 XHTML is a combination of HTML and XML, while HTML5 is a version of HTML. XHTML has its own parsing requirements, while HTML does not have any specific requirements and uses its own.
Is HTML a subset of XML : Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a cousin to HTML and a nephew to SGML. Although XML is a markup language and therefore part of the family, it has different functions than HTML. XML is a subset of SGML, which gives it rights that an application, such as HTML, does not have. XML can define applications of its own.
Does HTML use XML
XML can be embedded in HTML and parsed with the JavaScript programming language to create webpages that are dynamic.
Can HTML replace XML : 1 Does XML replace HTML No. XML itself does not replace HTML: instead, it provides an alternative which allows you to define your own set of markup elements. HTML is expected to remain in common use for some time to come, and a Document Type Definition for HTML is available in XML syntax as well as in original SGML.
1 Does XML replace HTML No. XML itself does not replace HTML: instead, it provides an alternative which allows you to define your own set of markup elements. HTML is expected to remain in common use for some time to come, and a Document Type Definition for HTML is available in XML syntax as well as in original SGML.

HTML5 is the latest version of HTML and supports new markup language functionalities such as multimedia, new tags and elements as well as new APIs. HTML5 also supports audio and video. HTML does not provide native audio and video support. HTML5 provides native audio and video support.
Is XHTML used anymore
Of the two serializations, the W3C suggests that most authors use the HTML syntax, rather than the XHTML syntax. The W3C recommendations of both XHTML 1.0 and XHTML 1.1 were retired on 27 March 2018, along with HTML 4.0, HTML 4.01, and HTML5.XML is short for Extensible Markup Language and is a specification from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It is not a replacement for HTML but is one level up: It is a meta-syntax, used to define new markup languages.HTML is commonly known as the language of the web. HTML's primary purpose is to display content, given in a text-based document, in a graphical form in the browser. In contrast, XML allows different applications to exchange and store data and its structure in a way that is universally understood.

Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used.
Is XML used anymore : Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used.
Why XML is obsolete : JSON has been readily praised due to its simplicity and terse semantics, and XML labeled as an antiquated standard of the past due to its verbosity and seemingly excessive complexity.
Does anyone use XML anymore
Although XML is an older technology, both JSON and XML are still commonly used.
The W3C retired HTML5 on 27 March 2018. Additionally, the retirement included HTML 4.0, HTML 4.01, XHTML 1.0, and XHTML 1.1. HTML 5.1, HTML 5.2 and HTML 5.3 were all retired on 28 January 2021, in favour of the HTML living standard.HTML5 is the final version that was released of HTML, which is the hypertext markup language used in the building and structuring of content to be displayed on web pages. Those who use it can also utilise coding such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as Javascript alongside it.
Why did XHTML fail : Others countered that the problems ascribed to the use of XHTML could mostly be attributed to two main sources: the production of invalid XHTML documents by some Web authors and the lack of support for XHTML built into Internet Explorer 6.