Before 1066. From before Roman times, slavery was prevalent in Britain, with indigenous Britons being routinely exported. Following the Roman conquest of Britain, slavery was expanded and industrialised. After the fall of Roman Britain, both the Angles and Saxons propagated the slave system.Pages in category "British slave owners"
Hugh Duncan Baillie.
James Evan Baillie.
Peter Beckford (hunter)
Thomas Brown (loyalist)
The Romans didn't exactly enslave Britain, but anywhere they conquered they took slaves, either prisoners of war captured during the various rebellions or people who defaulted upon their debts after borrowing from the Romans.
Did the Church of England own slaves : The Church of England had links to slavery… the bishop of Exeter personally owned slaves. Many evangelicals were interested in the physical as well as spiritual condition of enslaved Africans.
Who was the first black person in England
The increase in trade between London and West Africa resulted in the growth in the population of Africans. The first recorded Black resident was in 1593, a man named Cornelius. Another influx of Africans occurred in the 17th century when people were freed from Spanish slave ships.
When did slavery end in Europe : Slavery existed in Europe since at least the time of the ancient Greeks (circa 1100 BC). It ended within Europe around the 15th century.
It all strongly suggests that not only were monarchs complicit in the slave trade, but in some cases the Royal Family was even involved in day-to-day decision-making on how the trading was carried out, she said. "It was very much James's enterprise. President Abraham Lincoln
President Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, as the nation approached its third year of bloody civil war. The proclamation declared "that all persons held as slaves" within the rebellious states "are, and henceforward shall be free."
Was the British Empire built on slavery
The British empire was built on slavery. Slave Empire puts enslaved people at the centre the British empire in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. In intimate, human detail, Padraic Scanlon shows how British imperial power and industrial capitalism were inextricable from plantation slavery.Whipping, a common form of slave punishment, demanded the removal of clothing. For the female slave, this generally meant disrobing down to the waist. Although her state of half dress allowed the woman some modesty, it also exposed her naked breasts to all eyes.King Henry VIII’s
King Henry VIII's break with the Catholic Church is one of the most far-reaching events in English history. For the majority of the early modern period, most Christian churches—both Catholic and Protestant—supported slavery and benefited from the institution. Even the Quakers (Society of Friends), who were leaders in the abolitionist movement, took a century to disown enslavers from their congregations.
Were the original Britons black : We now know that the first modern humans who lived in Britain between around 40,000 and 6,000 years ago had dark skin, including complexions we see today among Black people.
Was ancient Britain black : Britain was Black for 7,000 years before that”. In 2018, it was announced that a genetic study of Cheddar Man, the oldest set of human remains to have been found in Briton, suggested that “giveaway” genes meant he likely had blue eyes and a range of possible skin pigmentations from “dark to black”.
Why did Britain ban slavery
The holiday had its roots in Jamaica, where a five-week revolt led by a Black preacher named Sam Sharpe in 1831-1832 had forced the British Parliament to make a calculated decision that maintaining slavery overseas was simply too expensive. Slavery, by contrast, was an ancient institution in Russia and effectively was abolished in the 1720s. Serfdom, which began in 1450, evolved into near-slavery in the eighteenth century and was finally abolished in 1906. Serfdom in its Russian variant could not have existed without the precedent and presence of slavery.On his state visit to Kenya, the King addressed the "wrongdoings" of Britain's colonial era. He told a state banquet in Nairobi of his "greatest sorrow and regret" and that there was "no excuse". But the King did not deliver a formal apology – which would have to be decided by government ministers.
How did royalty begin in England : England has had monarchs since at least the 800s CE, but the English monarchy is often said to have begun with William the Conqueror in 1066. The monarchy did not rule all of Britain until James I and VI took the throne in 1567, and Britain did not become one united country under a single monarch until 1707.
Antwort Did England ever have slaves? Weitere Antworten – When did slavery exist in England
Before 1066. From before Roman times, slavery was prevalent in Britain, with indigenous Britons being routinely exported. Following the Roman conquest of Britain, slavery was expanded and industrialised. After the fall of Roman Britain, both the Angles and Saxons propagated the slave system.Pages in category "British slave owners"
The Romans didn't exactly enslave Britain, but anywhere they conquered they took slaves, either prisoners of war captured during the various rebellions or people who defaulted upon their debts after borrowing from the Romans.
