In cosmic phenomena, we see echoes of our distant past. Massive clouds of gas and dust condense into centralized protostars, that in turn emit powerful solar wind and bursts of radiation. A newborn star emerges from its molecular cloud nursery. Material left over from the star's formation collapses into protoplanets.Scientists think planets, including the ones in our solar system, likely start off as grains of dust smaller than the width of a human hair. They emerge from the giant, donut-shaped disk of gas and dust that circles young stars. Gravity and other forces cause material within the disk to collide.Public Domain Image, source: NASA/JPL-Caltech. Yes, a star can turn into a planet, but this transformation only happens for a very particular type of star known as a brown dwarf.
Why can’t a star be a planet : Stars and brown dwarfs form from gas, whereas planets form from heavier elements. By definition, then, a star can never turn into a planet. Still, definitions evolve. For much of history, stars and planets were defined by their patterns of movement in the sky.
Do stars create galaxies
Galaxies form out of immense clouds of gas that collapse and rotate. As they evolve, stars form within them. Entire galaxies can collide, changing their appearance. Looking deep into space, we see galaxies at earlier stages in their lives, and learn more about their evolution.
Are we created from stars : Most of the elements of our bodies were formed in stars over the course of billions of years and multiple star lifetimes. However, it's also possible that some of our hydrogen (which makes up roughly 9.5% of our bodies) and lithium, which our body contains in very tiny trace amounts, originated from the Big Bang.
Construction of an artificial planet has been described as scientifically plausible but likely taking thousands of years and would be highly expensive. The planet covers a small circular area in space, when viewed from Earth. So, even if light from one point in the circular disc is blocked, light from other points reaches our eyes. As the light from the planets are not completely blocked from our sight and they do not twinkle.
Do planets still orbit a dead star
A new discovery suggests they can survive intact. Using NASA's JWST space telescope, astronomers have for the first time directly imaged planets on Solar System–like orbits around white dwarfs, the dead stars left after Sun-like stars swell into red giants and subside.Habitability and stability don't necessarily need to come from a nearby sun. Astronomers have spotted about 100 starless planets, some possibly formed from gas and dust clouds the way stars form, others probably ejected from their home solar systems (SN: 7/24/17)."Jupiter is called a failed star because it is made of the same elements (hydrogen and helium) as is the Sun, but it is not massive enough to have the internal pressure and temperature necessary to cause hydrogen to fuse to helium, the energy source that powers the sun and most other stars. Habitability and stability don't necessarily need to come from a nearby sun. Astronomers have spotted about 100 starless planets, some possibly formed from gas and dust clouds the way stars form, others probably ejected from their home solar systems (SN: 7/24/17).
Did planets exist before stars : We used to have this idea that stars entered adulthood first and were the mothers of planets that came afterwards, but now we see that protostars and planets grow and evolve together from early times like siblings." Observations also revealed implications for understanding the formation of our own solar system.
