Instead, Earth's natural cycles and greenhouse effects might delay the onset of the next ice age, expected within the next 10,000 to 100,000 years. Some theories suggest global warming could potentially trigger an ice age by disrupting ocean currents, specifically the Gulf Stream, leading to dramatic cooling in Europe.Predicted changes in orbital forcing suggest that the next glacial period would begin at least 50,000 years from now."Pink elephant in the room" time: There is no impending “ice age” or "mini ice age" if there's a reduction in the Sun's energy output in the next several decades. Through its lifetime, the Sun naturally goes through changes in energy output.
What will happen to Earth in 2030 : By 2030, the impacts of environmental change will probably be considerably more articulated than they are today. With temperatures proceeding to rise, outrageous climate occasions like typhoons, dry seasons, and rapidly spreading fires might turn out to be more regular and serious.
Could global warming cause human extinction
The most recent report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)—a group of hundreds of scientists working with the United Nations to analyze climate change research from around the world—names many serious risks brought on by the warming of our planet, but human extinction is not among them.
Will Earth go back to ice age : Will we enter into a new ice age No. Even if the amount of radiation coming from the Sun were to decrease as it has before, it would not significantly affect the global warming coming from long-lived, human-emitted greenhouse gases.
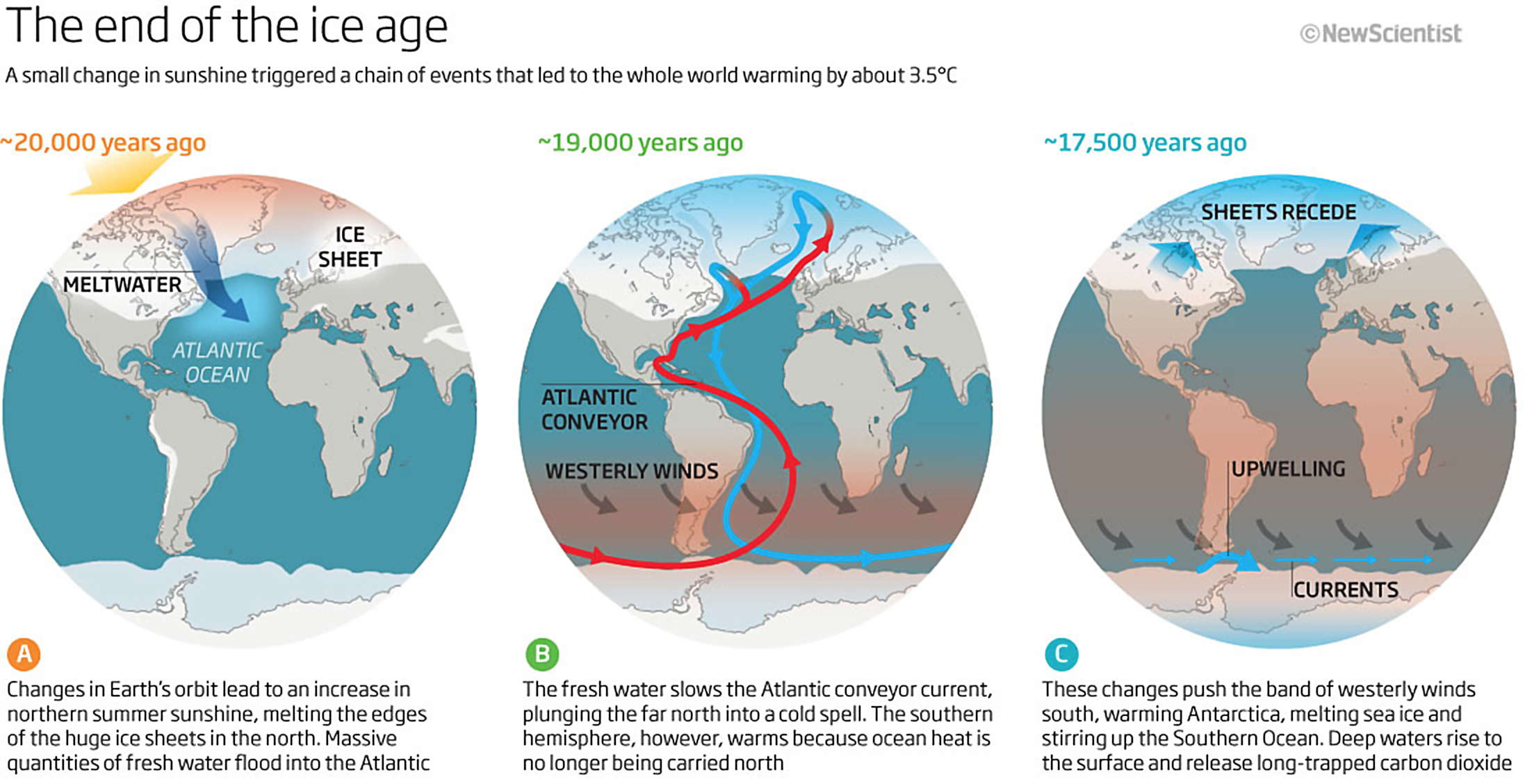
18,000 years ago – Cultivation of plants, herding of animals. Homo sapiens arrives in the Americas. 21,000 years ago – Last glacial maximum: ice sheets down to the Great Lakes, the mouth of the Rhine, and covering the British Isles. 32,000 years ago – Oldest known cave paintings. In general, it is felt that ice ages are caused by a chain reaction of positive feedbacks triggered by periodic changes in the Earth's orbit around the Sun. These feedbacks, involving the spread of ice and the release of greenhouse gases, work in reverse to warm the Earth up again when the orbital cycle shifts back.
Could humans survive an ice age