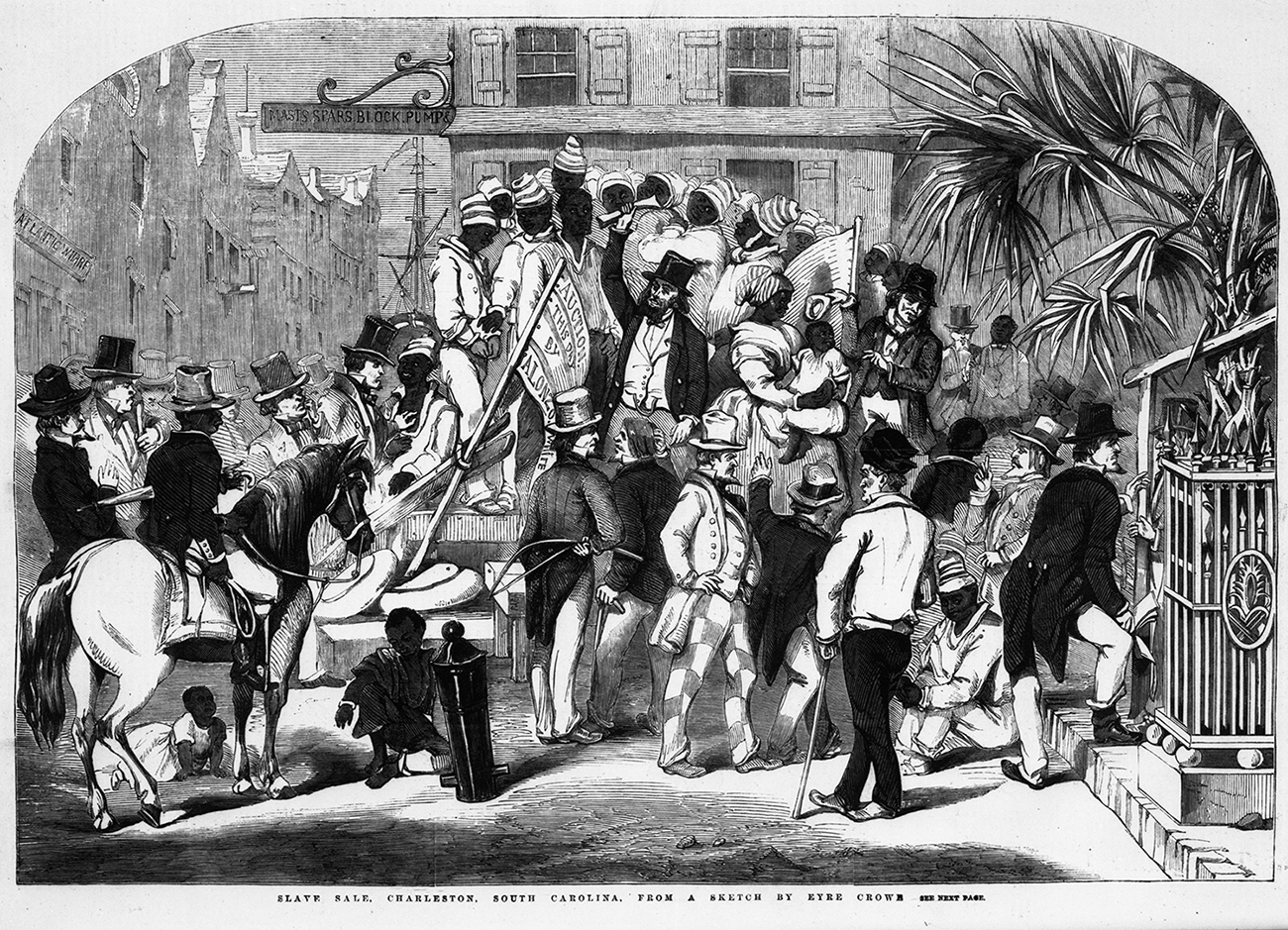
Did the Church of England own slaves : The Church of England had links to slavery… the bishop of Exeter personally owned slaves. Many evangelicals were interested in the physical as well as spiritual condition of enslaved Africans.
Who was the first black person in England
The increase in trade between London and West Africa resulted in the growth in the population of Africans. The first recorded Black resident was in 1593, a man named Cornelius. Another influx of Africans occurred in the 17th century when people were freed from Spanish slave ships.
When did slavery end in Europe : Slavery existed in Europe since at least the time of the ancient Greeks (circa 1100 BC). It ended within Europe around the 15th century.
It all strongly suggests that not only were monarchs complicit in the slave trade, but in some cases the Royal Family was even involved in day-to-day decision-making on how the trading was carried out, she said. "It was very much James's enterprise.

