In statistics, a misleading graph, also known as a distorted graph, is a graph that misrepresents data, constituting a misuse of statistics and with the result that an incorrect conclusion may be derived from it.For example: A company may claim that 90% of their customers are satisfied with their product but only surveyed 10 people. This sample size is not large enough to accurately represent the views of the entire customer base and may not be statistically significant.What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.
What are the components of graphical displays that can be misleading : INVESTIGATION: Misleading graphs
Omitting the baseline.
Showing an inappropriate or irregular scale.
Scale or labels not clearly given.
Leaving data out.
Using pictures or three-dimensional graphics that distort differences.
Using the wrong graph for a given data type.
What is an example of misleading data visualization
One of the most common, when it comes to misleading data visualization examples, is the pie charts. By definition, a complete pie chart always represents a total of 100%. This becomes confusing or misleading when it comes to using pie charts for showing the results of surveys with more than one answer.
Why is a bar chart misleading : This is one of the most common way graphs misrepresent data: by distorting the scale. Zooming in a small portion of the y-axis exaggerate a barely detectable difference, and it is especially misleading in bar graphs, since we assume the difference in the size of the bars is proportional to the values.
Statistics can be misleading in a number of ways. In this lesson, we'll discuss four different ways: inventing false statistical information, misinformation, neglecting the baseline, and making fallacious comparisons.
In 2007, toothpaste company Colgate ran an ad stating that 80% of dentists recommend their product. Based on the promotion, many shoppers assumed Colgate was the best choice for their dental health. But this wasn't necessarily true. In reality, this is a famous example of misleading statistics.
What are 5 ways in which data and graphs can be changed to be misleading
10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization
Pie charts that don't sum to 100% Pie charts should, by definition, sum to 100%.
Charts that use 3D styling.
Overlaid regression lines.
Inverted vertical axis.
Misleading Comparisons.
Percentages, not levels.
Maps.
Bar charts that don't start at zero.
Pie charts are one of the most misused data visualizations still in popular use.One of the most common, when it comes to misleading data visualization examples, is the pie charts. By definition, a complete pie chart always represents a total of 100%. This becomes confusing or misleading when it comes to using pie charts for showing the results of surveys with more than one answer.
Bad data visualization: 5 examples
A 3D bar chart gone wrong. “Don't ever use 3D bar charts,” says Cook.
A pie chart that should have been a bar chart.
A continuous line chart used to show discrete data.
A misleading geography visual.
A confusing (and aesthetically unappealing) graphic.
What is misleading visualization : Misleading data visualization rears its head when the actual data gets distorted by visual means. It's the difference between what your eyes see and what the facts really say, like y-axis manipulation or selective reportage.
How to tell if a graph is trustworthy : Tips include:
Check the data points plotted can be detected, and are not covered up or obscured.
Don't assume the viewer is a mind-reader … label titles and axes clearly and accurately.
Maintain constant measurement scales and avoid distortions.
What are 3 ways that statistics are commonly manipulated
This article delves into various tactics companies employ to misinterpret the truth through statistical manipulation.
Cherry-Picking Data:
Using Small Sample Sizes:
Overemphasising Percentages:
Correlation vs.
Statistical Significance:
Data Visualisations:
Ambiguous Wording:
Ignoring Outliers:
10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization
Pie charts that don't sum to 100%
Charts that use 3D styling.
Overlaid regression lines.
Inverted vertical axis.
Misleading Comparisons.
Percentages, not levels.
Maps.
Bar charts that don't start at zero.
Some examples of white lies include: Telling someone they look great in an outfit. Saying that you are on your way to meet someone so you can't stay and chat. Laughing at a joke that wasn't really funny.
What are 4 common mistakes made when making a graph chart :
1 Choosing the wrong type of display. One of the first decisions you have to make when creating a graphical display is what type of display to use.
