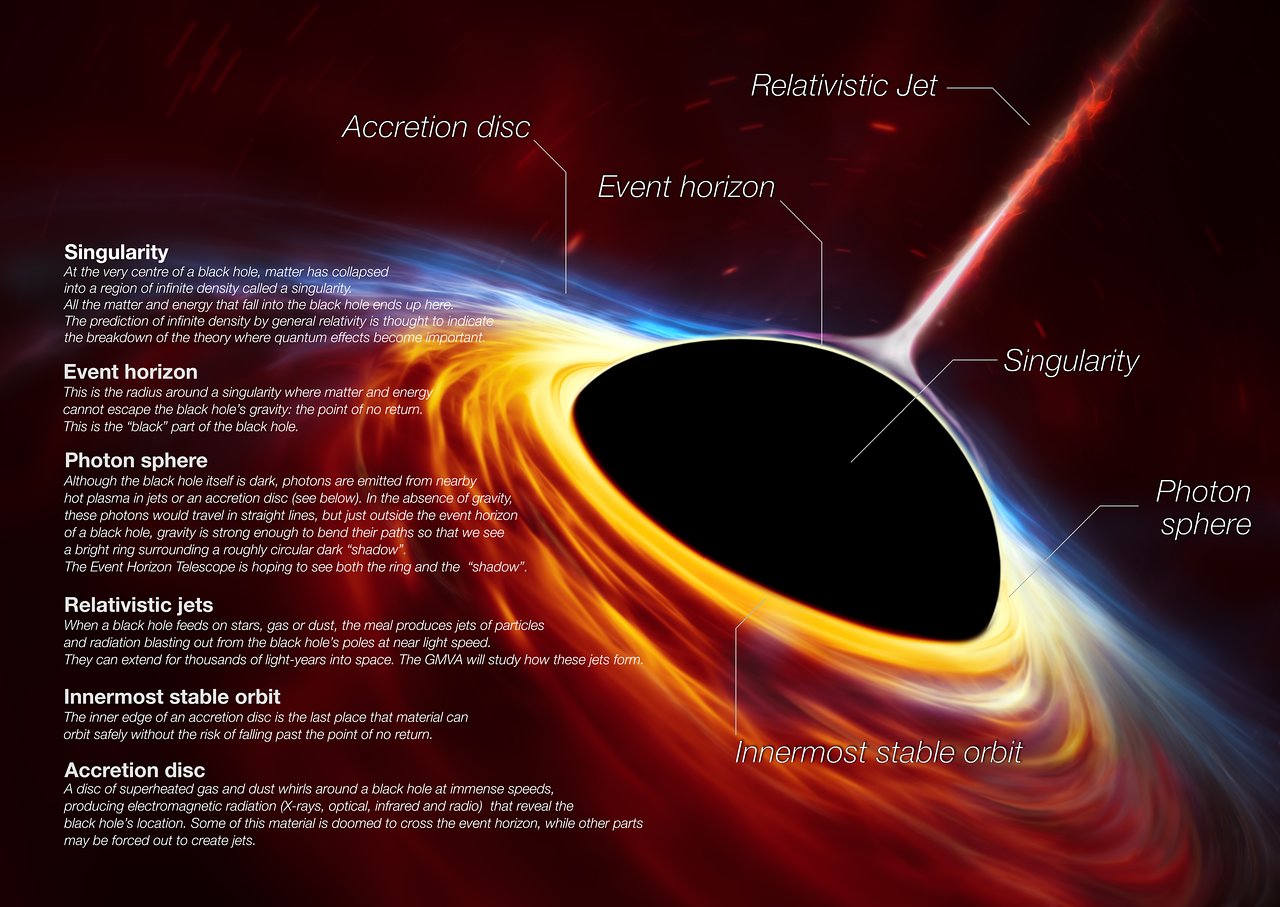
Scientists have found proof that every large galaxy contains a supermassive black hole at its center. The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy is called Sagittarius A. It has a mass equal to about 4 million suns and would fit inside a very large ball that could hold a few million Earths.Solitary black holes can generally only be detected by measuring their gravitational distortion of the light from more distant objects. As of February 2022, only one isolated black hole has been confirmed, OGLE-2011-BLG-0462, around 5,200 light-years away.Technology has advanced enough that we've been able to spot one of these supermassive black holes in a nearby galaxy. In 2019, astronomers took the first-ever picture of a black hole in a galaxy called M87, which is about 55 million light-years away.
Are black holes unsolved : But how they got there is one of the great unsolved mysteries of cosmology. We know that a stellar black hole forms in a supernova explosion in which the core of a star implodes. But nobody knows how a supermassive black hole forms.
Are we living in a black hole
Earth is not just tucked into a planet-size black hole or even one the size of the solar system. If that were the case, scientists would have noticed, Field told Live Science. There would be observable signatures of the black hole's spinning.
Can we go to a black hole : So much as we love to read about black holes in science and science fiction, and imagine superpowers to use them as gateways to travel the cosmos, the hard reality says that we could do no such thing, and that falling into one would result in a very brief final chapter to anyone's existence.
In four and a half billion years, Earth has not been hit by a star. The closest is 1,560 light years away. The closest black hole is almost certainly closer but isolated black holes are almost impossible to detect. Also not a threat, black holes are some of the oldest objects in the universe. Einstein's theory of general relativity mathematically predicts the existence of wormholes, but none have been discovered to date. A negative mass wormhole might be spotted by the way its gravity affects light that passes by.