President Abraham Lincoln
President Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, as the nation approached its third year of bloody civil war. The proclamation declared "that all persons held as slaves" within the rebellious states "are, and henceforward shall be free."
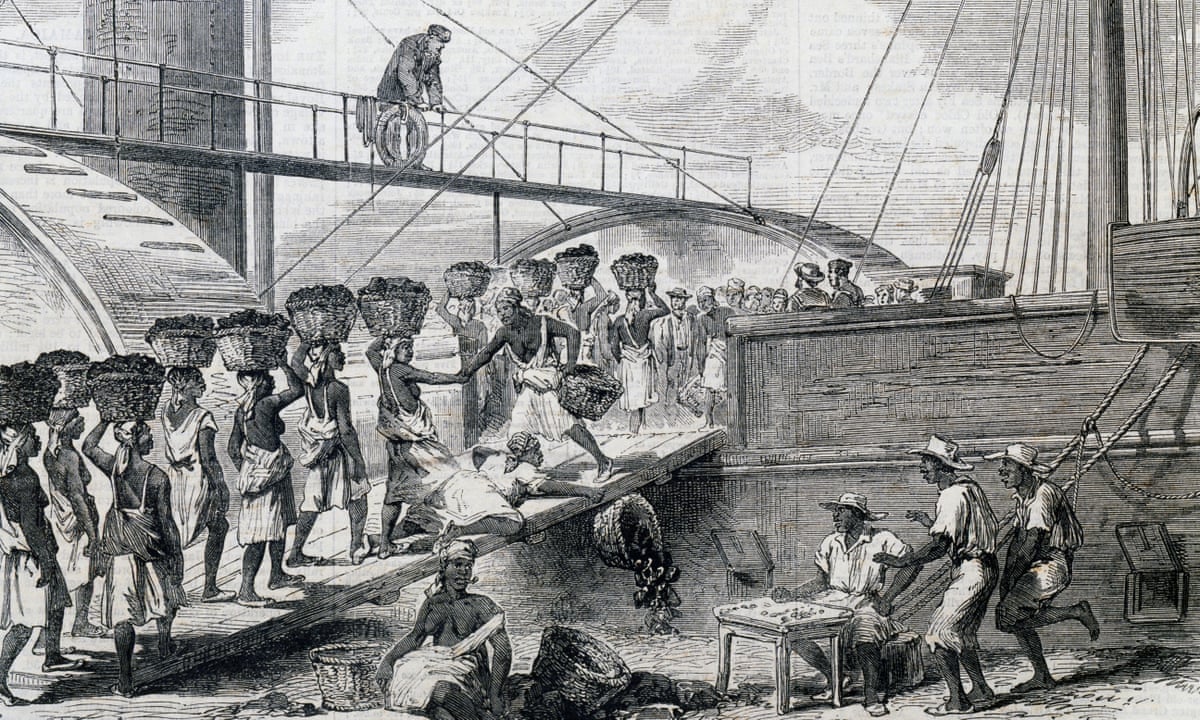
Was the British Empire built on slavery
The British empire was built on slavery. Slave Empire puts enslaved people at the centre the British empire in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. In intimate, human detail, Padraic Scanlon shows how British imperial power and industrial capitalism were inextricable from plantation slavery.Whipping, a common form of slave punishment, demanded the removal of clothing. For the female slave, this generally meant disrobing down to the waist. Although her state of half dress allowed the woman some modesty, it also exposed her naked breasts to all eyes.King Henry VIII’s
King Henry VIII's break with the Catholic Church is one of the most far-reaching events in English history.

For the majority of the early modern period, most Christian churches—both Catholic and Protestant—supported slavery and benefited from the institution. Even the Quakers (Society of Friends), who were leaders in the abolitionist movement, took a century to disown enslavers from their congregations.
Were the original Britons black : We now know that the first modern humans who lived in Britain between around 40,000 and 6,000 years ago had dark skin, including complexions we see today among Black people.
Was ancient Britain black : Britain was Black for 7,000 years before that”. In 2018, it was announced that a genetic study of Cheddar Man, the oldest set of human remains to have been found in Briton, suggested that “giveaway” genes meant he likely had blue eyes and a range of possible skin pigmentations from “dark to black”.
Why did Britain ban slavery
The holiday had its roots in Jamaica, where a five-week revolt led by a Black preacher named Sam Sharpe in 1831-1832 had forced the British Parliament to make a calculated decision that maintaining slavery overseas was simply too expensive.