Yes, people just like us lived through the ice age. Since our species, Homo sapiens, emerged about 300,000 years ago in Africa, we have spread around the world. During the ice age, some populations remained in Africa and did not experience the full effects of the cold.Humans in the year 3000 will have a larger skull but, at the same time, a very small brain. "It's possible that we will develop thicker skulls, but if a scientific theory is to be believed, technology can also change the size of our brains," they write.Temperatures will be dangerously hot in more places and at more times than ever before. Less of Earth will be as agreeably habitable as in the past. Ecosystems and our relationships with ecosystems will continue to change, creating even more insecurity on the planet. The scientific consensus is that there is a relatively low risk of near-term human extinction due to natural causes. The likelihood of human extinction through humankind's own activities, however, is a current area of research and debate.
Could humanity survive ice age : Yes, people just like us lived through the ice age. Since our species, Homo sapiens, emerged about 300,000 years ago in Africa, we have spread around the world. During the ice age, some populations remained in Africa and did not experience the full effects of the cold.
Who lived 8000 years ago : 8000 BC – 3000 BC: Identical ancestors point: sometime in this period lived the latest subgroup of human population consisting of those that were all common ancestors of all present day humans, the rest having no present day descendants. 7500 BC – 3500 BC: Neolithic Subpluvial in North Africa.
What were humans like 100,000 years ago
Abstract. By 100,000 years ago, humans walked the Earth who were very similar to us physically and genetically, but they lived in small family bands and their culture was much simpler than the culture of any humans living today. Will we enter into a new ice age No. Even if the amount of radiation coming from the Sun were to decrease as it has before, it would not significantly affect the global warming coming from long-lived, human-emitted greenhouse gases.Earth's Climate During the Last Ice Age
Unlike the relatively stable climate Earth has experienced over the last 10,000 years, Earth's climate system underwent a series of abrupt oscillations and reorganizations during the last ice age between 18,000 and 80,000 years ago (Dansgaard 1984, Bond et al.
Did humans almost go extinct 70,000 years ago : Human ancestors in Africa were pushed to the brink of extinction around 900,000 years ago, a study shows. The work, published in Science, suggests a drastic reduction in the population of our ancestors well before our species, Homo sapiens, emerged.