Antwort What are misleading charts or graphs? Weitere Antworten – What is a misleading graph
In statistics, a misleading graph, also known as a distorted graph, is a graph that misrepresents data, constituting a misuse of statistics and with the result that an incorrect conclusion may be derived from it.For example: A company may claim that 90% of their customers are satisfied with their product but only surveyed 10 people. This sample size is not large enough to accurately represent the views of the entire customer base and may not be statistically significant.What are some ways graphs can be misleading Graphs can be misleading if they include manipulations to the axes or scales, if they are missing relevant information, if the intervals an an axis are not the same size, if two y-axes are included, or if the graph includes cherry-picked data.
What are the components of graphical displays that can be misleading : INVESTIGATION: Misleading graphs
What is an example of misleading data visualization
One of the most common, when it comes to misleading data visualization examples, is the pie charts. By definition, a complete pie chart always represents a total of 100%. This becomes confusing or misleading when it comes to using pie charts for showing the results of surveys with more than one answer.
Why is a bar chart misleading : This is one of the most common way graphs misrepresent data: by distorting the scale. Zooming in a small portion of the y-axis exaggerate a barely detectable difference, and it is especially misleading in bar graphs, since we assume the difference in the size of the bars is proportional to the values.
Statistics can be misleading in a number of ways. In this lesson, we'll discuss four different ways: inventing false statistical information, misinformation, neglecting the baseline, and making fallacious comparisons.

In 2007, toothpaste company Colgate ran an ad stating that 80% of dentists recommend their product. Based on the promotion, many shoppers assumed Colgate was the best choice for their dental health. But this wasn't necessarily true. In reality, this is a famous example of misleading statistics.
What are 5 ways in which data and graphs can be changed to be misleading
10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization
Pie charts are one of the most misused data visualizations still in popular use.One of the most common, when it comes to misleading data visualization examples, is the pie charts. By definition, a complete pie chart always represents a total of 100%. This becomes confusing or misleading when it comes to using pie charts for showing the results of surveys with more than one answer.
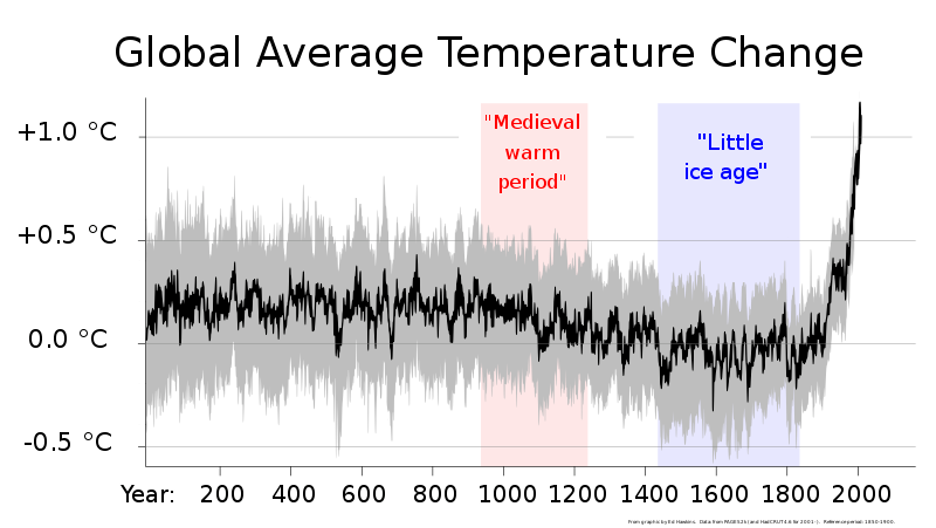
Bad data visualization: 5 examples
What is misleading visualization : Misleading data visualization rears its head when the actual data gets distorted by visual means. It's the difference between what your eyes see and what the facts really say, like y-axis manipulation or selective reportage.
How to tell if a graph is trustworthy : Tips include:
What are 3 ways that statistics are commonly manipulated
This article delves into various tactics companies employ to misinterpret the truth through statistical manipulation.
10 Ways to Mislead with Data Visualization
Some examples of white lies include: Telling someone they look great in an outfit. Saying that you are on your way to meet someone so you can't stay and chat. Laughing at a joke that wasn't really funny.
What are 4 common mistakes made when making a graph chart :