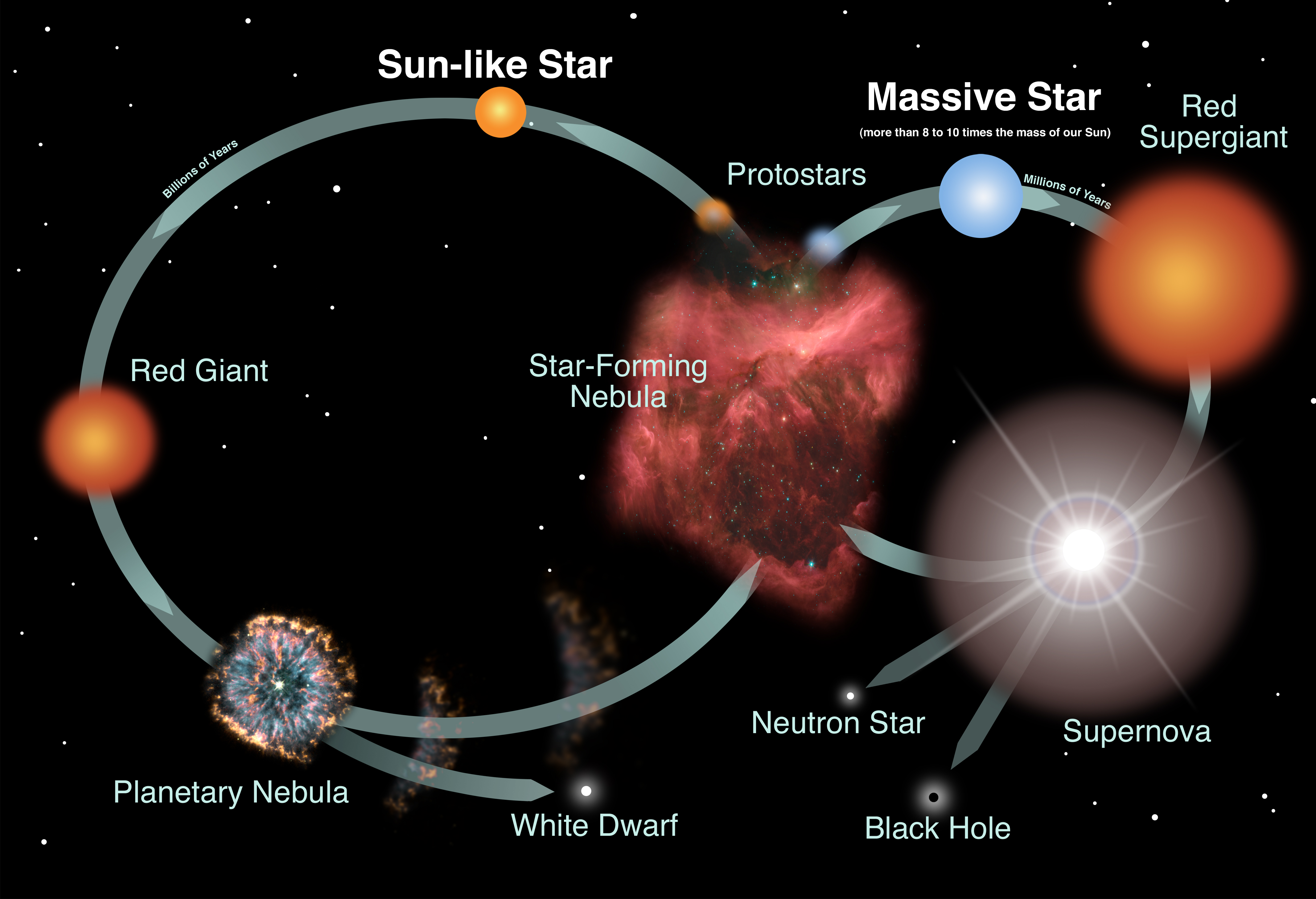
What happens when a star dies : When the helium fuel runs out, the core will expand and cool. The upper layers will expand and eject material that will collect around the dying star to form a planetary nebula. Finally, the core will cool into a white dwarf and then eventually into a black dwarf. This entire process will take a few billion years.
Is stardust in human DNA
Planetary scientist and stardust expert Dr Ashley King explains. 'It is totally 100% true: nearly all the elements in the human body were made in a star and many have come through several supernovas. ' The observable universe is certainly finite, and indeed we know approximately how large it is. It's very large—literally incomprehensibly so to human intuition, in fact—but still finite. Current cosmological evidence suggest the entire universe is isotropic, spatially flat, and infinite.Planets are naturally occurring celestial bodies. It would be extremely hard for us to imitate that process and build another one. But again, islands were once a naturally occurring feature. We've managed to make a handful of artificial islands today.
Could we create a mini Earth : A miniature earth would have almost no gravity and it wouldn't orbit a star, so you can't call it a planet. Apart from that, the miniature earth would be affected by earth's gravitational field. To make it float, you would have to build it in a satellite or create a strong magnetic field.