Antwort Could global warming cause an ice age? Weitere Antworten – Does global warming lead to ice age
Instead, Earth's natural cycles and greenhouse effects might delay the onset of the next ice age, expected within the next 10,000 to 100,000 years. Some theories suggest global warming could potentially trigger an ice age by disrupting ocean currents, specifically the Gulf Stream, leading to dramatic cooling in Europe.Predicted changes in orbital forcing suggest that the next glacial period would begin at least 50,000 years from now."Pink elephant in the room" time: There is no impending “ice age” or "mini ice age" if there's a reduction in the Sun's energy output in the next several decades. Through its lifetime, the Sun naturally goes through changes in energy output.
What will happen to Earth in 2030 : By 2030, the impacts of environmental change will probably be considerably more articulated than they are today. With temperatures proceeding to rise, outrageous climate occasions like typhoons, dry seasons, and rapidly spreading fires might turn out to be more regular and serious.
Could global warming cause human extinction
The most recent report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)—a group of hundreds of scientists working with the United Nations to analyze climate change research from around the world—names many serious risks brought on by the warming of our planet, but human extinction is not among them.
Will Earth go back to ice age : Will we enter into a new ice age No. Even if the amount of radiation coming from the Sun were to decrease as it has before, it would not significantly affect the global warming coming from long-lived, human-emitted greenhouse gases.
18,000 years ago – Cultivation of plants, herding of animals. Homo sapiens arrives in the Americas. 21,000 years ago – Last glacial maximum: ice sheets down to the Great Lakes, the mouth of the Rhine, and covering the British Isles. 32,000 years ago – Oldest known cave paintings.

In general, it is felt that ice ages are caused by a chain reaction of positive feedbacks triggered by periodic changes in the Earth's orbit around the Sun. These feedbacks, involving the spread of ice and the release of greenhouse gases, work in reverse to warm the Earth up again when the orbital cycle shifts back.
Could humans survive an ice age
Yes, people just like us lived through the ice age. Since our species, Homo sapiens, emerged about 300,000 years ago in Africa, we have spread around the world. During the ice age, some populations remained in Africa and did not experience the full effects of the cold.Humans in the year 3000 will have a larger skull but, at the same time, a very small brain. "It's possible that we will develop thicker skulls, but if a scientific theory is to be believed, technology can also change the size of our brains," they write.Temperatures will be dangerously hot in more places and at more times than ever before. Less of Earth will be as agreeably habitable as in the past. Ecosystems and our relationships with ecosystems will continue to change, creating even more insecurity on the planet.

The scientific consensus is that there is a relatively low risk of near-term human extinction due to natural causes. The likelihood of human extinction through humankind's own activities, however, is a current area of research and debate.
Could humanity survive ice age : Yes, people just like us lived through the ice age. Since our species, Homo sapiens, emerged about 300,000 years ago in Africa, we have spread around the world. During the ice age, some populations remained in Africa and did not experience the full effects of the cold.
Who lived 8000 years ago : 8000 BC – 3000 BC: Identical ancestors point: sometime in this period lived the latest subgroup of human population consisting of those that were all common ancestors of all present day humans, the rest having no present day descendants. 7500 BC – 3500 BC: Neolithic Subpluvial in North Africa.
What were humans like 100,000 years ago
Abstract. By 100,000 years ago, humans walked the Earth who were very similar to us physically and genetically, but they lived in small family bands and their culture was much simpler than the culture of any humans living today.
Will we enter into a new ice age No. Even if the amount of radiation coming from the Sun were to decrease as it has before, it would not significantly affect the global warming coming from long-lived, human-emitted greenhouse gases.Earth's Climate During the Last Ice Age
Unlike the relatively stable climate Earth has experienced over the last 10,000 years, Earth's climate system underwent a series of abrupt oscillations and reorganizations during the last ice age between 18,000 and 80,000 years ago (Dansgaard 1984, Bond et al.
Did humans almost go extinct 70,000 years ago : Human ancestors in Africa were pushed to the brink of extinction around 900,000 years ago, a study shows. The work, published in Science, suggests a drastic reduction in the population of our ancestors well before our species, Homo sapiens, emerged.