Is anyone went inside a black hole
Fortunately, this has never happened to anyone — black holes are too far away to pull in any matter from our solar system. But scientists have observed black holes ripping stars apart, a process that releases a tremendous amount of energy.Earth is not just tucked into a planet-size black hole or even one the size of the solar system. If that were the case, scientists would have noticed, Field told Live Science. There would be observable signatures of the black hole's spinning.Fortunately, this has never happened to anyone — black holes are too far away to pull in any matter from our solar system. But scientists have observed black holes ripping stars apart, a process that releases a tremendous amount of energy. Despite their abundance, there is no reason to panic: black holes will not devour Earth nor the Universe. It is incredibly unlikely Earth would fall into a black hole because, at a distance, their gravitational pull is no more compelling than a star of the same mass.
Do white holes exist : White holes are the opposite of black holes, in that they spit out light and matter, rather than trapping it. So far, white holes are purely hypothetical objects, but astronomers are contemplating how they could form in reality.
Would a black hole hurt : The fate of anyone falling into a black hole would be a painful “spaghettification,” an idea popularized by Stephen Hawking in his book “A Brief History of Time.” In spaghettification, the intense gravity of the black hole would pull you apart, separating your bones, muscles, sinews and even molecules.
Are we at risk of a black hole
Unlike tigers, black holes don't hunt. They're not roaming around space eating stars and planets. There is no black hole near our Solar System, so there is no chance of Earth ever getting sucked into a black hole. In fact, the closest black hole to Earth is 1560 light years away from us. White holes are the opposite of black holes, in that they spit out light and matter, rather than trapping it. So far, white holes are purely hypothetical objects, but astronomers are contemplating how they could form in reality.Cosmologists aren't sure if the universe is infinitely big or just extremely large. To measure the universe, astronomers instead look at its curvature. The geometric curve on large scales of the universe tells us about its overall shape. If the universe is perfectly geometrically flat, then it can be infinite.
What is 1 hour in a black hole : Expert-Verified Answer. For a black hole observer, one hour is equivalent to 100,000,000 years on Earth. In contrast to time distant from a black hole, time moves more slowly as you approach closer to one.
Antwort Do black holes exist? Weitere Antworten – Are black holes a real thing
Scientists have found proof that every large galaxy contains a supermassive black hole at its center. The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy is called Sagittarius A. It has a mass equal to about 4 million suns and would fit inside a very large ball that could hold a few million Earths.Solitary black holes can generally only be detected by measuring their gravitational distortion of the light from more distant objects. As of February 2022, only one isolated black hole has been confirmed, OGLE-2011-BLG-0462, around 5,200 light-years away.Technology has advanced enough that we've been able to spot one of these supermassive black holes in a nearby galaxy. In 2019, astronomers took the first-ever picture of a black hole in a galaxy called M87, which is about 55 million light-years away.
Are black holes unsolved : But how they got there is one of the great unsolved mysteries of cosmology. We know that a stellar black hole forms in a supernova explosion in which the core of a star implodes. But nobody knows how a supermassive black hole forms.
Are we living in a black hole
Earth is not just tucked into a planet-size black hole or even one the size of the solar system. If that were the case, scientists would have noticed, Field told Live Science. There would be observable signatures of the black hole's spinning.
Can we go to a black hole : So much as we love to read about black holes in science and science fiction, and imagine superpowers to use them as gateways to travel the cosmos, the hard reality says that we could do no such thing, and that falling into one would result in a very brief final chapter to anyone's existence.
In four and a half billion years, Earth has not been hit by a star. The closest is 1,560 light years away. The closest black hole is almost certainly closer but isolated black holes are almost impossible to detect. Also not a threat, black holes are some of the oldest objects in the universe.

Einstein's theory of general relativity mathematically predicts the existence of wormholes, but none have been discovered to date. A negative mass wormhole might be spotted by the way its gravity affects light that passes by.
Is anyone went inside a black hole
Fortunately, this has never happened to anyone — black holes are too far away to pull in any matter from our solar system. But scientists have observed black holes ripping stars apart, a process that releases a tremendous amount of energy.Earth is not just tucked into a planet-size black hole or even one the size of the solar system. If that were the case, scientists would have noticed, Field told Live Science. There would be observable signatures of the black hole's spinning.Fortunately, this has never happened to anyone — black holes are too far away to pull in any matter from our solar system. But scientists have observed black holes ripping stars apart, a process that releases a tremendous amount of energy.

Despite their abundance, there is no reason to panic: black holes will not devour Earth nor the Universe. It is incredibly unlikely Earth would fall into a black hole because, at a distance, their gravitational pull is no more compelling than a star of the same mass.
Do white holes exist : White holes are the opposite of black holes, in that they spit out light and matter, rather than trapping it. So far, white holes are purely hypothetical objects, but astronomers are contemplating how they could form in reality.
Would a black hole hurt : The fate of anyone falling into a black hole would be a painful “spaghettification,” an idea popularized by Stephen Hawking in his book “A Brief History of Time.” In spaghettification, the intense gravity of the black hole would pull you apart, separating your bones, muscles, sinews and even molecules.
Are we at risk of a black hole
Unlike tigers, black holes don't hunt. They're not roaming around space eating stars and planets. There is no black hole near our Solar System, so there is no chance of Earth ever getting sucked into a black hole. In fact, the closest black hole to Earth is 1560 light years away from us.
White holes are the opposite of black holes, in that they spit out light and matter, rather than trapping it. So far, white holes are purely hypothetical objects, but astronomers are contemplating how they could form in reality.Cosmologists aren't sure if the universe is infinitely big or just extremely large. To measure the universe, astronomers instead look at its curvature. The geometric curve on large scales of the universe tells us about its overall shape. If the universe is perfectly geometrically flat, then it can be infinite.
What is 1 hour in a black hole : Expert-Verified Answer. For a black hole observer, one hour is equivalent to 100,000,000 years on Earth. In contrast to time distant from a black hole, time moves more slowly as you approach closer to one.