Antwort Can dead stars create new planets? Weitere Antworten – Do stars create planets
In cosmic phenomena, we see echoes of our distant past. Massive clouds of gas and dust condense into centralized protostars, that in turn emit powerful solar wind and bursts of radiation. A newborn star emerges from its molecular cloud nursery. Material left over from the star's formation collapses into protoplanets.Scientists think planets, including the ones in our solar system, likely start off as grains of dust smaller than the width of a human hair. They emerge from the giant, donut-shaped disk of gas and dust that circles young stars. Gravity and other forces cause material within the disk to collide.Public Domain Image, source: NASA/JPL-Caltech. Yes, a star can turn into a planet, but this transformation only happens for a very particular type of star known as a brown dwarf.
Why can’t a star be a planet : Stars and brown dwarfs form from gas, whereas planets form from heavier elements. By definition, then, a star can never turn into a planet. Still, definitions evolve. For much of history, stars and planets were defined by their patterns of movement in the sky.
Do stars create galaxies
Galaxies form out of immense clouds of gas that collapse and rotate. As they evolve, stars form within them. Entire galaxies can collide, changing their appearance. Looking deep into space, we see galaxies at earlier stages in their lives, and learn more about their evolution.
Are we created from stars : Most of the elements of our bodies were formed in stars over the course of billions of years and multiple star lifetimes. However, it's also possible that some of our hydrogen (which makes up roughly 9.5% of our bodies) and lithium, which our body contains in very tiny trace amounts, originated from the Big Bang.
Construction of an artificial planet has been described as scientifically plausible but likely taking thousands of years and would be highly expensive.
The planet covers a small circular area in space, when viewed from Earth. So, even if light from one point in the circular disc is blocked, light from other points reaches our eyes. As the light from the planets are not completely blocked from our sight and they do not twinkle.
Do planets still orbit a dead star
A new discovery suggests they can survive intact. Using NASA's JWST space telescope, astronomers have for the first time directly imaged planets on Solar System–like orbits around white dwarfs, the dead stars left after Sun-like stars swell into red giants and subside.Habitability and stability don't necessarily need to come from a nearby sun. Astronomers have spotted about 100 starless planets, some possibly formed from gas and dust clouds the way stars form, others probably ejected from their home solar systems (SN: 7/24/17)."Jupiter is called a failed star because it is made of the same elements (hydrogen and helium) as is the Sun, but it is not massive enough to have the internal pressure and temperature necessary to cause hydrogen to fuse to helium, the energy source that powers the sun and most other stars.

Habitability and stability don't necessarily need to come from a nearby sun. Astronomers have spotted about 100 starless planets, some possibly formed from gas and dust clouds the way stars form, others probably ejected from their home solar systems (SN: 7/24/17).
Did planets exist before stars : We used to have this idea that stars entered adulthood first and were the mothers of planets that came afterwards, but now we see that protostars and planets grow and evolve together from early times like siblings." Observations also revealed implications for understanding the formation of our own solar system.
What happens when a star dies : When the helium fuel runs out, the core will expand and cool. The upper layers will expand and eject material that will collect around the dying star to form a planetary nebula. Finally, the core will cool into a white dwarf and then eventually into a black dwarf. This entire process will take a few billion years.
Is stardust in human DNA
Planetary scientist and stardust expert Dr Ashley King explains. 'It is totally 100% true: nearly all the elements in the human body were made in a star and many have come through several supernovas. '

The observable universe is certainly finite, and indeed we know approximately how large it is. It's very large—literally incomprehensibly so to human intuition, in fact—but still finite. Current cosmological evidence suggest the entire universe is isotropic, spatially flat, and infinite.Planets are naturally occurring celestial bodies. It would be extremely hard for us to imitate that process and build another one. But again, islands were once a naturally occurring feature. We've managed to make a handful of artificial islands today.
Could we create a mini Earth : A miniature earth would have almost no gravity and it wouldn't orbit a star, so you can't call it a planet. Apart from that, the miniature earth would be affected by earth's gravitational field. To make it float, you would have to build it in a satellite or create a strong magnetic field.