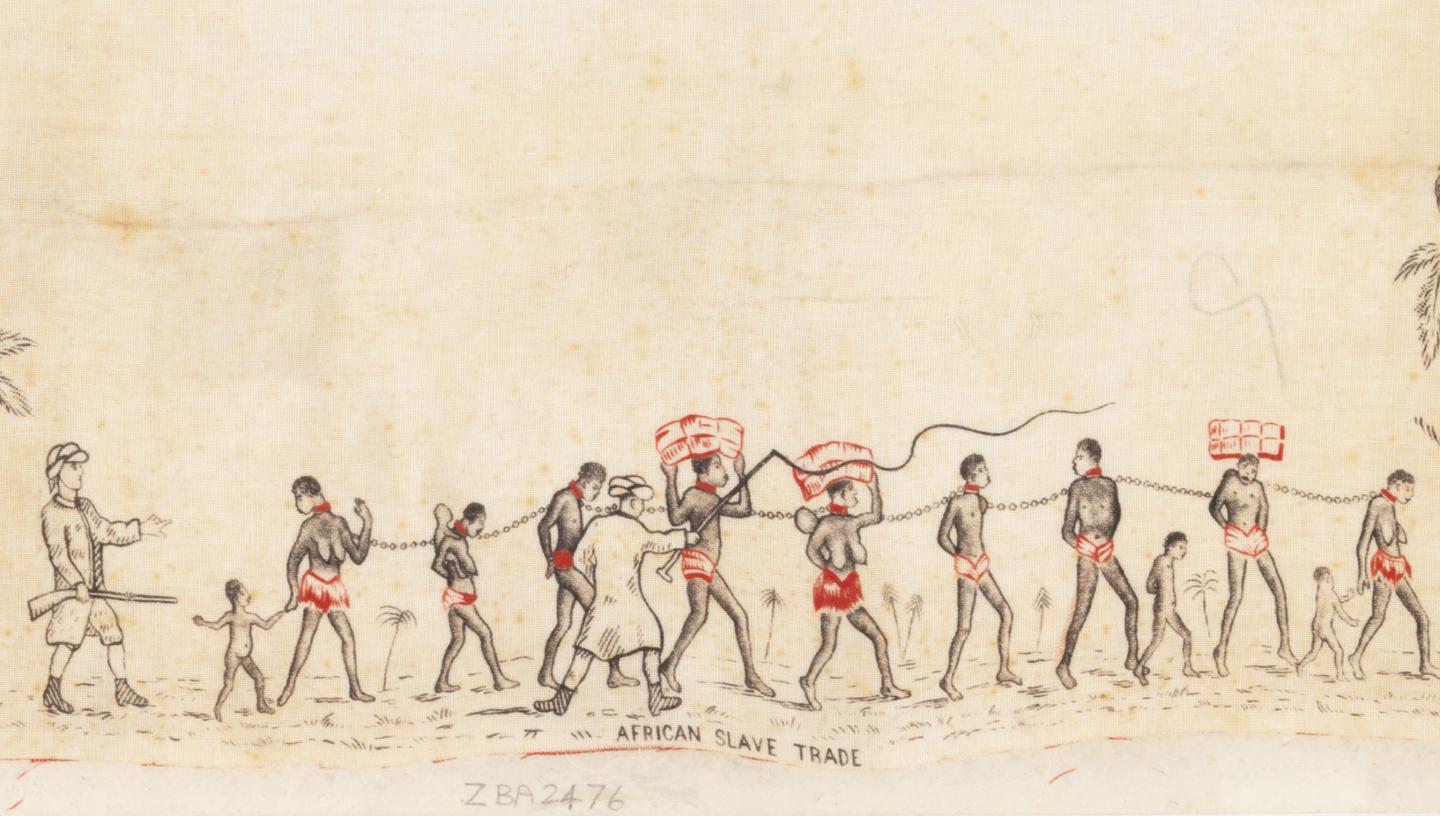

Slavery, by contrast, was an ancient institution in Russia and effectively was abolished in the 1720s. Serfdom, which began in 1450, evolved into near-slavery in the eighteenth century and was finally abolished in 1906. Serfdom in its Russian variant could not have existed without the precedent and presence of slavery.On his state visit to Kenya, the King addressed the "wrongdoings" of Britain's colonial era. He told a state banquet in Nairobi of his "greatest sorrow and regret" and that there was "no excuse". But the King did not deliver a formal apology – which would have to be decided by government ministers.
How did royalty begin in England : England has had monarchs since at least the 800s CE, but the English monarchy is often said to have begun with William the Conqueror in 1066. The monarchy did not rule all of Britain until James I and VI took the throne in 1567, and Britain did not become one united country under a single monarch until 1707.